如何在laravel中使用Repository Pattern(仓库模式)
好记性不如烂笔头,学习php开发也不能懒,作笔记是一种学习的好习惯!
文章来自:mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Z3YsMYeYq3Gg0ll...
学习与交流:Laravel技术交流微信群
Repository 模式主要思想是建立在一个数据操作代理层上的,把controller里的数据操作分离出来,这样做的好处有以下几点:
- 把数据处理逻辑分离使得代码更容易维护
- 数据处理逻辑和业务逻辑分离,可以对这两个代码分别进行测试
- 减少代码重复
- 降低代码出错的几率
- 让controller代码的可读性大大提高
如图所示Repository的分层关系
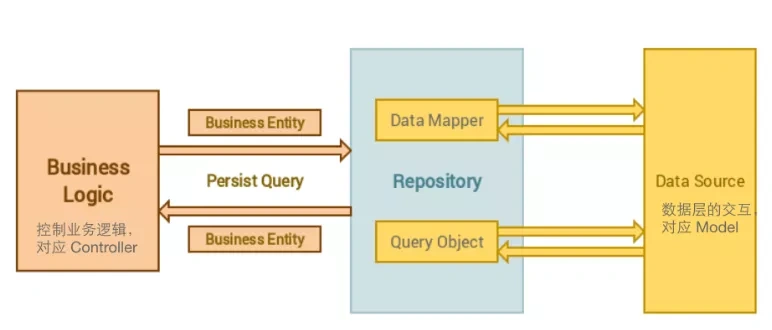
然而,要独立一个操作层出来,那就会增加大量代码,非常繁琐。如果你是小项目,未必需要使用这一模式。但如果是4-5年以上的复杂大型项目,这种模式的好处就比较明显了。
学习Repository Pattern的意义不只是为了使用它,更会让你深入思考框架的分层思想,你开始不仅关注怎么使用一个框架,还会想了解怎样设计一个框架,也许会成为你往高阶段编程的入口。当你感悟到什么是一种思想的时候。。。
Repository Pattern(仓库模式)
虽然说设计模式和语言及框架无关,但是脱离了语言及框架,我们很难理解,所以我们还是在laravel的语境下来学习。
public function index()
{
$posts = Post::whereIn('category_id', [1, 2])
->where('is_draft', 0)
->orderBy('created_at', 'desc')
->take(5)
->get();
return view('front.index', compact('posts'));
}以上是典型的Eloquent数据查询代码,如果你编程经验丰富,你会发现这种代码在控制器里到处都是,而且有很多是重复的,可读性很差;我们的目标是把它精简:
仔细观察
Post::whereIn('category_id', [1, 2])->where('is_draft', 0)->orderBy('created_at', 'desc')->take(5)->get();其实它由3部分组成.
第一是 Post 数据模型;
第二个是 whereIn('category_id', [1, 2])->where('is_draft', 0)->orderBy('created_at', 'desc')->take(5) ,数据操作条件;
第三个是 get() 数据获取的方法;
我们知道, Eloquent 里有个 Query Scope ,可以用来把第二部分,也就是查询条件精简。所以,在使用了 Query Scope 后,我们可以把精简成:
Post::ofCategory([1, 2])->isDraft()->orderBy('created_at', 'desc')->take(5)->get();咋一看上去,好像也没怎么精简啊,但实际上你已经实现代码解耦和复用了,比如说 isDraft() , 这个代码可以到处用,而不用担心耦合问题。
精简程度和你的逻辑抽象程度有关,比如说你完全可以写成:
Post::findPosts([1, 2], 0, 'desc' ,5)->get();在轻型项目中,强烈推荐使用 Query Scope ,这是一种良好的编程习惯。
在更复杂的项目中, Query Scope 就不够用了,因为它和数据模型还是一种强耦合, Repository Pattern 就是要把第一,第二,第三部分全部解耦;
说到解耦,我们在 Laravel 的文档攻略中讲过,第一神器就是PHP中的接口( Interface )
下面来看例子
第一步 建立文件夹
├── app
├── Implements
├── Interfaces
└── RepositoriesInterfaces里面用来放接口,Implements用来放接口的实现;
第二步 建立一个接口
在上面的 Interfaces 目录新建一个文件 PostInterface.php :
<?php
namespace App\Repositories\Interfaces;
interface PostInterface{
public function findPosts(array $cat_id, $is_draft, $order, $take)
{
}
}第三步 建立一个接口对应的实现
在上面的 Implements 目录新建一个文件 PostRepository.php :
<?php
namespace App\Repositories\Implements;
use Post;
class PostRepository Implements PostInterface{
public function findPosts(array $cat_id, $is_draft, $order, $take){
$query = Post::whereIn('category_id', $cat_id)
->where('is_draft', $is_draft)
->orderBy('created_at', $order)
->take($take)
->get();
return $query;
}
}很明显,仓库指的就是一个仓库接口的实现;这里定义你的业务逻辑;
第四步 在ServiceProvider中绑定接口
打开 app/Providers/AppServiceProvider 在 register() 加入代码:
<?php
namespace App\Providers;
use Illuminate\Support\ServiceProvider;
class AppServiceProvider extends ServiceProvider
{
public function boot()
{
//
}
public function register()
{
$this->app->bind('App\Repositories\Interfaces\PostInterface', 'App\Repositories\Implements\PostRepository');
}
}我们知道,ServiceProvider是 Laravel IOC 容器实现动态换接口实现的地方,所以我们在这里绑定一下,这样我们在使用的时候,不直接使用接口实现,而是用ioc容器解析接口,它会帮你自动找到对应好的实现。这就意味着,以后需要更换实现,可以在这里更换;
第五步 使用仓库
回到我们的controller里来
<?php
use App\Repositories\Interfaces\PostInterface;
class PostController extends BaseController{
public function __construct(PostInterface $post){
$this->postRepo = $post;
}
public function index(){
$this->postRepo->findPosts([1, 2], 0, 'desc' ,5);
}
}从上面的例子看,我们的业务逻辑变得非常精简,完全不用管查询;而且也现实了数据查询部分的解耦;
好记性不如烂笔头,学习php开发也不能懒,作笔记是一种学习的好习惯!
文章来自:mp.weixin.qq.com/s/g_nJn271pjRJHTE...
学习与交流:Laravel技术交流微信群
本作品采用《CC 协议》,转载必须注明作者和本文链接





 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu




更难维护了
然后插入更新啥的更难维护了
MVC的设计模式, 足够解决90%以上的应用开发, 如果增加一个维度, 虽然会增加代码可读性, 但也增加了维护的困难程度. :grin: