散列表 ADT 分离链接法【数据结构与算法分析 c 语言描述】
1. 前言
前面看了
- 链表 ADT
- 栈 ADT
- 队列 ADT
- 树 ADT
各自 ADT 都有自己特有的优势跟劣势以及应用场景,散列表也不例外。
散列表
常数平均时间执行插入、查找、删除操作。不支持像二叉查找树的 find_min、find_max、以及排序等等,相对来说它在插入、查找、删除上面的时间复杂度是相当优异的(常数)。
2. 实现思路
2.1 散列表的基本概念
- 关键字
- 散列函数
- 散列表
- 冲突
一个关键字通过 散列函数将之映射到一个固定长度的散列表里面的一个单元上。
关键字 x;散列函数 f(x) = 0; 此时就把 x映射到 散列表 0 单元上。
如果 一个关键字 a、b;有 f(a) = 0、f(b) = 0;两个关键字通过散列函数处理后得到相同的值,这叫冲突
散列函数的设计跟编写尤为重要,它决定了关键字映射到散列表的规则,尽量少的冲突、能否均匀分布到散列表中。通常会对把表长设计为素数,同时对表长取模来计算散列值。
这样一来散列表的主要时间消耗在了 散列函数的计算上面。散列函数的设计原则
- 复杂度低。
- 散列的结果接近均匀分布。
3. 具体实现
关键字:1 <= 长度 <= 8 的字符串。
散列函数:根据 Horner 法则计算 32 的多项式然后 mod 表长(表长取素数)。
冲突解决:分离链接法。
对分布在相同单元的关键字采用单链表来存储以解决冲突。hash_sep.h 头文件
typedef unsigned int index;
typedef char* element_type;
struct list_node;
typedef struct list_node *position;
struct hash_table_node;
typedef struct hash_table_node *hash_table;
index hash(const char *key, int table_size);
hash_table initialize_table(int table_size);
void destory_table(hash_table h);
void delete(element_type key, hash_table h);
position find(element_type key, hash_table h);
void insert(element_type key, hash_table h);
element_type retrieve(position p);
int next_prime(int table_size);
void print_hash_table(hash_table h);
void random_hash_table(hash_table h, int len);
void test();
struct list_node
{
element_type element;
position next;
};
typedef position list;
struct hash_table_node
{
int table_size;
list *list_arr;
};hash_sep.c 实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "hash_sep.h"
#define error(str) fatal_error(str)
#define fatal_error(str) fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", str),exit(1)
index hash(const char *key, int table_size)
{
unsigned int hash_value = 0;
while (*key != '\0') {
hash_value = (hash_value << 5) + *key++;
}
return hash_value % table_size;
}
hash_table initialize_table(int table_size)
{
hash_table h;
int i;
h = (hash_table)malloc(sizeof(struct hash_table_node));
if (NULL == h)
fatal_error("Out of space");
h->table_size = next_prime(table_size); // 保证是素数
// 数组分配空间
h->list_arr = malloc(sizeof(list) * h->table_size);
if (NULL == h->list_arr)
fatal_error("Out of space");
// 为 list_arr 的每一项分配表头
for (int i = 0; i < h->table_size; i++) {
h->list_arr[i] = (list)malloc(sizeof(struct list_node));
if (NULL == h->list_arr[i])
fatal_error("out of space");
else
h->list_arr[i]->next = NULL;
}
return h;
}
void destory_table(hash_table h)
{
int i;
for (int i = 0; i < h->table_size; i++) {
free(h->list_arr[i]);
}
free(h->list_arr);
free(h);
}
void delete(element_type key, hash_table h)
{
// 找到然后释放
position pos, p;
list l;
pos = find(key, h);
if (NULL == pos) {
return;
} else {
l = h->list_arr[hash(key, h->table_size)];
p = l;
while (NULL != p->next && key != p->next->element)
p = p->next;
p->next = pos->next;
free(pos->element);
free(pos);
pos = NULL;
}
}
position find(element_type key, hash_table h)
{
position p;
list l;
l = h->list_arr[hash(key, h->table_size)];
p = l->next;
while(NULL != p && p->element != key)
p = p->next;
return p;
}
void insert(element_type key, hash_table h)
{
position pos, p, temp_cell;
list l;
pos = find(key, h);
if (NULL == pos) {
temp_cell = (position)malloc(sizeof(struct list_node));
if (NULL == temp_cell)
fatal_error("out of space");
temp_cell->element = key;
temp_cell->next = NULL;
l = h->list_arr[hash(key, h->table_size)];
p = l;
while (NULL != p->next)
p = p->next;
p->next = temp_cell;
}
}
element_type retrieve(position p)
{
if (NULL == p)
error("NULL position");
return p->element;
}
int next_prime(int table_size)
{
int i, j = 2, k;
for(i = table_size; i > 0; i--)
{
k = sqrt(i);
while( j <= k )
{
if(i % j == 0)
break;
j++;
}
if(j > k)
break;
}
return i;
}
void print_hash_table(hash_table h)
{
int i;
list l;
position p;
for (i = 0; i < h->table_size; i++) {
printf("%d =>", i);
l = h->list_arr[i];
p = l->next;
while (p) {
printf("\t%s", p->element);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void random_hash_table(hash_table h, int len)
{
char dictionary[52] = "adcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
int str_len, i, j;
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
str_len = rand() % 8 + 1; // 1-8
char* str;
str = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (str_len + 1));
for (j = 0; j < str_len; j++) {
str[j] = dictionary[rand() % 52];
// str[j] = rand() % 26 + 97; // 97-122
// printf("%c\n", str[j]);
}
str[j] = '\0';
// printf("%s\t", str);
insert(str, h);
str = NULL;
}
}
void test()
{
hash_table h;
h = initialize_table(9);
printf("\t\tinsert adc into hash table.\n");
char* str = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * 4);
str[0] = 'a';
str[1] = 'b';
str[2] = 'c';
str[3] = '\0';
insert(str, h);
print_hash_table(h);
printf("\t\tdelete abc.\n");
delete(str, h);
print_hash_table(h);
random_hash_table(h, 7);
printf("\t\ta random hash table\n");
print_hash_table(h);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
test();
return 0;
}4. 运行结果
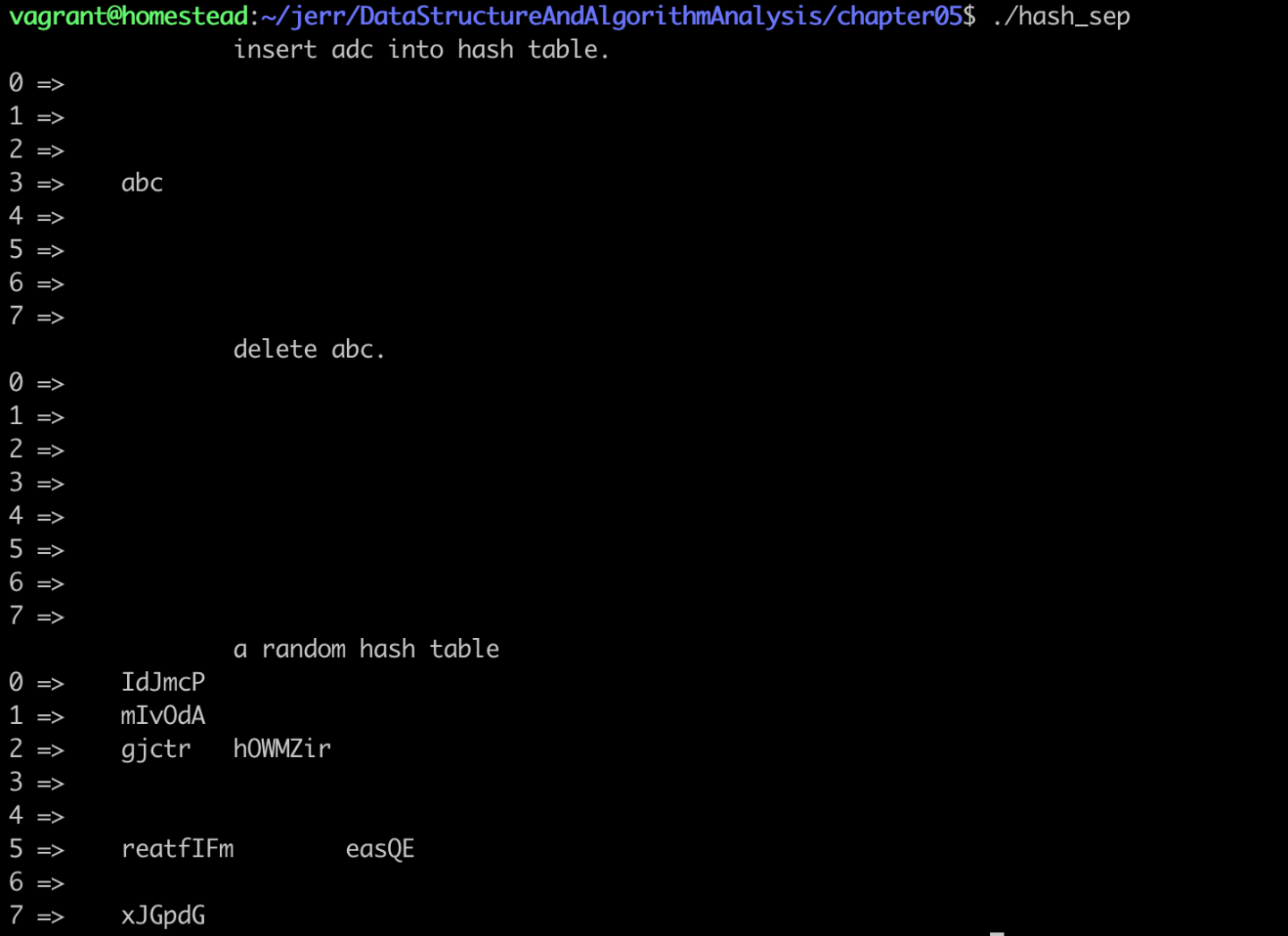
5. 总结
- 散列表
- 散列函数
- 关键字
- 冲突
- 分离链接法解决冲突
- 如何设计优秀的散列函数
- c 语言 char 跟 字符串
- 素数
以上是涉及到的知识点
本作品采用《CC 协议》,转载必须注明作者和本文链接





 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu



