kmp 算法
#kmp算法
在一个长的字符串中匹配指定字符串我们想到的是一个一个比较 如果发现一个不相等,就把长字符串向前移动一位,然后再重头开始继续比较;
function kmp($str1,$str2){
$l1 = strlen($str1);
$l2 = strlen($str2);
$i=0;
$j=0;
while($j<$l2 && $i<$l1){
if($str1[$i] == $str2[$j]){
$i++;
$j++;
}else{
$i=$i-$j+1;//先回到i位置 然后起始位置向后移动一位
$j=0; j回到初始位置;
}
}
if($j == $l2){//如果查到此时$j的长度肯定是等于$l2 的
return $i-$j;
}else{
return -1;
}
}这种算法效率低下 最坏情况下比较 ($l2 -$l1+1)*$l2次
kpm 算法
function getNext($str) {
$next[0] = -1;
$j = 0;
$k = -1;
$len = strlen($str);
while ($j < $len - 1) {
if ($k == -1 || $str[$j] == $str[$k]) {
if ($str[++$j] == $str[++$k]) {
$next[$j] = $next[$k];
} else {
$next[$j] = $k;
}
} else {
$k = $next[$k];
}
}
return $next;
}
function kmp($str1,$str2) {
$l1 = strlen($str1);
$l2 = strlen($str2);
$i=0;
$j=0;
$next = getNext($str2);
while ($j < $l2 && $i < $l1) {
if ($j == -1 || $str1[$i] == $str2[$j]) { // 当j为-1时,要移动的是i,当然j也要归0
$i++;
$j++;
} else {
$j = $next[$j]; // j回到指定位置
}
}
if ($j == $l2) {
return $i-$j;
}else{
return -1;
}
}- 二叉树的遍历
因为好多算法都是c语言实现的实现方式跟php可能有些区别 ,但是原理本质上都差不多,所以希望不要纠结,有思考不到位的地方希望大家指出来
生成后的树 如图class node{ public $left = null; public $right = null; public $data ; public $flag ; public function __construct($data, $left=null, $right=null,$flag=0){ $this->data = $data; $this->left = $left; $this->right = $right; $this->flag = $flag; //在后序遍历时候有用标志位,是否访问过的标志 0 没访问过 1 访问过 } } $root_0 = new node(10); $node1_1 = new node(11); $node1_2 = new node(12); $node2_1 = new node(21); $node2_2 = new node(22); $node2_3 = new node(23); $node2_4 = new node(24); $node3_1 = new node(31); $node3_2 = new node(32); $node3_3 = new node(33); $node3_4 = new node(34); $root_0->left = $node1_1; $root_0->right = $node1_2; $node1_1->left = $node2_1; $node1_1->right = $node2_2; $node1_2->left = $node2_3; $node1_2->right = $node2_4; $node2_1->left = $node3_1; $node2_1->right = $node3_2; $node2_2->left = $node3_3; $node2_2->right = $node3_4;
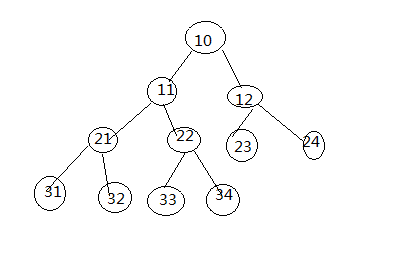
1.1 二叉树广度优先递归遍历
function breadthTraversal($root){
$queue = [];
array_push($queue,$root);
while($queue){
$node = array_pop($queue);
if($node->left){
array_unshift($queue,$node->left);
}
if($node->right){
array_unshift($queue,$node->right);
}
echo $node->data.'----';
}
}
breadthTraversal($root_0);
结果 :10----11----12----21----22----23----24----31----32----33----34- 一层一层的遍历相当1.2 二叉树深度优先递归遍历(递归版本)
function deepTraversal($root){
// echo $root->data.' '; 前续遍历
if($root->left){
dbs($root->left);
}
// echo $root->data.' '; 中序遍历
if($root->right){
dbs($root->right);
}
//echo $root->data.' '; 后序遍历
}
deepTraversal($root_0);
前序遍历:10 11 21 31 32 22 33 34 12 23 24
中序遍历:31 21 32 11 33 22 34 10 23 12 24
后序遍历:31 32 21 33 34 22 11 23 24 12 10 1.3 二叉树深度优先递归遍历(非递归递归版本)
1.3.1 前序遍历非递归
function preOrderTraversal($node){
$queue = [];
array_push($queue,$node);
while($queue){
$node = array_pop($queue);
while($node){
echo $node->data.' ';
array_push($queue,$node->right);
$node = $node->left;
}
}
}
preOrderTraversal($root_0);
前续遍历非递归结果:10 11 21 31 32 22 33 34 12 23 24 1.3.2 中序遍历非递归
function inOrderTraversal($root){
$queue = [];
array_push($queue,$root);
while($queue){
while($node = array_pop($queue)){
array_push($queue,$node);
// if($node->left){//$node->left 为null 时候 //没有表示无子节点了 千万不能加 if 判断 除非加个完的标志 我刚开始在这里加判断 结果死循环
array_push($queue,$node->left);
// }
}
if($queue){
$node = array_pop($queue);
echo $node->data.' ';
//if($node->right){$node->right 为null 时候 没有表示右节点遍历完 当为root节点时候表示 全部遍历完 千万不能加 if 判断 我刚开始在这里加判断 结果死循环 因为 这里,$node->right 要是不存在表示这node节点递归完毕
array_push($queue,$node->right);
//}
}
}
}
inOrderTraversal($root_0);
中序遍历非递归结果:31 21 32 11 33 22 34 10 23 12 24 1.3.3 后序遍历非递归
function postOrderTraversal($root){
$queue = [];
array_push($queue,$root);
while($queue){
while($node = array_pop($queue)){
array_push($queue,$node);
array_push($queue,$node->left);
}
if($queue){
$node = array_pop($queue);
// 这步之前其实跟前面差不多,我刚开始也写这里然后怎么想也搞不定后面的步奏,后来看了一篇博客别人写的
if($node->flag==0){
$node->flag=1;
array_push($queue,$node);
// $node->right=null 时候,push($queue,null)后就当$node= null==pop($queue)不在while中循环,总的来说就是表示node节点右节点遍历完
array_push($queue,$node->right);
}else{
echo $node->data.' ';// 表示node节点后的所有子节点节点都遍历完了
array_push($queue,null);
}
}
}
}
postOrderTraversal($root_0);
后序遍历非递归结果:31 32 21 33 34 22 11 23 24 12 10 2 堆排
function heapSort(&$a){
$count = count($a)-1;
for($i=intval($count/2); $i >=1; $i--) {//重最后一个元素开始构建一个大顶堆
moveHeap($a,$i,$count);
}
for ($j=$count; $j >=1 ; $j--) {
swap($a,1,$j);//交换第一个元素和最后一个元素
moveHeap($a,1,$j-1);//重新构建大顶堆
}
function moveHeap(&$a,$j,$n){\
$left = 2*$j;
$right = 2*$j+1;
$max = $j;
if($left<=$n && $a[$left]>$a[$max] ){
$max = $left;
}
if($right<=$n && $a[$right]>$a[$max]){
$max = $right;
}
if($max!=$j){
swap($a,$max,$j);
moveHeap($a,$max,$n);//递归版本
// while($max!=$j){//非递归版本
// $j = $max;
// $left = 2*$j;
// $right = 2*$j+1;
// if($left<=$n && $a[$left]>$a[$j]){
// $max = $left;
// }
// if($right<=$n && $a[$right]>$a[$right]){
// $max = $right;
// }
// if($max!=$j){
// swap($a,$max,$j);
// }
//
// }
}
function swap(&$a,$l,$r){//交换方法
$tem = $a[$l];
$a[$l] = $a[$r];
$a[$r] = $tem;
}
$a = [0,12,2,31,22,6,23,11,9,32,4];
print_r($a);
heapSort($a);
print_r($a);
Array
(
[0] => 0
[1] => 2
[2] => 4
[3] => 6
[4] => 9
[5] => 11
[6] => 12
[7] => 22
[8] => 23
[9] => 31
[10] => 32
)
第0个是占位符归并排序
function mergeSort($a){
$count = count($a);
if ($count <= 1) {
return $a;
} else {
$mid = intval(($count)/2);
$left = array_slice($a, 0,$mid);
$right = array_slice($a,$mid);
$s = mergeSort($left);
$e = mergeSort($right);
return array_m($s,$e);
}
}
function array_m($s,$e)
{
$r = array();
$i = 0;
$j = 0;
$count_s = count($s);
$count_e = count($e);
while ($i < $count_s && $j < $count_e) {
if ($s[$i] > $e[$j]) {
$r[] = $e[$j];
$j++;
} else {
$r[] = $s[$i];
$i++;
}
}
while($j<$count_e){
$r[] = $e[$j];
$j++;
}
while($i<$count_s){
$r[] = $s[$i];
$i++;
}
return $r;
}
快排
function quickSort($a){
$count=count($a);
if($count<=1)return $a;
$l = [];
$r = [];
$p = [];
$m = $a[0];
for ($i=0; $i <$count ; $i++) {
if($a[$i]<$m){
$l[]=$a[$i];
}elseif($a[$i]==$m){
$p[]=$a[$i];
}else{
$r[]=$a[$i];
}
}
$l = quickSort($l);
$p = quickSort($p);
$r = quickSort($r);
return array_merge($l,$p,$r);
}总结
非递归版本其实就是通过栈去模拟递归函数调用的栈
根节点最好看成是两个没有孩子的父节点便于去模拟函数的运行流程
这三个遍历 我也还没完全想明白 还需要时刻回想,模拟递归的思维去思考,我们可以先简单用三个节点去走通流程。
折半查找算法
单链表反转
function reverse($x) {
$head=$current=$x;
if($x && !$x->next){
return $head;
}elseif(!$x){
return false;
}
elseif($x && $x->next){
while($next = $current->next){//
$current->next = $next->next//把下下个节点指向当前节点的next指针
$next->next = $head;//把节点插入到头节点前面
$head = $next;//把头节点重新指向第一个节点
}
return $head;
}获取二叉树的深度
深度就是树的层数,当我们层序遍历树的时候,遍历完一层我们就加一,但是什么时候才是遍历完一层呢,我们需要一个队列用来存储遍历当前节点的子节点,比如当我们遍历完第n层的时候,队列里面的节点肯定全部是第n+1层节点的,此时子需要获取队列长度就知道第n+1层节点个数,这样往前推到第0层(就是根节点)此时,下一层节点个数是1,以此往后推遍历完当前层就能知道下一层节点个数。
function findLevel($node){
if(!$node->left && !$node->right){
return false;
}
$arr = [];
array_push($arr,$node);//把根节点push进队列
$count = 0;当前层已经遍历的数量
$depth=0;//树的深度初始值
$nextcount=1;//第一层节点的数量初始化为1,根节点
while(count($arr)){
$node = array_pop($arr);
$count++;
if($node->left){
array_push($arr,$node->left);
}
if($node->right){
array_push($arr,$node->right);
}
if($count==$nextcount){//当前层遍历完
$nextcount=count($arr);//获取下层节点数量
$count=0;
$depth++;//当前层遍历完和深度加1
}
}本作品采用《CC 协议》,转载必须注明作者和本文链接

 nongnong 的个人博客
nongnong 的个人博客




 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu



