11.用 TDD 的方式开发第三方库
本系列文章为
laracasts.com的系列视频教程——Testing Laravel 的学习笔记。若喜欢该系列视频,可去该网站订阅后下载该系列视频,支持正版。
本节说明
- 对应第 11 小节:Design a Fluent API With TDD
本节内容
VerbalExpressions 是一个 JavaScript 库,用于构建困难的正则表达式,它也提供了其他语言如 C#,Java,PHP等的实现。本节我们来学习如何设计和开发这个库的 PHP 版本。
首先新建测试文件:
php artisan make:test ExpressionTest --unit建立第一个单元测试:通过给定字符串构造正则表达式,例如,给定 www 构造 /www/ 的正则表达式。如下:
tests/Unit/ExpressionTest.php
<?php
namespace Tests\Unit;
use Tests\TestCase;
use App\Expression;
class ExpressionTest extends TestCase
{
/** @test */
public function it_finds_s_string()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->find('www');
$this->assertRegExp($regex,'www');
}
}
运行测试当然会失败:
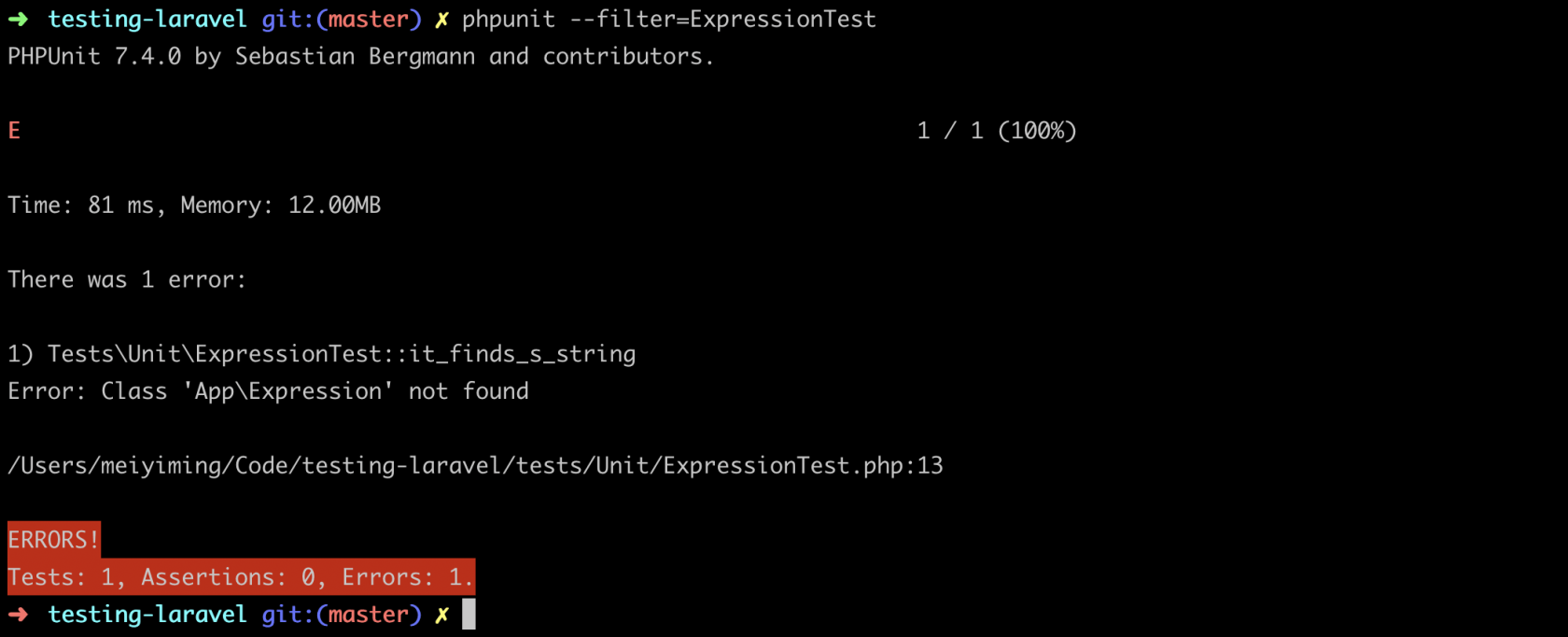
向前推进,新建 ExpressionTest 类文件:
app/Expression.php
<?php
namespace App;
class Expression
{
public static function make()
{
}
public function find()
{
}
}再次测试:
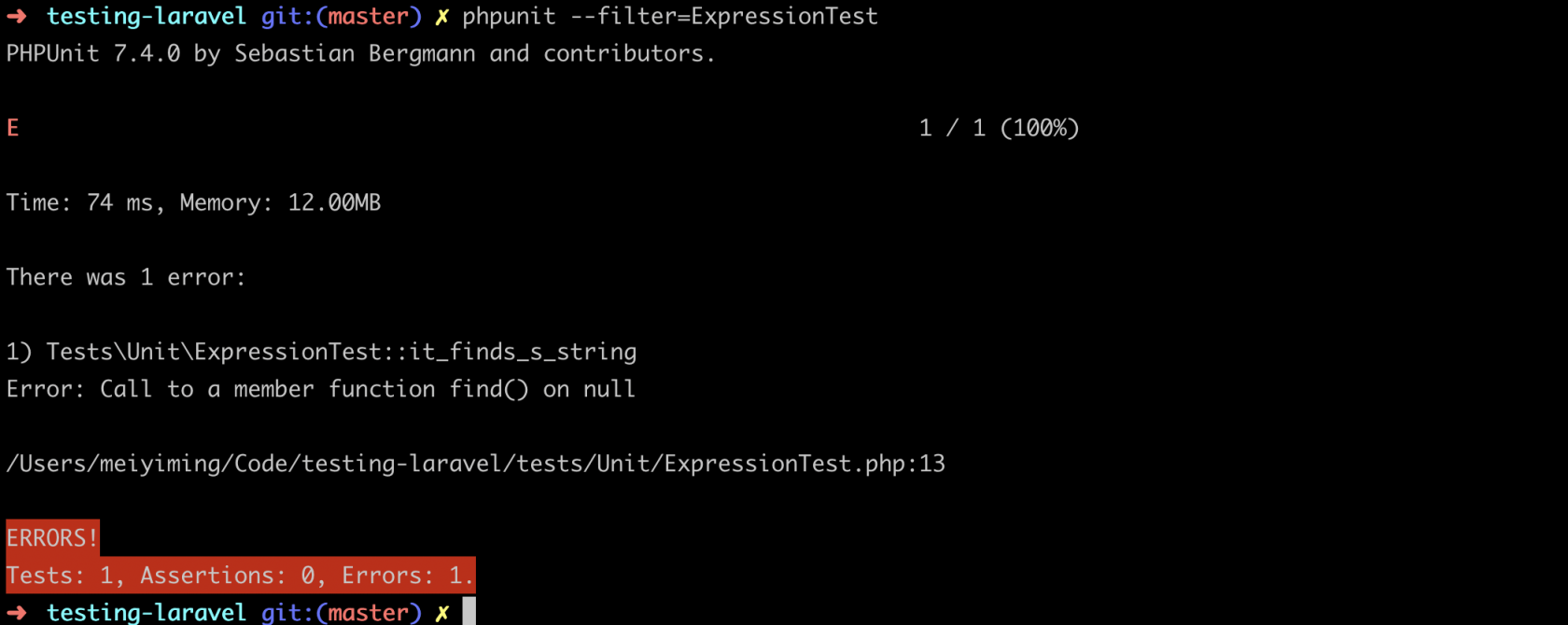
再来看下我们的代码:
$regex = Expression::make()->find('www');在我们的设计中,make() 方法是某种意义上的构造函数,会返回一个对象。但是,此时此刻我们并不知道我们期望得到的对象的具体信息,所以我们暂且先返回类本身:
app/Expression.php
<?php
namespace App;
class Expression
{
public static function make()
{
return new Static;
}
public function find()
{
}
}再次测试:
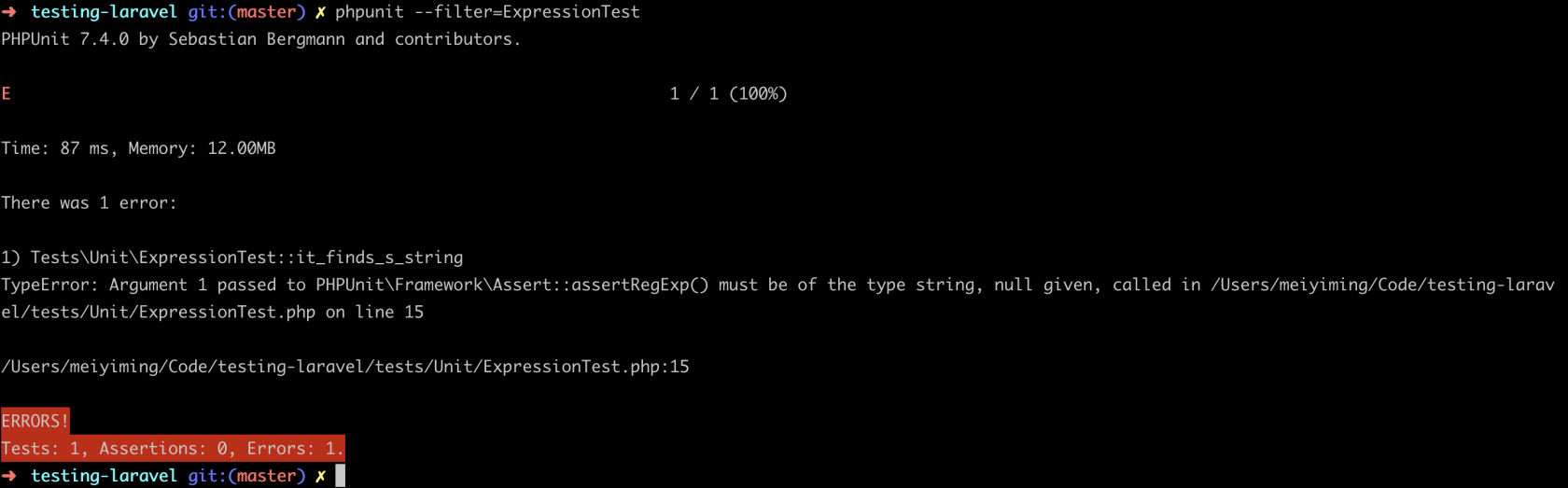
错误发生了改变,下面让我们做最小的改动以使我们的测试通过:
app/Expression.php
<?php
namespace App;
class Expression
{
public static function make()
{
return new Static;
}
public function find($value)
{
return '/' . $value .'/';
}
}再次测试:
