[Laravel 5.4] 集合增加高阶信息传递(HOM)支持
概述
今天要讲的是高阶信息传递( Higher Order Messages ),个人对这方面真的是见解不深,个人理解应该属于柯里化那种吧。
使用起来就像 Taylor 这条推一样如此神奇。
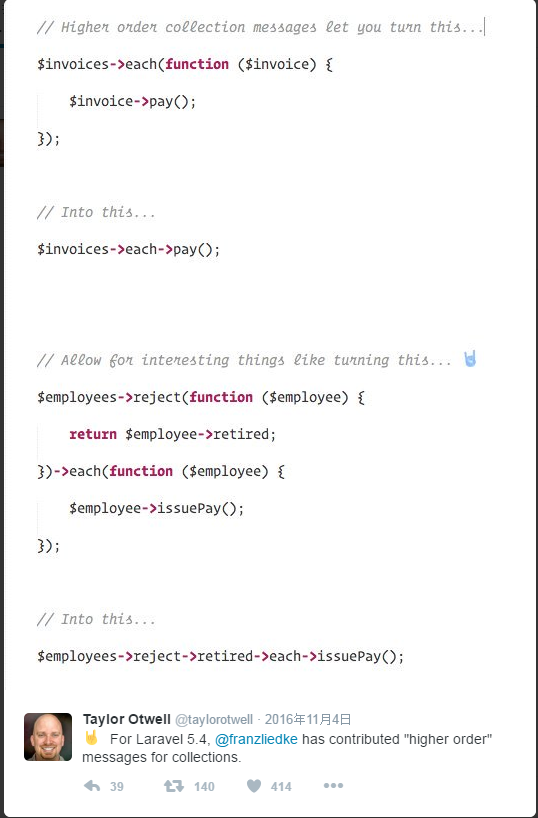
Higher Order Messages(HOM)
集合方法中,目前支持高阶信息传递的方法有
| 方法 | 备注 |
|---|---|
| contains | 使用方法 |
| each | 使用方法 |
| every | 使用方法 |
| filter | 使用方法 |
| first | 使用方法 |
| map | 使用方法 |
| partition | Laravel 5.4新增,使用方法 |
| reject | 使用方法 |
| sortBy | 使用方法 |
| sortByDesc | 使用方法 |
| sum | 使用方法 |
毫不意外,以上方法的参数都是可以接一个闭包,我猜测可能这是实现 HOM 的基本要求吧。
HOM 实现的原理如下
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Support;
...
class Collection implements ArrayAccess, Arrayable, Countable, IteratorAggregate, Jsonable, JsonSerializable
{
...
/**
* The methods that can be proxied.
*
* @var array
*/
protected static $proxies = [
'contains', 'each', 'every', 'filter', 'first', 'map',
'partition', 'reject', 'sortBy', 'sortByDesc', 'sum',
];
/**
* Add a method to the list of proxied methods.
*
* @param string $method
* @return void
*/
public static function proxy($method)
{
static::$proxies[] = $method;
}
/**
* Dynamically access collection proxies.
*
* @param string $key
* @return mixed
*
* @throws \Exception
*/
public function __get($key)
{
if (! in_array($key, static::$proxies)) {
throw new Exception("Property [{$key}] does not exist on this collection instance.");
}
return new HigherOrderCollectionProxy($this, $key);
}
}在 protected static $proxies 中定义了可以 HOM 的方法,使用魔术方法 __get() 来传递给 HigherOrderCollectionProxy
<?php
namespace Illuminate\Support;
class HigherOrderCollectionProxy
{
/**
* The collection being operated on.
*
* @var \Illuminate\Support\Collection
*/
protected $collection;
/**
* The method being proxied.
*
* @var string
*/
protected $method;
/**
* Create a new proxy instance.
*
* @param \Illuminate\Support\Collection $collection
* @param string $method
* @return void
*/
public function __construct(Collection $collection, $method)
{
$this->method = $method;
$this->collection = $collection;
}
/**
* Proxy accessing an attribute onto the collection items.
*
* @param string $key
* @return mixed
*/
public function __get($key)
{
return $this->collection->{$this->method}(function ($value) use ($key) {
return is_array($value) ? $value[$key] : $value->{$key};
});
}
/**
* Proxy a method call onto the collection items.
*
* @param string $method
* @param array $parameters
* @return mixed
*/
public function __call($method, $parameters)
{
return $this->collection->{$this->method}(function ($value) use ($method, $parameters) {
return $value->{$method}(...$parameters);
});
}
}
这里的黑科技就是 HigherOrderCollectionProxy 类中的 __get($key) 和 __call($method, $parameters) 这两个魔术方法了,使得这一切从不可能变得可能,这脑洞想想都感觉到可怕。
使用
以下 Demo 由本人小小的脑袋挤出来的,本人对此理解也不深,如有错误,烦请留言指正,感谢!
测试用例在 这里
contains
场景:假设目前有两个用户,一个 User ,一个 Editor,他们分别有不同的用户权限。
// 如果是一个用户,拥有最基础的用户权限
$permissions = [
'User' => [
'create' => false,
'update' => false,
'read' => true, // 注意: User 只有 read 为 true
'delete' => false,
],
];
$c = new Collection($permissions);
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| 传统用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
//用户只能 读
$this->assertTrue($c->contains('read', true));
// 不能 增 改 删
$this->assertFalse($c->contains('create', true));
$this->assertFalse($c->contains('update', true));
$this->assertFalse($c->contains('delete', true));
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| HOM 用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
//用户只能 读
$this->assertTrue($c->contains->read);
// 不能 增 改 删
$this->assertFalse($c->contains->create);
$this->assertFalse($c->contains->update);
$this->assertFalse($c->contains->delete); // 如果是一个编辑,拥有最基础的用户权限,还有编辑的权限
$permissions = [
'User' => [
'create' => false,
'update' => false,
'read' => true, // 注意: User 只有 read 为 true
'delete' => false,
],
'Editor' => [
'create' => true,
'update' => true,
'read' => true,
'delete' => false, // 注意: Editor 只有 delete 为 false
],
];
$c = new Collection($permissions);
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| 传统用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
// 编辑可以 增 改 读
$this->assertTrue($c->contains('create', true));
$this->assertTrue($c->contains('update', true));
$this->assertTrue($c->contains('read', true));
// 不能 删
$this->assertFalse($c->contains('delete', true));
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| HOM 用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
// 编辑可以 增 改 读
$this->assertTrue($c->contains->create);
$this->assertTrue($c->contains->update);
$this->assertTrue($c->contains->read);
// 不能 删
$this->assertFalse($c->contains->delete);each
场景:现在有一些未读通知,我们需要把它们标记为已读。参考这里
先创建一个 UnreadNotifications 类进行模拟
class UnreadNotifications
{
public $title;
public $read_at = null;
/**
* UnreadNotifications constructor.
*
* @param $title
*/
public function __construct($title)
{
$this->title = $title;
}
public function markAsRead()
{
$this->read_at = $this->title.' read at 20170119';
}
} /*
|------------------------------------------------
| 传统用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$c = new Collection([
'first' => new UnreadNotifications('first'),
'second' => new UnreadNotifications('second'),
'third' => new UnreadNotifications('third')
]);
$readNotifications = $c->each(function ($notification) {
$notification->markAsRead();
});
$this->assertEquals('first read at 20170119', $readNotifications['first']->read_at);
$this->assertEquals('second read at 20170119', $readNotifications['second']->read_at);
$this->assertEquals('third read at 20170119', $readNotifications['third']->read_at);
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| HOM 用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$c = new Collection([
'four' => new UnreadNotifications('four'),
'five' => new UnreadNotifications('five'),
'six' => new UnreadNotifications('six')
]);
$readNotifications = $c->each->markAsRead();
$this->assertEquals('four read at 20170119', $readNotifications['four']->read_at);
$this->assertEquals('five read at 20170119', $readNotifications['five']->read_at);
$this->assertEquals('six read at 20170119', $readNotifications['six']->read_at);every
场景:假设用户个人资料都必须完善之后才能发言
$confirmProfile = [
[
'title' => 'avatar',
'finish' => true
],
[
'title' => 'email',
'finish' => true
]
];
$notConfirmProfile = [
[
'title' => 'avatar',
'finish' => true
],
[
'title' => 'email',
'finish' => true
],
[
'title' => 'wechat',
'finish' => false // 注意:这里微信还没填写
],
];
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| 传统用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$cConfirm = new Collection($confirmProfile);
$this->assertTrue($cConfirm->every('finish'));
$cNotConfirm = new Collection($notConfirmProfile);
$this->assertFalse($cNotConfirm->every('finish'));
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| HOM 用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$cConfirm = new Collection($confirmProfile);
$this->assertTrue($cConfirm->every->finish);
$cNotConfirm = new Collection($notConfirmProfile);
$this->assertFalse($cNotConfirm->every->finish);filter 和 reject
场景:需要筛选出退休员工和没退休员工
先创建一个 Employees 类来模拟员工
class Employees
{
public $name;
public $retired;
/**
* Employees constructor.
*
* @param $name
* @param $retired
*/
public function __construct($name, $retired)
{
$this->name = $name;
$this->retired = $retired;
}
} $employees = [
'Alice' => new Employees('Alice', true),
'Milkmeowo' => new Employees('Milkmeowo', false),
'Bob' => new Employees('Bob', true),
];
$expectRetired = [
'Alice' => new Employees('Alice', true),
'Bob' => new Employees('Bob', true)
];
$expectNotRetired = [
'Milkmeowo' => new Employees('Milkmeowo', false)
];
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| 传统用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$c = new Collection($employees);
// filter
$actualRetired = $c->filter(function ($employee) {
return $employee->retired;
})->all();
$this->assertEquals($expectRetired, $actualRetired);
// reject
$actualNotRetired = $c->reject(function ($employee) {
return $employee->retired;
})->all();
$this->assertEquals($expectNotRetired, $actualNotRetired);
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| HOM 用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$c = new Collection($employees);
// filter
$actualRetired = $c->filter->retired->all();
$this->assertEquals($expectRetired, $actualRetired);
// reject
$actualNotRetired = $c->reject->retired->all();
$this->assertEquals($expectNotRetired, $actualNotRetired);first
场景:还是退休员工,我们需要得到第一个退休员工
$employees = [
'Alice' => new Employees('Alice', false), // 注意:这里把 Alice 设置为还没退休
'Milkmeowo' => new Employees('Milkmeowo', false),
'Bob' => new Employees('Bob', true),
];
$expect = new Employees('Bob', true);
$c = new Collection($employees);
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| 传统用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$actual = $c->first(function ($value, $key) {
return $value->retired;
});
$this->assertEquals($expect, $actual);
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| HOM 用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$this->assertEquals($expect, $c->first->retired);map
场景:我们有两个人,1、我们需要拿到他们的名字,2、把他们名字转为全大写再拿到他们的名字
先创建一个 Person 类来模拟人
class Person
{
public $name;
/**
* Person constructor.
*
* @param string $name
*/
public function __construct($name)
{
$this->name = $name;
}
public function uppercase()
{
$this->name = strtoupper($this->name);
}
} $person1 = [ 'name' => 'Taylor' ];
$person2 = [ 'name' => 'Yaz' ];
$expectName = [ 'Taylor', 'Yaz' ];
$expectUppercaseName = [ 'TAYLOR', 'MILKMEOWO' ];
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| 传统用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$collection = collect([ $person1, $person2 ]);
$actual = $collection->map(function ($item, $key) {
return $item['name'];
})->toArray();
$this->assertEquals($expectName, $actual);
$collection = collect([
new Person('taylor'),
new Person('milkmeowo')
]);
$actual = $collection->each(function ($item, $key) {
return $item->uppercase();
})->map(function ($item, $key) {
return $item->name;
})->toArray();
$this->assertEquals($expectUppercaseName, $actual);
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| HOM 用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$collection = collect([ $person1, $person2 ]);
$actual = $collection->map->name->toArray();
$this->assertEquals($expectName, $actual);
$collection = collect([
new Person('taylor'),
new Person('milkmeowo')
]);
$actual = $collection->each->uppercase()->map->name->toArray();
$this->assertEquals($expectUppercaseName, $actual);partition
场景:假设课程有免费收费两种,我们需要把他们分离开来
$courses = new Collection([
'a' => [ 'free' => true ],
'b' => [ 'free' => false ],
'c' => [ 'free' => true ],
]);
$expectFree = [
'a' => [ 'free' => true ],
'c' => [ 'free' => true ],
];
$expectPremium = [
'b' => [ 'free' => false ],
];
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| 传统用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
list( $free, $premium ) = $courses->partition('free');
$this->assertSame($expectFree, $free->toArray());
$this->assertSame($expectPremium, $premium->toArray());
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| HOM 用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
list( $free, $premium ) = $courses->partition->free;
$this->assertSame($expectFree, $free->toArray());
$this->assertSame($expectPremium, $premium->toArray());sortBy 和 sortByDesc
场景:我们有一些家私,价格不一样,我们想按照价格来排序。
$collection = collect([
[ 'name' => 'Desk', 'price' => 200 ],
[ 'name' => 'Chair', 'price' => 100 ],
[ 'name' => 'Bookcase', 'price' => 150 ],
]);
$expectSorted = [
[ 'name' => 'Chair', 'price' => 100 ],
[ 'name' => 'Bookcase', 'price' => 150 ],
[ 'name' => 'Desk', 'price' => 200 ],
];
$expectSortedByDesc = [
[ 'name' => 'Desk', 'price' => 200 ],
[ 'name' => 'Bookcase', 'price' => 150 ],
[ 'name' => 'Chair', 'price' => 100 ],
];
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| 传统用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$sorted = $collection->sortBy('price');
$this->assertEquals($expectSorted, $sorted->values()->all());
$sortedByDesc = $collection->sortByDesc('price');
$this->assertEquals($expectSortedByDesc, $sortedByDesc->values()->all());
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| HOM 用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$sortedHOM = $collection->sortBy->price;
$this->assertEquals($expectSorted, $sortedHOM->values()->all());
$sortedByDescHOM = $collection->sortByDesc->price;
$this->assertEquals($expectSortedByDesc, $sortedByDescHOM->values()->all());sum
场景:小 L 和女朋友出去吃雪糕,买了两款雪糕,价格不一样,问最后小 L 花了多少钱。
$iceCreams = [ (object) [ 'iceCream' => 40 ], (object) [ 'iceCream' => 60 ] ];
$c = new Collection($iceCreams);
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| 传统用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$this->assertEquals(100, $c->sum('iceCream'));
$this->assertEquals(100, $c->sum(function ($i) {
return $i->iceCream;
}));
/*
|------------------------------------------------
| HOM 用法
|------------------------------------------------
*/
$this->assertEquals(100, $c->sum->iceCream);自定义 HOM 函数
Collection::macro('adults', function ($callback) {
return $this->filter(function ($item) use ($callback) {
return $callback($item) >= 18;
});
});
Collection::proxy('adults');
$c = new Collection([['age' => 3], ['age' => 12], ['age' => 18], ['age' => 56]]);
$this->assertSame([['age' => 18], ['age' => 56]], $c->adults->age->values()->all());总结
HOM 某种场合下显得得更简洁,更易读,更方便。然而我对 HOM 还不是很熟悉,没搞清楚他的套路,硬来使用可能会变成八阿哥制造机,东西是好的,可惜我现在还吃不透,希望各位大大能指点迷津,提供更多的场景,最好和实际业务能关联上,能提供更多的代码示例,感谢!
本作品采用《CC 协议》,转载必须注明作者和本文链接






 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu




你的测试用例能给官方提过去吗?好辛苦 :+1:
@Summer 额,今天没空了,改天吧,其实我还想看官方的测试用例 2333
@milkmeowo 有可能你等不到。
// 注意: Editor 只有 delete 为 true
这里笔误了
@quericy fixed 感谢!
感谢分享,但crate是什么鬼
@Payne create笔误
这个高阶
each, map使用方法,HOM后面调用函数,如果需要调用自身,比如:(将用户组下的所有权限,转换keyBy的方式)
$v就不知道怎么传递了,$v从何而来sum用闭包了吗???
牛 !
一个小问题 最后 自创 collection macro 加了个 Collection::proxy 不是很明白. 不加的话是提示adult 找不到 但是 laravel 官方文档是不用这个proxy 的.
五年前的东西了,到现在还是看的一脸懵逼 :cry: