8.3. 使用 sql
持之以恒,方得始终!
sql 是什么?
structured query language 结构化查询语言。
MySQL,oracle,postgresql 中都可以用它处理数据的增删改查等操作。
sql 有它自己的 ANSI 标准,可能和一些数据库中的实现有细微的差别。
插入数据 insert
INSERT [INTO] table [(column1, column2, ...)] VALUES
(value1,value2, ...)[,('v1', 'v2',...), ...];在之前建好的 customers 表中插入一行
insert into customers values (null, 'junwind', 'hubei', 'vo');
// 字符串需要给单双引号,数字,日期不需要引号。创建一个 book_insert.sql 文件,插入更多数据:
use books;
insert into customers values
(3, 'Julie Smith', '25 Oak Street', 'Airport West'),
(4, 'Alan Wong', '1/47 Haines Avenue', 'Box Hill'),
(5, 'Michelle Arthur', '357 North Road', 'Yarraville');
insert into orders values
(null, 3, 69.98, '2007-04-02'),
(null, 1, 49.99, '2007-04-15'),
(null, 2, 74.98, '2007-04-19'),
(null, 3, 24.99, '2007-05-01');
insert into books values
('0-672-31679-8', 'Michael Morgan', 'java 2 for professional developers', 34.99),
('0-672-31745-1', 'Thomas Down', 'Installing Debian CUN/Linux', 24.99),
('0-672-31509-2', 'Pruitt et al.', 'Teach yourself GIMP in 24 Hours', 24.99),
('0-672-31769-9', 'Thomas Schenk', 'Caldera OpenLinux System Administration Unleashed', 49.99);
insert into order_books values
(1, '0-672-31697-8', 2),
(2, '0-672-31769-9', 1),
(3, '0-672-31769-9', 1),
(3, '0-672-31509-2', 1),
(4, '0-672-31745-1', 3);
insert into book_reviews values
('0-672-31697-8', 'The Morgan book is clearly written and goes well beyond most of the basic Java books out there.');mysql -h host -u username -p 'xxx' < /path/to/book_insert.sql
// 也可以在登录 mysql 后
source /path/to/book_insert.sql查询数据 select
SELECT [options] items
[INFO file_details]
FROM tables
[WHERE conditions]
[GROUP BY group_type]
[HAVING where_definition]
[ORDER BY order_type]
[LIMIT limit_criteria]
[PROCEDURE proc_name(arguments)]
[lock_options];select name,city from customers;
select * from order_books;
select * from orders where customerid = 3;where 字句中常用的运算符
= 等于
> 大于
< 小于
>= 大于等于
<= 小于等于
!= , <> 不等
is not null 值不为空, 测试字段是否包含一个值
is null 值是空的
between 比如 18 <= age <= 99
in city in('beijing', 'hubei') city的值是否是beijng或hubei
not in city not in('beijing', 'hubei') 不在这个集合中
like name like("fred %") 模糊匹配, %任意个任意字符, _任意单个字符
not like name not like("fred %)
regexp name regexp 正则匹配
and 多个条件,并且
or 多个条件,或者select * from orders where customerid = 3 or customerid = 4;多表联查
一般项目开发中,多表联查才是比较常见的。
比如,我想知道哪些客户在本月有订单,我需要查 orders,customers表,如果还想知道下单的物品是什么,还需要查 order_books, books表。
当然,联表多了,is bad,我们建表,其实有时候并不一定非要遵守什么范式,根据自己的系统,数据而定,适当的反范式,也有可能起到一个 good idea。
inner join
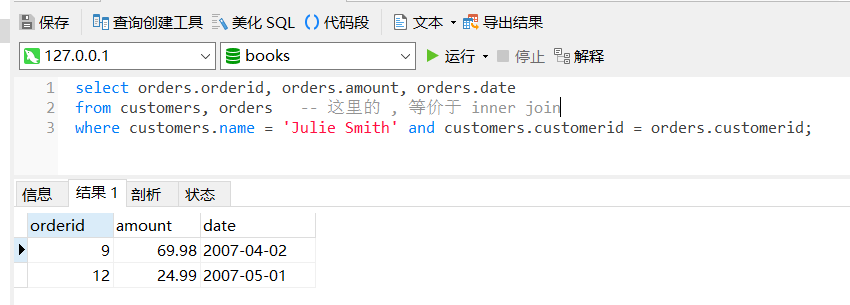
我想查 Julie Smith的订单,我需要先在 customers中查到 customerid,然后从 orders 表中查 customerid对应的单子。
select orders.orderid, orders.amount, orders.date
from customers, orders // 这里的 , 等价于 inner join
where customers.name = 'Julie Smith' and customers.customerid = orders.customerid;inner join类似笛卡尔乘积(两个表行数相乘),将两个表的数据合成一个大表。我们可以看一下大表的数据
select * from customers, orders;打个简单比方,我左表customers有数据 1,2,3,右表orders有数据a,b,c,则最终形成 1a,1b,1c,2a,2b,2c,3a,3b,3c。
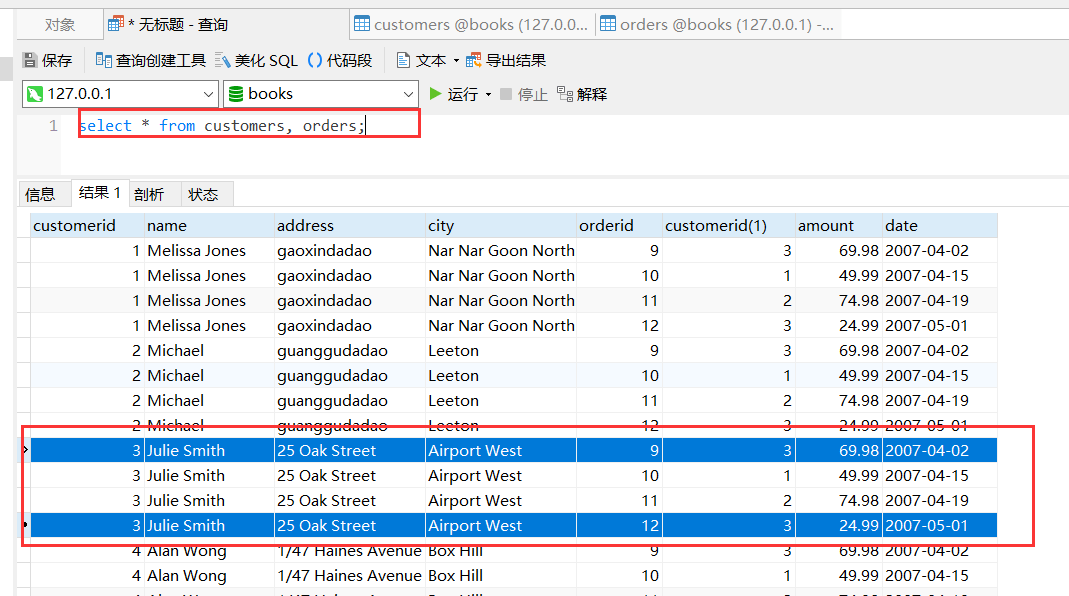
我们执行一下上面的查询,看结果对不对:
注意:-- 是 sql 中的注释。
用下面的.写法,表示列是哪个表的,更易维护。
table.column , database.table.column
books.orders.customerid = other_db.orders.customerid多于2张表的关联
比如,我想查询哪些客户订购了 java 的书,后续向这些用户发送关于 java 的新书推送。我们先来分析下:
- 从 books 中通过 java 模糊查询到 isbn。
- 从 orders_books 中通过 isbn 查询到 orderid。
- 从 orders 中通过 orderid 查到 customerid。
- 从 customers 中通过 customerid 查询用户。
select customers.name
from customers, orders, order_books, books
where books.title like "%java%"
and books.isbn = order_books.isbn
and order_books.orderid = orders.orderid
and orders.customerid = customers.customerid;left join
比如,我想查询从来没有下单的客户,或从没有被订购的书。
select customers.customerid, customers.name, orders.orderid
from customers left join orders
on customers.customerid = orders.customerid;以左表为主,左表中的都列出来,如果右边没有满足条件的,则为null。
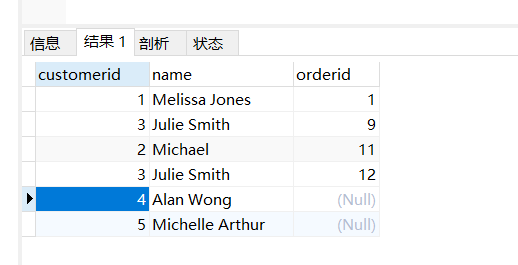
如果我们只想要没有任何订单的客户,也就是上面 orderid 为null的行,我们可以这样:
select customers.customerid, customers.name
from customers left join orders
using (customerid) // 两个表字段名称相同才能用 using
where orders.orderid is null;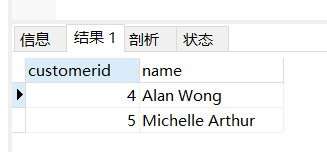
别名 alias
表,字段,都可以起一个别名。
比如,重写前面的一个查询
select c.name
from customers as c, orders as o, order_books as ob, books as b
where c.customerid = o.customerid
and o.orderid = ob.orderid
and ob.isbn = b.isbn
and b.title like "%java%";下面这种情况,就必须得用别名了: 如果要查同一个表中,值相同的行。 比如,我想查询住在同一个城市的客户
select c1.name, c2.name, c1.city
from customers as c1, customers as c2
where c1.city = c2.city
and c1.name != c2.name;order by
order by 字句,可以将 select 查询的字段做排序。
select name, address from customers order by name; // 查询后的结果,根据 name字段,做正序排序默认是升序 asc,也可以用 desc 倒序
select name,address from customers order by name desc;还可以对多个字段排序,还可以用字段的别名,甚至它们的位置数字代替字段名称。
group by,统计函数,having
我们有时候,可能会希望把数据分组来统计,比如,我的 books表,加了一个新的字段 type,表示图书类型,现在有计算机类,机械类,我们可以根据 type 分组,统计它们两类的销量,或者两个类别下共有多少本书。
统计函数
avg() 求平均值
count() 求结果的总行数
distinct count() 不是查询结果的行数
min() 最小值
max() 最大值
std() 背离值
sun() 求和求 orders 表,所有订单总金额的平均值。
select avg(amount) from orders;分组
按客户分组,求他们各自的总金额平均值。
select customerid, avg(amount) from orders group by customerid;如果使用了一个统计函数,或group by,出现在 select 中的必须是统计函数,或group by 中的列名称。
同样,如果希望在 group by 中使用一列,该列必须在 select 中出现。
having
对分组,统计的数据,再做条件筛选。
如果希望知道哪些客户的订单总金额平均值超过 $50
select customerid, avg(amount) as aver_amount
from orders
group by customerid
having aver_amount > 50;limit
返回结果中的哪几行。
limit offset, linenum // offset起始行,从0开始; linenum行数select name from customers limit 2, 3; // 从结果中的第2行开始,返回 2 3 4 这三条数据注意:行号是从0开始的。
常用于分页功能中。
子查询
一个查询里面又嵌套了另个查询,一般子查询可以当做一个值,或一行,或一个表。
作为一个值
找到一个金额最大的订单
select customerid, amount
from orders
where amount = (select max(amount) from orders);
// 当然,仅仅针对这个例子,其实还有更好的办法
select customerid, amount from orders order by amount desc limit 1;子查询操作符
any , select c1 from t1 where c1 > any(select c1 from t2); c1 的值大于子查询中的任何一个即为true
in , select c1 from t1 where c1 in(select c1 from t2); c1 的值在子查询中有,则为true
all , select c1 from t1 where c1 > all(select c1 from t2); c1 大于子查询中的所有结果,才为true
exists在子查询中使用外面查询的结果
查找还没被下单的书。
select isbn, title
from books
where not exists
(select * from order_books where order_books.isbn = books.isbn);作为行
select c1,c2,c3
from t1
where (c1,c2,c3) in (select c1,c2,c3 from t2);作为表
放在 from 后面
select *
from (select customerid,name from customers where city = 'Box Hill') as box_hill; // 子查询的结果作为临时表,并且必须给起个别名修改数据 update
UPDATE [LOW_PRIORITY] [IGNORE] table
set column1 = v1, column2 = v2, ...
[where condition]
[order by xx asc|desc]
[limit offset linenum]将图书的价格提高 10%:
update books set price = price*1.1;更新一个客户的地址
update customers
set address = '250 olsens road'
where customerid = 4;alter 修改表结构
alter table tablename alter字句添加新列
add 字段 字段属性 first|after 字段
alter table orders add tax float(6,2) after amount;添加索引
add index 索引 字段...
add primary key 字段...
add unique 字段...添加,删除字段的默认值
alter 字段 set default value
alter 字段 drop default 修改列名称
change 字段 新字段 属性修改列属性
modify 字段 字段属性
alter table customers modify name char(70) not null;删除指定列
drop 字段
alter table orders drop tax;删除主键
drop primary key删除指定的索引
drop index 索引删除外键
drop foreign key 更改表名
rename 新表设置字符集和排序
default character set xx collate xxdelete 删除行
delete from table
where xx
order by xx
limit xx xx;删除请一定要加上 where条件,否则就是删除整张表了,除非你真的想这么干。
delete from customers where customerid = 5;删除表
drop table 表名;删除库
drop database 库名称;如有任何侵权行为,请通知我删除,谢谢大家!
个人邮箱:865460609@qq.com

 读书笔记:《PHP和MySQL Web开发》
读书笔记:《PHP和MySQL Web开发》

 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu