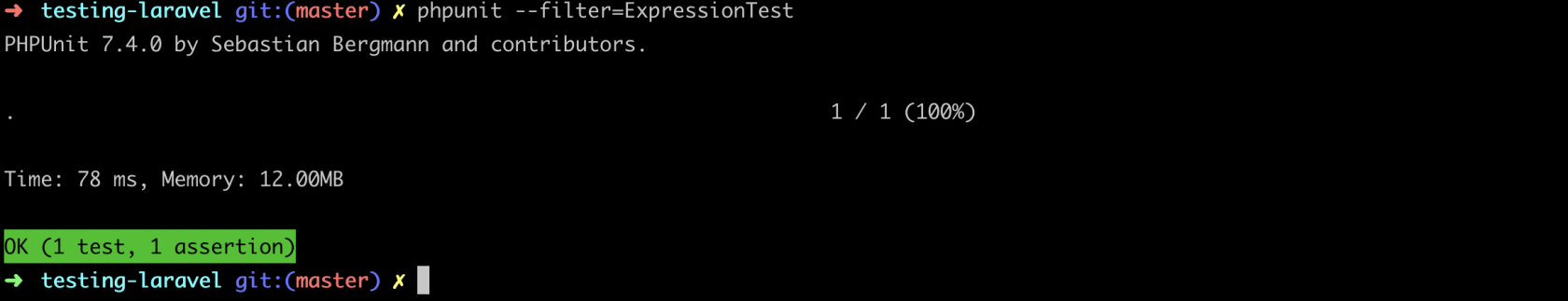
接下来我们新增 then() API,它实际上等同于 find(),但是更语义化。所以我们来为此增加测试逻辑:
/** @test */
public function it_finds_s_string()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->find('www');
$this->assertRegExp($regex,'www');
$regex = Expression::make()->then('www');
$this->assertRegExp($regex,'www');
}增加 then() 方法:
.
.
public function find($value)
{
return '/' . $value .'/';
}
public function then($value)
{
return $this->find($value);
}
}再次测试,成功通过。接下来为我们新增 anything() API,它匹配任意字符,所以正则表达式会是这样:/.*/。还是从测试开始:
.
.
/** @test */
public function it_checks_for_anything()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->anything();
$this->assertRegExp($regex,'foo');
}
}添加 anything() API:
.
.
public function anything()
{
return '/.*/';
}运行测试:
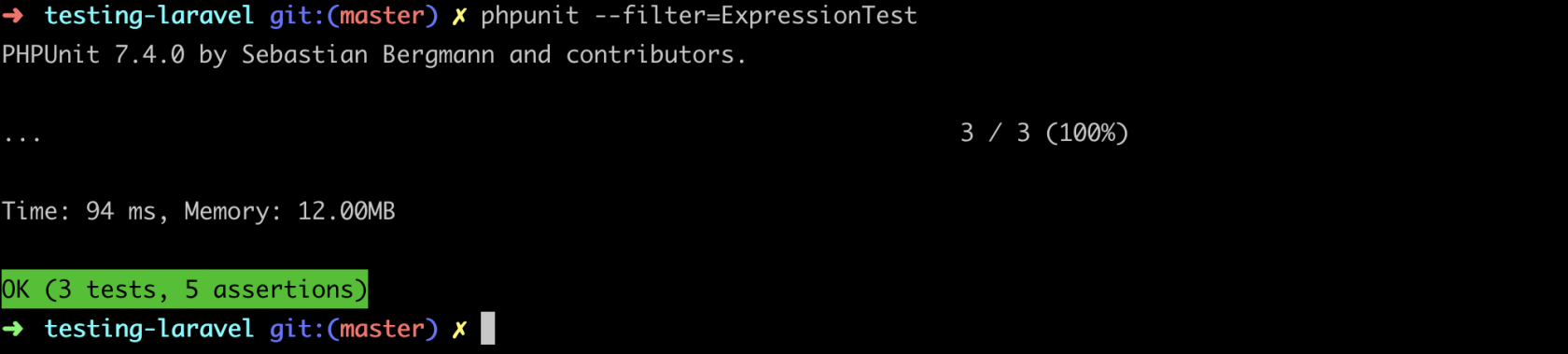
接下来为我们新增 maybe() API,它选择性匹配给定字符串。例如给定 http,正则表达式会是这样:/(http)?/。还是从测试开始:
.
.
/** @test */
public function it_maybe_has_a_value()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->maybe('http');
$this->assertRegExp($regex,'http');
$this->assertRegExp($regex,'');
}
}添加 maybe() 方法:
.
.
public function maybe($value)
{
return '/(' . $value . ')?/';
}
}再次测试即可成功通过。接下来我们来做点有意思的事情,为我们的方法加上链式调用,同时应用不同的规则构建正则表达式,比如:Expression::make()->find('foo')->maybe('nar')->then('biz'),则会构建 // 的正则表达式。我们先写测试:
.
.
/** @test */
public function it_can_chain_method_calls()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->find('foo')->maybe('bar')->then('biz');
$this->assertRegExp($regex,'foobarbiz');
}
}运行测试:
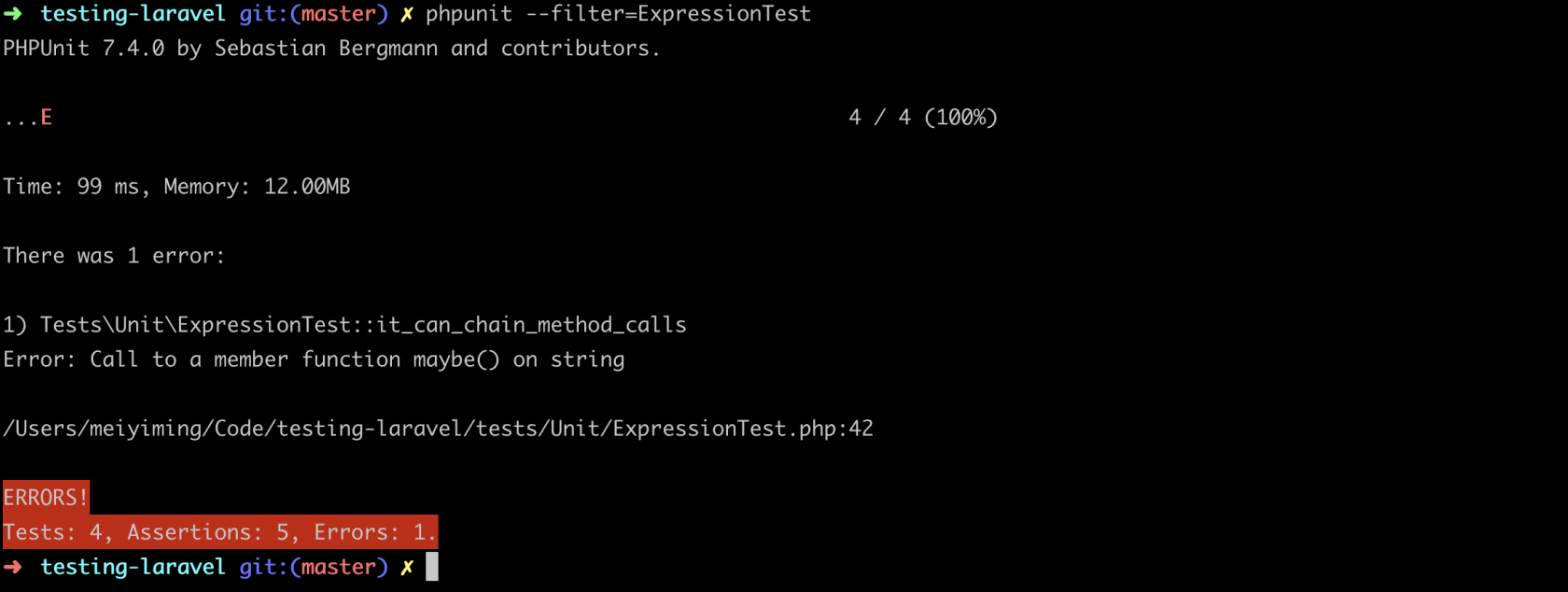
既然我们想要链式调用,那么我们的方法要返回的是实例化的类,所以我们要把正则表达式保存在该实例化的类属性中:
app/Expression.php
<?php
namespace App;
class Expression
{
protected $expression;
public static function make()
{
return new Static;
}
public function find($value)
{
$this->expression .= '/' . $value .'/';
return $this;
}
public function then($value)
{
return $this->find($value);
}
public function anything()
{
$this->expression .= '/.*/';
return $this;
}
public function maybe($value)
{
$this->expression .= '/(' . $value . ')?/';
return $this;
}
}现在我们每个方法的调用都会返回实例化的类,但是你会发现,我们在每一个方法都组装成正则表达式的形式,当链式调用时就会出现格式错误;并且,在我们的测试中,我们直接以字符型类型访问类,这样程序会报错:
$regex = Expression::make()->then('www');
$this->assertRegExp($regex,'www');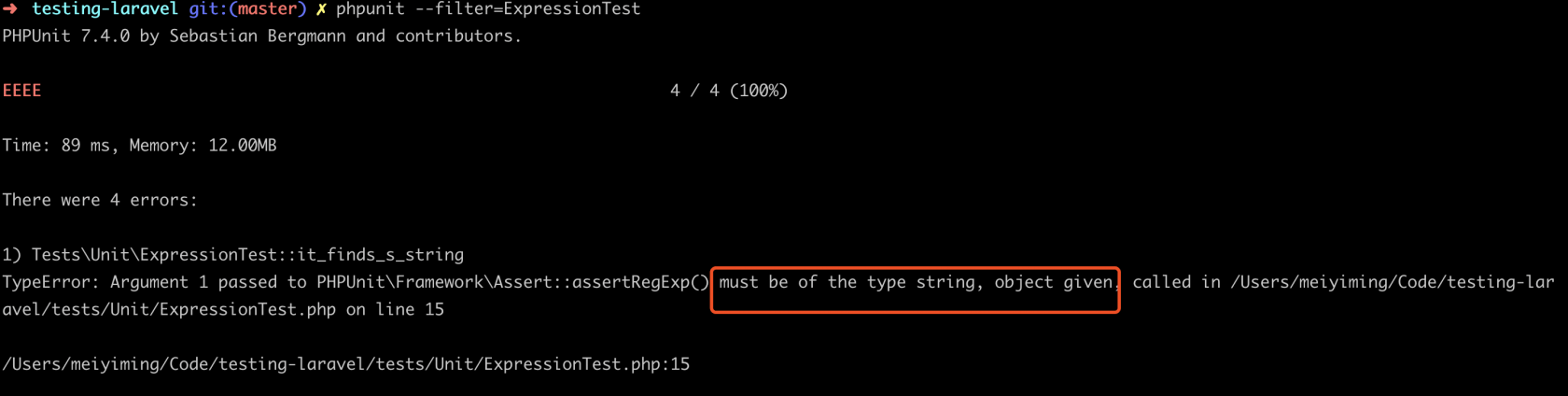
我们利用 PHP 的魔术方法 __toString() 来为我们解决上面的两个问题:
<?php
namespace App;
class Expression
{
protected $expression;
public static function make()
{
return new Static;
}
public function find($value)
{
$this->expression .= $value;
return $this;
}
public function then($value)
{
return $this->find($value);
}
public function anything()
{
$this->expression .= '.*';
return $this;
}
public function maybe($value)
{
$this->expression .= '(' . $value . ')?';
return $this;
}
public function __toString()
{
return '/' . $this->expression . '/';
}
}这样一来,我们只需做类型转换就能得到我们想要的正则表达式:
<?php
namespace Tests\Unit;
use Tests\TestCase;
use App\Expression;
class ExpressionTest extends TestCase
{
/** @test */
public function it_finds_s_string()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->find('www');
$this->assertRegExp((string)$regex,'www');
}
/** @test */
public function it_checks_for_anything()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->anything();
$this->assertRegExp((string)$regex,'foo');
}
/** @test */
public function it_maybe_has_a_value()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->maybe('http');
$this->assertRegExp((string)$regex,'http');
$this->assertRegExp((string)$regex,'');
}
/** @test */
public function it_can_chain_method_calls()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->find('foo')->maybe('bar')->then('biz');
$this->assertRegExp((string)$regex,'foobarbiz');
}
}注意
(string)$regex的使用
现在再次运行测试:

但是你一定不愿意每次测试时都要进行类型转换,所以我们来增加一个方法,专门为我们进行正则表达式的匹配校验:
app/Expression.php
.
.
public function test($value)
{
return (bool)preg_match($this->__toString(),$value);
}
public function __toString()
{
return '/' . $this->expression . '/';
}
}
preg_match()返回的是 0 或 1,所以要进行类型转换
接下来修改测试:
<?php
namespace Tests\Unit;
use Tests\TestCase;
use App\Expression;
class ExpressionTest extends TestCase
{
/** @test */
public function it_finds_s_string()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->find('www');
$this->assertTrue($regex->test('www'));
}
/** @test */
public function it_checks_for_anything()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->anything();
$this->assertTrue($regex->test('foo'));
}
/** @test */
public function it_maybe_has_a_value()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->maybe('http');
$this->assertTrue($regex->test('http'));
$this->assertTrue($regex->test(''));
}
/** @test */
public function it_can_chain_method_calls()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->find('foo')->maybe('bar')->then('biz');
$this->assertTrue($regex->test('foobarbiz'));
}
}
运行测试,测试通过。接下来我们来修复一个隐藏的很深的 bug,首先我们来修改下最后一个测试:
.
.
/** @test */
public function it_can_chain_method_calls()
{
$regex = Expression::make()->find('www')->maybe('.')->then('laracasts');
$this->assertTrue($regex->test('www.laracasts'));
$this->assertFalse($regex->test('wwwXlaracasts'));
}
}但是运行测试会失败,因为在正则表达式中 . 字符具有特殊的意义,它会匹配任意一个字符。所以我们如果想要匹配 . 字符本身时,我们需要进行转义:\.。我们来利用 PHP 提供的 preg_quote() 方法转义正则表达式字符:
.
.
public function find($value)
{
$value = preg_quote($value,'/');
$this->expression .= $value;
return $this;
}
.
.
public function maybe($value)
{
$value = preg_quote($value,'/');
$this->expression .= '(' . $value . ')?';
return $this;
}
.
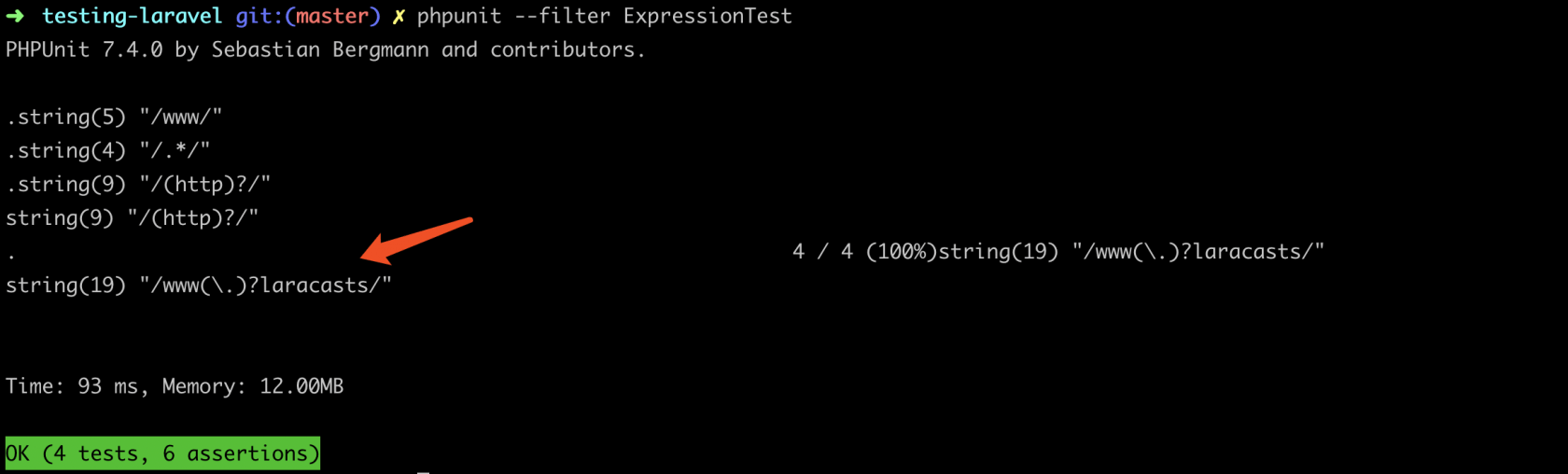
.再次运行测试即可成功通过。我们来打印出每一个测试时生成的正则表达式:
.
.
public function getRegex()
{
return '/' . $this->expression . '/';
}
public function test($value)
{
var_dump($this->getRegex());
return (bool)preg_match($this->getRegex(),$value);
}我们新增了
getRegex()方法来获取生成的正则表达式
一个月之后我可能不知道 $value = preg_quote($value,'/') 的目的是什么,所以我们来把它抽取到函数中,取一个可读性高的名字:
public function find($value)
{
$value = $this->sanitize($value);
$this->expression .= $value;
return $this;
}
.
.
public function maybe($value)
{
$value = $this->sanitize($value);
$this->expression .= '(' . $value . ')?';
return $this;
}
protected function sanitize($value)
{
return preg_quote($value,'/');
}当然,重构之后需要运行测试,并且要让测试全部通过。然后,我们发现很多地方重复了以下代码:
$value = $this->sanitize($value);
$this->expression .= '(' . $value . ')?';
return $this;我们来进行重构:
<?php
namespace App;
class Expression
{
protected $expression;
public static function make()
{
return new Static;
}
public function find($value)
{
return $this->add($this->sanitize($value));
}
public function then($value)
{
return $this->find($value);
}
public function anything()
{
return $this->add('.*');
}
public function maybe($value)
{
$value = $this->sanitize($value);
return $this->add("($value)?");
}
protected function sanitize($value)
{
return preg_quote($value,'/');
}
protected function add($value)
{
$this->expression .= $value;
return $this;
}
public function getRegex()
{
return '/' . $this->expression . '/';
}
public function test($value)
{
return (bool)preg_match($this->getRegex(),$value);
}
public function __toString()
{
return $this->getRegex();
}
}我们将构造表达式的逻辑放在 add() 方法中统一处理,当然,测试仍旧是通过的。接下来为我们新增 anythingBut() API,它会排除指定的字符串。依然是从测试开始:
.
.
/** @test */
public function it_can_exclude_values()
{
$regex = Expression::make()
->find('foo')
->anythingBut('bar')
->then('biz');
$this->assertTrue($regex->test('foobazbiz'));
$this->assertFalse($regex->test('foobarbiz'));
}
}这个时候运行测试会失败,我们来添加 anything() 方法:
.
.
public function anything()
{
return $this->add('.*');
}
public function anythingBut($value)
{
$value = $this->sanitize($value);
return $this->add("(?!$value).*?");
}
.
.运行测试,测试通过。现在我们已经有了一个基础,在这个基础上你可以开发任意你想要添加的 API,不试一试吗?

 Testing Laravel 单元测试入门笔记
Testing Laravel 单元测试入门笔记



 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu



