5.记录网球得分
- 本系列文章为
laracasts.com的系列视频教程——Code Katas in PHP 的学习笔记。若喜欢该系列视频,可去该网站订阅后下载该系列视频,支持正版。- Kata 是一个简短,可重复的编程挑战,可以帮助我们进行快速地编程练习。
- 开发模型仍旧是 TDD(测试驱动开发),视频中使用的是 phpspec 进行开发,笔记中使用了 Laravel 应用,因此代码有不同。
本节说明
- 对应第 5 小节:Tennis Scoring
本节内容
这一节我们的练习是网球得分的计算。首先你需要花点时间熟悉一下 网球计分 的规则,然后我们简单记录一下:
| 得分/比分 | 英文表示 |
|---|---|
| 0 | Love |
| 1-0 | Fifteen-Love |
| 2-0 | Thirty-Love |
| 3-0 | Forty-Love |
| 4-0 | Winner |
| 4-3 | Advantage Player |
| 4-4 | Deuce |
| 1-1 | Fifteen-All |
| 2-2 | Thirty-All |
现在我们来开始练习。首先新建测试:
$ php artisan make:test TennisMatchTest --unit然后添加第一个测试:
tests\Unit\TennisMatchTest.php
<?php
namespace Tests\Unit;
use Tests\TestCase;
use App\TennisMatch;
class TennisMatchTest extends TestCase
{
public function setUp()
{
parent::setUp();
$this->tennisMatch = new TennisMatch();
}
/** @test */
public function it_scores_a_scoreless_game()
{
$this->assertEquals($this->tennisMatch->score(),'Love-All');
}
}
运行测试: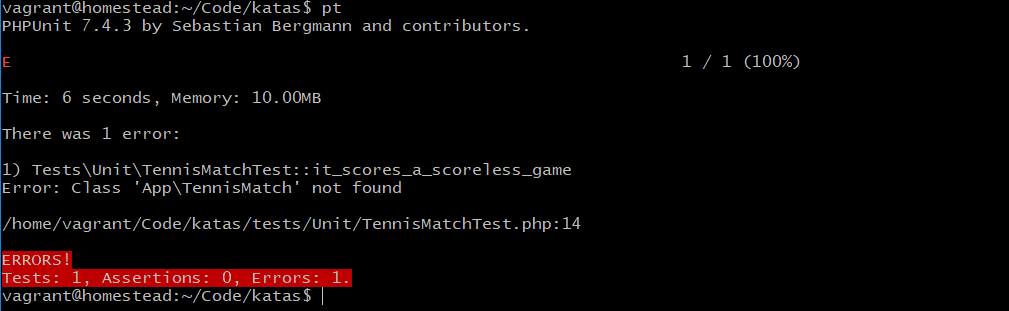
我们来让测试通过:
app\TennisMatch.php
<?php
namespace App;
class TennisMatch
{
public function score()
{
return 'Love-All';
}
}再次运行测试: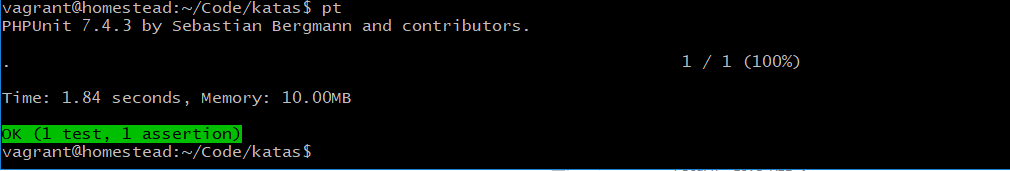
向前推进,当两个选手的比分为 1:0 时,我们应该记录为 Fifteen-Love。但是在我们添加新的测试之前,我们先需要引入选手的概念。我们建立Player模型:
app\Player.php
<?php
namespace App;
class Player
{
public $name;
public $points;
public function __construct($name,$points)
{
$this->name = $name;
$this->points = $points;
}
public function earnPoints($points)
{
$this->points = $points;
}
}选手拥有name和points属性,并且可以得分:earnPoints。然后我们在TennisMatch中注入两个选手:
app\TennisMatch.php
<?php
namespace App;
class TennisMatch
{
protected $player1;
protected $player2;
public function __construct(Player $player1,Player $player2)
{
$this->player1 = $player1;
$this->player2 = $player2;
}
public function score()
{
return 'Love-All';
}
}最后我们在测试时实例化两个选手,并给定初始分数为 0:
tests\Unit\TennisMatchTest.php
<?php
namespace Tests\Unit;
use Tests\TestCase;
use App\TennisMatch;
use App\Player;
class TennisMatchTest extends TestCase
{
public function setUp()
{
parent::setUp();
$this->john = new Player('John',0);
$this->jane = new Player('Jane',0);
$this->tennisMatch = new TennisMatch($this->john,$this->jane);
}
/** @test */
public function it_scores_a_scoreless_game()
{
$this->assertEquals($this->tennisMatch->score(),'Love-All');
}
}再来运行之前的测试: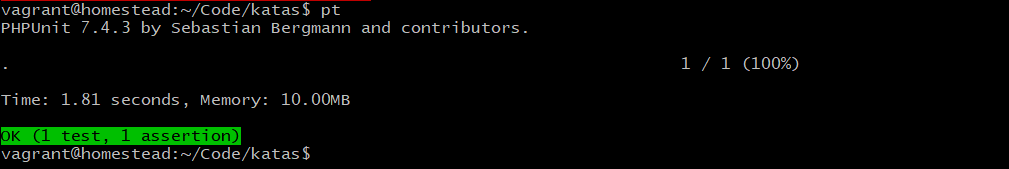
然后添加新的测试:
.
.
/** @test */
public function it_scores_a_1_0_game()
{
$this->john->earnPoints(1);
$this->assertEquals($this->tennisMatch->score(),'Fifteen-Love');
}
}运行测试会失败: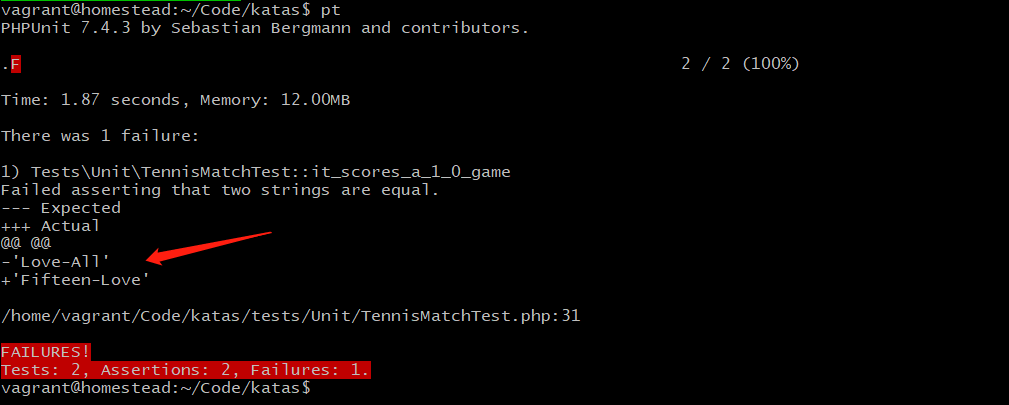
我们来让测试通过:
app\TennisMatch.php
.
.
public function score()
{
if($this->player1->points == 1 && $this->player2->points == 0){
return 'Fifteen-Love';
}
return 'Love-All';
}
}运行测试: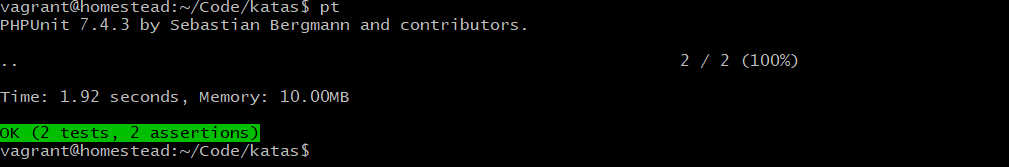
按照相同的逻辑,我们再来添加 2-0 以及 3-0 的测试:
.
.
/** @test */
public function it_scores_a_2_0_game()
{
$this->john->earnPoints(2);
$this->assertEquals($this->tennisMatch->score(),'Thirty-Love');
}
/** @test */
public function it_scores_a_3_0_game()
{
$this->john->earnPoints(3);
$this->assertEquals($this->tennisMatch->score(),'Forty-Love');
}
}来让测试通过:
.
.
public function score()
{
if($this->player1->points == 3 && $this->player2->points == 0)
{
return 'Forty-Love';
}
if($this->player1->points == 2 && $this->player2->points == 0)
{
return 'Thirty-Love';
}
if($this->player1->points == 1 && $this->player2->points == 0)
{
return 'Fifteen-Love';
}
return 'Love-All';
}
}运行测试: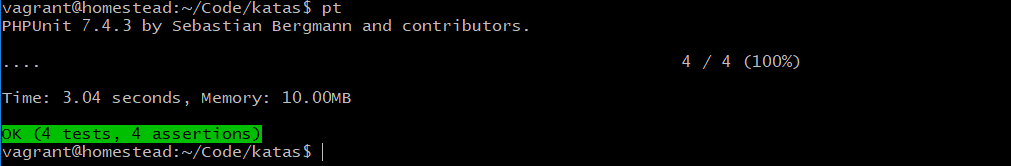
你已经发现了,我们在重复写代码,所以是时候来进行重构了。在之前的 Kata 中,我们说过,像这种 if-else 驱动方式,我们可以很容易地转换成表驱动。所以我们进行重构:
app\TennisMatch.php
<?php
namespace App;
class TennisMatch
{
protected $player1;
protected $player2;
protected $lookup = [
0 => 'Love',
1 => 'Fifteen',
2 => 'Thirty',
3 => 'Forty'
];
.
.
public function score()
{
$score = $this->lookup[$this->player1->points] . '-';
$score .= $this->lookup[$this->player2->points];
return $score;
}
}我们来运行测试: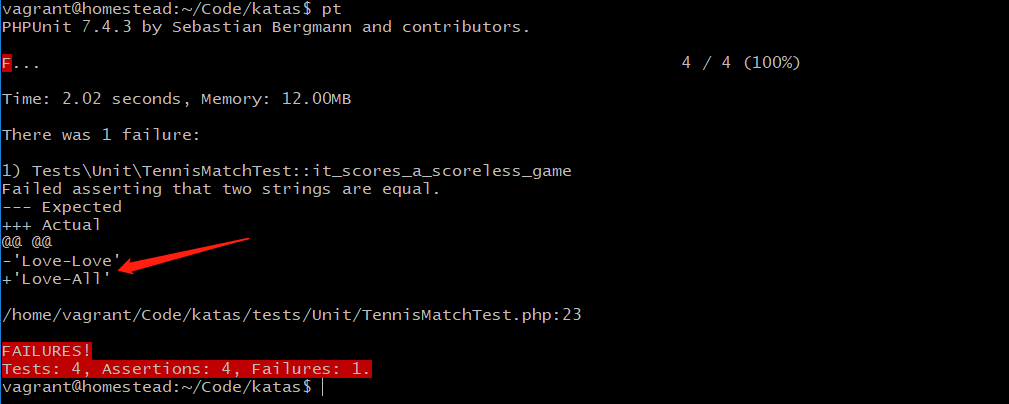
可以看到有测试失败了,因为对于 0-0,1-1 的比分,我们表示为 Love-All,Fifteen-All,所以我们需要进行下转换:
<?php
namespace App;
class TennisMatch
{
.
.
public function score()
{
$score = $this->lookup[$this->player1->points] . '-';
$score .= $this->player1->points == $this->player2->points ? 'All' : $this->lookup[$this->player2->points];
return $score;
}
}再次运行测试: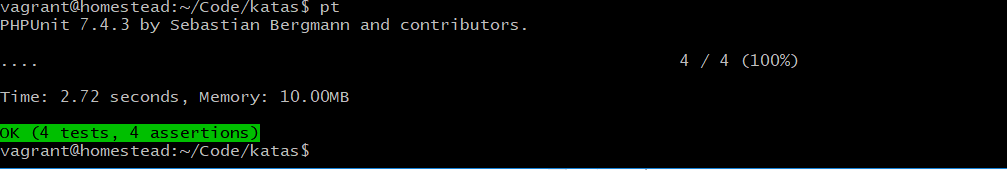
假如时隔半年,我们再来看这段代码,我们会一眼看出这段代码的含义吗?如果不能,那说明我们要进行重构了:
.
.
public function score()
{
$score = $this->lookup[$this->player1->points] . '-';
return $score .= $this->tied() ? 'All' : $this->lookup[$this->player2->points];
}
public function tied()
{
return $this->player1->points == $this->player2->points;
}
}再次运行测试:
好了,我们继续推进:
.
.
/** @test */
public function it_scores_a_4_0_game()
{
$this->john->earnPoints(4);
$this->assertEquals($this->tennisMatch->score(),'Win For John');
}
}对于 4-0 的比赛,即代表 john 胜出。但是网球对于胜出有两个条件:
- 得分大于或等于 4 分;
- 领先至少 2 分;
只有这两个条件同时满足,那么才会出现胜利者。所以我们的代码如下:
.
.
public function score()
{
if($this->hasAWinner())
{
return 'Win For John';
}
$score = $this->lookup[$this->player1->points] . '-';
return $score .= $this->tied() ? 'All' : $this->lookup[$this->player2->points];
}
.
.
private function hasAWinner()
{
return (max([$this->player1->points,$this->player2->points]) >= 4) &&
(abs($this->player1->points - $this->player2->points) >= 2);
}
}运行测试:
为了让测试快速通过,我们暂时进行了硬编码,接下来我们需要做重构:
.
.
public function score()
{
if($this->hasAWinner())
{
return 'Win For ' . $this->leader()->name;
}
$score = $this->lookup[$this->player1->points] . '-';
return $score .= $this->tied() ? 'All' : $this->lookup[$this->player2->points];
}
.
.
private function leader()
{
return $this->player1->points > $this->player2->points ? $this->player1 : $this->player2;
}
}运行测试:
正如之前所说,当半年之后你再来看这段代码时,如果你认为不能看懂的话,那么你应该进行重构:
.
.
public function score()
{
if($this->hasAWinner())
{
return 'Win For ' . $this->leader()->name;
}
$score = $this->lookup[$this->player1->points] . '-';
return $score .= $this->tied() ? 'All' : $this->lookup[$this->player2->points];
}
private function tied()
{
return $this->player1->points == $this->player2->points;
}
private function hasAWinner()
{
return $this->hasEnoughPointsToBeWon() && $this->isLeadingAtLeastByTwo();
}
private function hasEnoughPointsToBeWon()
{
return max([$this->player1->points,$this->player2->points]) >= 4;
}
private function isLeadingAtLeastByTwo()
{
return abs($this->player1->points - $this->player2->points) >= 2;
}
private function leader()
{
return $this->player1->points > $this->player2->points ? $this->player1 : $this->player2;
}
}运行测试:
我们向前推进:
.
.
/** @test */
public function it_scores_a_0_4_game()
{
$this->jane->earnPoints(4);
$this->assertEquals($this->tennisMatch->score(),'Win For Jane');
}
}运行测试: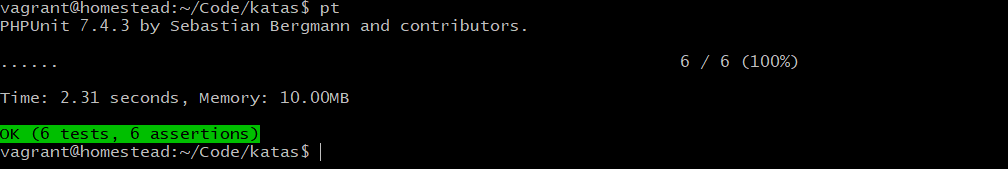
我们继续推进:
.
.
/** @test */
public function it_scores_a_4_3_game()
{
$this->john->earnPoints(4);
$this->jane->earnPoints(3);
$this->assertEquals($this->tennisMatch->score(),'Advantage John');
}
}对于 4-3 的比分,会得到 Advantage 的记录。我们来运行测试: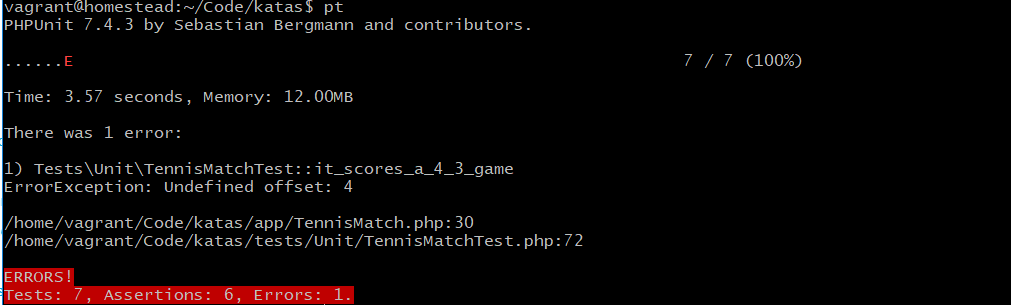
对于 Advantage 必须同时满足两个条件:
- 得分大于或等于 4 分;
- 某一方领先且仅领先 1 分;
我们来让测试通过:
<?php
namespace App;
class TennisMatch
{
protected $player1;
protected $player2;
protected $lookup = [
0 => 'Love',
1 => 'Fifteen',
2 => 'Thirty',
3 => 'Forty'
];
public function __construct(Player $player1,Player $player2)
{
$this->player1 = $player1;
$this->player2 = $player2;
}
public function score()
{
if($this->hasAWinner())
{
return 'Win For ' . $this->leader()->name;
}
if($this->hasTheAdvantage())
{
return 'Advantage ' . $this->leader()->name;
}
$score = $this->lookup[$this->player1->points] . '-';
return $score .= $this->tied() ? 'All' : $this->lookup[$this->player2->points];
}
private function tied()
{
return $this->player1->points == $this->player2->points;
}
private function hasAWinner()
{
return $this->hasEnoughPointsToBeWon() && $this->isLeadingAtLeastByTwo();
}
private function hasTheAdvantage()
{
return $this->hasEnoughPointsToBeWon() && $this->isLeadingByOne();
}
private function hasEnoughPointsToBeWon()
{
return max([$this->player1->points,$this->player2->points]) >= 4;
}
private function isLeadingAtLeastByTwo()
{
return abs($this->player1->points - $this->player2->points) >= 2;
}
private function isLeadingByOne()
{
return abs($this->player1->points - $this->player2->points) == 1;
}
private function leader()
{
return $this->player1->points > $this->player2->points ? $this->player1 : $this->player2;
}
}运行测试:
让我们继续推进。我们来引入 Deuce 的定义:当比分出现 3-3 及 之后的 4-4 之类的平分时,我们称之为 Deuce。所以 Deuce 要满足两个条件:
- 比分之后要大于或等于 6,即大于等于 3 + 3;
- 两个选手的比分相同;
我们依然先从测试开始:
.
.
/** @test */
public function it_scores_a_3_3_game()
{
$this->john->earnPoints(3);
$this->jane->earnPoints(3);
$this->assertEquals($this->tennisMatch->score(),'Deuce');
}
}运行测试:
添加 Deuce 的处理逻辑:
.
.
public function score()
{
if($this->hasAWinner())
{
return 'Win For ' . $this->leader()->name;
}
if($this->hasTheAdvantage())
{
return 'Advantage ' . $this->leader()->name;
}
if($this->inDeuce())
{
return 'Deuce';
}
$score = $this->lookup[$this->player1->points] . '-';
return $score .= $this->tied() ? 'All' : $this->lookup[$this->player2->points];
}
.
.
private function hasTheAdvantage()
{
return $this->hasEnoughPointsToBeWon() && $this->isLeadingByOne();
}
private function inDeuce()
{
return $this->player1->points + $this->player2->points >= 6 && $this->tied();
}
.
.再次运行测试:
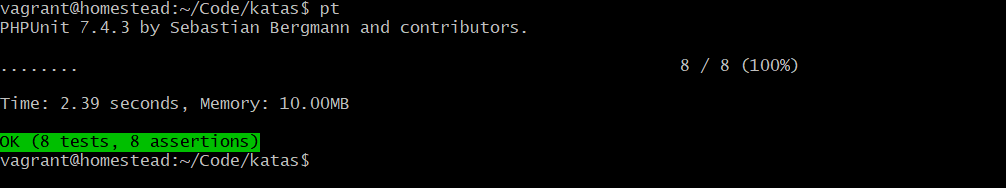
现在我们的测试已经全部通过,你可以继续添加测试用以测试我们的代码逻辑是否完备。然后我们可以来做点你认为有意义的重构,比如说:
.
.
public function score()
{
if($this->hasAWinner())
{
return 'Win For ' . $this->leader()->name;
}
if($this->hasTheAdvantage())
{
return 'Advantage ' . $this->leader()->name;
}
if($this->inDeuce())
{
return 'Deuce';
}
return $this->generalScore();
}
private function generalScore()
{
$score = $this->lookup[$this->player1->points] . '-';
return $score .= $this->tied() ? 'All' : $this->lookup[$this->player2->points];
}
.
.再次测试: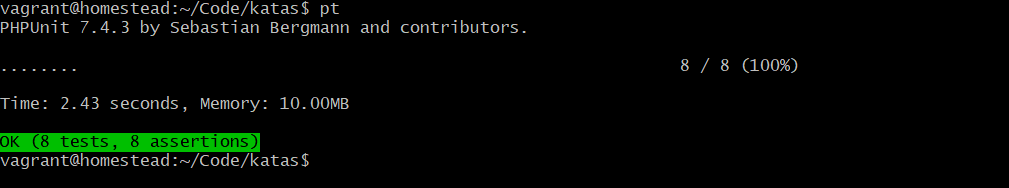
玩得愉快~

 PHP 实战技巧课程笔记
PHP 实战技巧课程笔记

 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu



