2023-04-18:ffmpeg中的hw_decode.c的功能是通过使用显卡硬件加速器
2023-04-18:ffmpeg中的hw_decode.c的功能是通过使用显卡硬件加速器(如 NVIDIA CUDA、Intel Quick Sync Video 等)对视频进行解码,从而提高解码效率和性能。在进行硬件加速解码时,相较于 CPU 的软件解码方式,GPU 可以利用其并行处理能力和更高的带宽进行更高效的解码操作。请用go语言改写hw_decode.c文件。
答案2023-04-18:
hw_decode.c 功能和执行过程
ffmpeg 中的 hw_decode.c 代码,其功能是通过使用显卡硬件加速器对视频进行解码,从而提高解码效率和性能。下面将分步骤描述该代码的功能和执行过程。
引入头文件
代码开头引入了必要的头文件,包括 libavcodec/avcodec.h、libavformat/avformat.h、libavutil/pixdesc.h 等,这些头文件定义了解码和编码相关的结构体和函数。初始化变量和数据
接下来的一段代码初始化了一些变量和数据,例如 hw_device_ctx 是显卡设备上下文的引用,hw_pix_fmt 是像素格式等。它们都将在后面的代码中使用到。硬件加速器初始化
在 hw_decoder_init 函数中,调用 av_hwdevice_ctx_create 创建指定类型的硬件加速器,并将它保存到 ctx->hw_device_ctx 所指向的 AVBufferRef 缓冲区中。获取硬件支持的像素格式
在 get_hw_format 函数中,遍历 pix_fmts 数组,查找是否有与 hw_pix_fmt 相等的像素格式,如果找到则返回该像素格式,否则返回 AV_PIX_FMT_NONE。解码和输出
decode_write 函数是该代码的核心部分,实现了解码和输出功能。首先调用 avcodec_send_packet 将输入的 packet 数据发送给解码器,然后进入一个无限循环,直到所有数据都被解码并输出。在循环中,先调用 av_frame_alloc 分配 AVFrame 帧空间,然后调用 avcodec_receive_frame 从解码器中接收已解码的帧数据。如果返回的是 EAGAIN 或 EOF,则退出循环;如果出现错误则跳转到 fail 标签处处理。如果解码得到的帧格式与硬件支持的像素格式相同,则将该帧数据从 GPU 拷贝到 CPU 上,再调用 av_image_copy_to_buffer 将帧数据复制到内存缓冲区中,并通过 fwrite 函数将数据写入文件中。最后通过 av_frame_free 和 av_freep 函数释放内存空间。主函数
main 函数首先解析命令行参数,包括设备类型、输入文件名和输出文件名。然后通过 avformat_open_input 打开输入文件,通过 av_find_best_stream 查找视频流,并获取硬件支持的像素格式。接下来创建 AVCodexContext 上下文,设置 get_format 回调函数和硬件加速器上下文。通过 avcodec_open2 打开解码器,并打开输出文件。最后通过 av_read_frame 读取文件数据,调用 decode_write 函数进行解码和输出,直到读取完毕。
综上所述,该代码实现了使用显卡硬件加速器对视频进行解码的功能,并通过调用相关的结构体和函数实现了硬件加速器的初始化、解码和输出等操作。其主要思路是将显卡的并行处理能力和更高的带宽用于视频解码,从而提高解码效率和性能。
go代码如下:
github/moonfdd/ffmpeg-go库,把hw_decode.c改写成了go代码。如下:
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"unsafe"
"github.com/moonfdd/ffmpeg-go/ffcommon"
"github.com/moonfdd/ffmpeg-go/libavcodec"
"github.com/moonfdd/ffmpeg-go/libavformat"
"github.com/moonfdd/ffmpeg-go/libavutil"
)
func main0() (ret ffcommon.FInt) {
var input_ctx *libavformat.AVFormatContext
var video_stream ffcommon.FInt
var video *libavformat.AVStream
var decoder_ctx *libavcodec.AVCodecContext
var decoder *libavcodec.AVCodec
var packet libavformat.AVPacket
var type0 libavutil.AVHWDeviceType
var i ffcommon.FInt
if len(os.Args) < 4 {
fmt.Printf("Usage: %s <device type> <input file> <output file>\n", os.Args[0])
return -1
}
type0 = libavutil.AvHwdeviceFindTypeByName(os.Args[1])
if type0 == libavutil.AV_HWDEVICE_TYPE_NONE {
fmt.Printf("Device type %s is not supported.\n", os.Args[1])
fmt.Printf("Available device types:")
type0 = libavutil.AvHwdeviceIterateTypes(type0)
for type0 != libavutil.AV_HWDEVICE_TYPE_NONE {
fmt.Printf(" %s", libavutil.AvHwdeviceGetTypeName(type0))
type0 = libavutil.AvHwdeviceIterateTypes(type0)
}
fmt.Printf("\n")
return -1
}
/* open the input file */
if libavformat.AvformatOpenInput(&input_ctx, os.Args[2], nil, nil) != 0 {
fmt.Printf("Cannot open input file '%s'\n", os.Args[2])
return -1
}
if input_ctx.AvformatFindStreamInfo(nil) < 0 {
fmt.Printf("Cannot find input stream information.\n")
return -1
}
/* find the video stream information */
ret = input_ctx.AvFindBestStream(libavutil.AVMEDIA_TYPE_VIDEO, -1, -1, &decoder, 0)
if ret < 0 {
fmt.Printf("Cannot find a video stream in the input file\n")
return -1
}
video_stream = ret
for i = 0; ; i++ {
config := decoder.AvcodecGetHwConfig(i)
if config == nil {
fmt.Printf("Decoder %s does not support device type %s.\n",
ffcommon.StringFromPtr(decoder.Name), libavutil.AvHwdeviceGetTypeName(type0))
return -1
}
if config.Methods&libavcodec.AV_CODEC_HW_CONFIG_METHOD_HW_DEVICE_CTX != 0 && config.DeviceType == type0 {
hw_pix_fmt = config.PixFmt
break
}
}
decoder_ctx = decoder.AvcodecAllocContext3()
if decoder_ctx == nil {
return -libavutil.ENOMEM
}
video = input_ctx.GetStream(uint32(video_stream))
if decoder_ctx.AvcodecParametersToContext(video.Codecpar) < 0 {
return -1
}
decoder_ctx.GetFormat = ffcommon.NewCallback(get_hw_format)
if hw_decoder_init(decoder_ctx, type0) < 0 {
return -1
}
ret = decoder_ctx.AvcodecOpen2(decoder, nil)
if ret < 0 {
fmt.Printf("Failed to open codec for stream #%d\n", video_stream)
return -1
}
/* open the file to dump raw data */
output_file, _ = os.Create(os.Args[3])
/* actual decoding and dump the raw data */
for ret >= 0 {
ret = input_ctx.AvReadFrame(&packet)
if ret < 0 {
break
}
if uint32(video_stream) == packet.StreamIndex {
ret = decode_write(decoder_ctx, &packet)
}
packet.AvPacketUnref()
}
/* flush the decoder */
packet.Data = nil
packet.Size = 0
ret = decode_write(decoder_ctx, &packet)
packet.AvPacketUnref()
if output_file != nil {
output_file.Close()
}
libavcodec.AvcodecFreeContext(&decoder_ctx)
libavformat.AvformatCloseInput(&input_ctx)
libavutil.AvBufferUnref(&hw_device_ctx)
return 0
}
var hw_device_ctx *libavutil.AVBufferRef
var hw_pix_fmt libavutil.AVPixelFormat
var output_file *os.File
func hw_decoder_init(ctx *libavcodec.AVCodecContext, type0 libavutil.AVHWDeviceType) ffcommon.FInt {
var err ffcommon.FInt = 0
err = libavutil.AvHwdeviceCtxCreate(&hw_device_ctx, type0, "", nil, 0)
if err < 0 {
fmt.Printf("Failed to create specified HW device.\n")
return err
}
ctx.HwDeviceCtx = hw_device_ctx.AvBufferRef()
return err
}
func get_hw_format(ctx *libavcodec.AVCodecContext, pix_fmts *libavutil.AVPixelFormat) uintptr {
var p *libavutil.AVPixelFormat
for p = pix_fmts; *p != -1; p = (*libavutil.AVPixelFormat)(unsafe.Pointer(uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(p)) + uintptr(4))) {
if *p == hw_pix_fmt {
return uintptr(*p)
}
}
fmt.Printf("Failed to get HW surface format.\n")
r := libavutil.AVPixelFormat(libavutil.AV_PIX_FMT_NONE)
return uintptr(r)
}
func decode_write(avctx *libavcodec.AVCodecContext, packet *libavcodec.AVPacket) ffcommon.FInt {
var frame, sw_frame *libavutil.AVFrame
var tmp_frame *libavutil.AVFrame
var buffer *ffcommon.FUint8T
var size ffcommon.FInt
var ret ffcommon.FInt = 0
var e error
ret = avctx.AvcodecSendPacket(packet)
if ret < 0 {
fmt.Printf("Error during decoding\n")
return ret
}
for {
frame = libavutil.AvFrameAlloc()
sw_frame = libavutil.AvFrameAlloc()
if frame == nil || sw_frame == nil {
fmt.Printf("Can not alloc frame\n")
ret = -libavutil.ENOMEM
goto fail
}
ret = avctx.AvcodecReceiveFrame(frame)
if ret == -libavutil.EAGAIN || ret == libavutil.AVERROR_EOF {
libavutil.AvFrameFree(&frame)
libavutil.AvFrameFree(&sw_frame)
return 0
} else if ret < 0 {
fmt.Printf("Error while decoding\n")
goto fail
}
if frame.Format == hw_pix_fmt {
/* retrieve data from GPU to CPU */
ret = libavutil.AvHwframeTransferData(sw_frame, frame, 0)
if ret < 0 {
fmt.Printf("Error transferring the data to system memory\n")
goto fail
}
tmp_frame = sw_frame
} else {
tmp_frame = frame
}
size = libavutil.AvImageGetBufferSize(tmp_frame.Format, tmp_frame.Width,
tmp_frame.Height, 1)
buffer = (*byte)(unsafe.Pointer(libavutil.AvMalloc(uint64(size))))
if buffer == nil {
fmt.Printf("Can not alloc buffer\n")
ret = -libavutil.ENOMEM
goto fail
}
ret = libavutil.AvImageCopyToBuffer(buffer, size,
(*[4]*byte)(unsafe.Pointer(&tmp_frame.Data)),
(*[4]int32)(unsafe.Pointer(&tmp_frame.Linesize)), tmp_frame.Format,
tmp_frame.Width, tmp_frame.Height, 1)
if ret < 0 {
fmt.Printf("Can not copy image to buffer\n")
goto fail
}
_, e = output_file.Write(ffcommon.ByteSliceFromByteP(buffer, int(size)))
if e != nil {
fmt.Printf("Failed to dump raw data.\n")
goto fail
}
fail:
libavutil.AvFrameFree(&frame)
libavutil.AvFrameFree(&sw_frame)
libavutil.AvFreep(uintptr(unsafe.Pointer(&buffer)))
if ret < 0 {
return ret
}
}
}
func main() {
// go run ./examples/internalexamples/hw_decode/main.go cuda ./resources/big_buck_bunny.mp4 ./out/hw.yuv
// ./lib/ffplay -pixel_format yuv420p -video_size 640x360 ./out/hw.yuv
os.Setenv("Path", os.Getenv("Path")+";./lib")
ffcommon.SetAvutilPath("./lib/avutil-56.dll")
ffcommon.SetAvcodecPath("./lib/avcodec-58.dll")
ffcommon.SetAvdevicePath("./lib/avdevice-58.dll")
ffcommon.SetAvfilterPath("./lib/avfilter-56.dll")
ffcommon.SetAvformatPath("./lib/avformat-58.dll")
ffcommon.SetAvpostprocPath("./lib/postproc-55.dll")
ffcommon.SetAvswresamplePath("./lib/swresample-3.dll")
ffcommon.SetAvswscalePath("./lib/swscale-5.dll")
genDir := "./out"
_, err := os.Stat(genDir)
if err != nil {
if os.IsNotExist(err) {
os.Mkdir(genDir, 0777) // Everyone can read write and execute
}
}
main0()
}
执行命令如下:
go run ./examples/internalexamples/hw_decode/main.go cuda ./resources/big_buck_bunny.mp4 ./out/hw.yuv
./lib/ffplay -pixel_format yuv420p -video_size 640x360 ./out/hw.yuv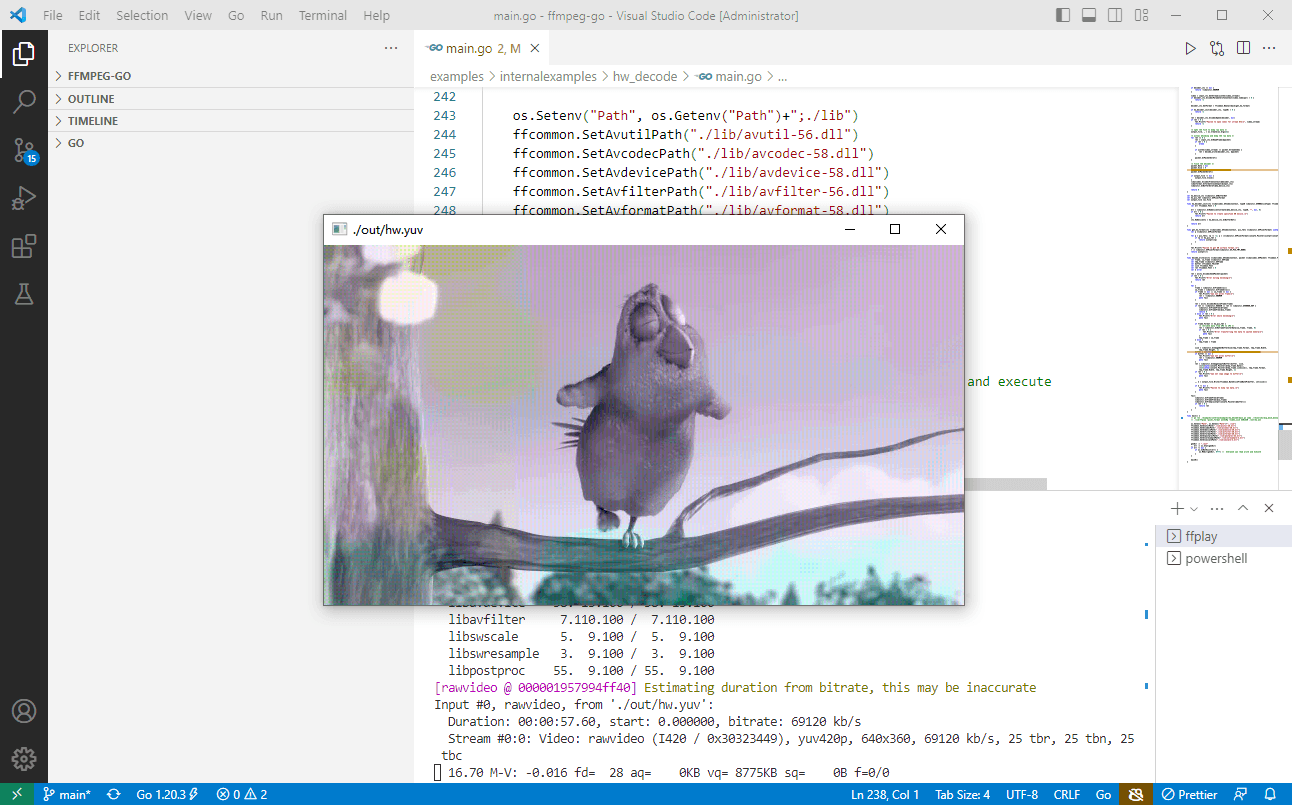
解码出来的视频,看起来有点失真的。
代码分析
首先,我们需要导入所需的库文件。在主函数中,我们首先检查输入参数数量是否正确,如果不正确则输出使用说明并返回错误。
接下来,我们通过设备类型名称获取设备类型,如果不支持该设备类型,则输出可用设备类型列表并返回错误。
在打开输入文件之后,我们使用AvFindBestStream函数查找最佳视频流,并使用其参数初始化解码器并打开解码器。
我们得到每帧数据之后,解码函数AvcodecSendPacket和AvcodecReceiveFrame会被循环调用,以将解码后的帧数据写入输出文件。
最后,我们关闭所有打开的资源,包括输入、输出文件和解码器等。
结语
本文介绍了如何使用Golang实现FFmpeg硬解码程序。通过对FFmpeg官方的HW Decode示例进行适当修改,我们成功地完成了设备类型检查、输入文件打开、解码器配置和输出文件处理等功能。此外,我们也介绍了如何在实际应用中使用FFmpeg库,并提供了一些代码片段供读者参考。
本作品采用《CC 协议》,转载必须注明作者和本文链接


 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu



