golang 多级指针-为什么要用三级指针? 借助于一个 C 的例子来进行讲解
背景
今天学习到了 :
一级指针 指向变量的地址
二级指针 指向一级指针的地址
三级指针指向二级指针的地址
但是很不理解,为什么要三级 甚至N级指针呢?
在哪里会用到呢?
我们往下看:
借助于C代码的三级指针的应用场景
1、问题:将指针数组和二维数组中的字符串存放到第三个指针所指向的内存空间中,并进行排序(默认升序)输出,必须通过函数来完成。
(1)、代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<malloc.h>
void destorySpace_2(char ***p3, int len3);
void destorySpace_1(char **p3, int len3);
int sort(char **myp1, int len1, char (*myp2)[30], int len2, char ***myp3, int *len3);
int sort(char **myp1, int len1, char (*myp2)[30], int len2, char ***myp3, int *len3){
int len;
int i;
int j;
char **p3 = NULL;
int temLen;
char *tmp1;
len = len1 + len2;
p3 = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * len);
//先将第一个指针数组的内容拷贝到p3所指向的空间中
for(i = 0; i < len1; i++){
temLen = strlen(myp1[i])+1;
p3[i] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * temLen);
strcpy(p3[i], myp1[i]);
}
//先将第二个二维数组的内容拷贝到p3所指向的空间中
for(j = 0; j < len2; j++, i++){
temLen = strlen(myp2[j])+1;
p3[i] = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * temLen);
strcpy(p3[i], myp2[j]);
}
//最后对p3所指向的空间的字符串在进行排序;
for(i = 0; i < len; i++){
for(j = i+1; j < len; j++){
if(strcmp(p3[i], p3[j]) > 0){
tmp1 = p3[i];
p3[i] = p3[j];
p3[j] = tmp1;
}
}
}
*myp3 = p3;
*len3 = len;
return 0;
}
//销毁p3所指向空间的第一种方法,自己必须在调用下面对p3 = NULL;
void destorySpace_1(char **p3, int len3){
int i;
if(p3 != NULL){
for(i = 0; i < len3; i++){
if(p3[i] != NULL){
free(p3[i]);
}
}
free(p3);
}
}
//销毁p3所指向空间的第二种方法
void destorySpace_2(char ***p3, int len3){
int i;
char **p;
if(p3 == NULL){
return;
}
p = *p3;
if(p != NULL){
for(i = 0; i < len3; i++){
if(p[i] != NULL){
free(p[i]);
}
}
free(p);
*p3 = NULL;
}
}
int main(void){
char *p1[] = {"aaaaa", "bbbbb", "ccccc", "eeeeeee"};
char buf1[][30] = {"fffff", "kkkkkkk"};
char **p3;
int len1;
int len2;
int len3;
int ret;
int i;
len1 = sizeof(p1)/sizeof(p1[0]);
len2 = sizeof(buf1)/sizeof(buf1[0]);
ret = sort(p1, len1, buf1, len2, &p3, &len3);
if(ret != 0){
printf("sort() err\n");
return ret;
}
for(i = 0; i < len3; i++){
printf("%s\n", p3[i]);
}
//destorySpace_2(&p3, len3);
destorySpace_1(p3, len3);
p3 = NULL;
return 0;
}(2)、运行结果:
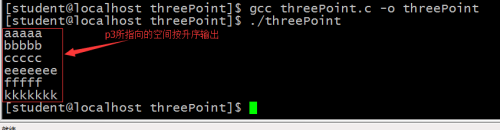
(3)、模型分析
思想:因为要用函数完成,对二维数组和指针数组中的字符串先进行存放到p3所指向的空间中,就必须的使用三级指针来接收了,然后在对其所指向的空间进行排序!
在进行空间的释放时,要是在函数内部避免野指针问题,就必须的用三级指针来接收了!
在进行空间的释放时,要是用二级指针来接收的话,则自己必须在调用的下面对其进行赋空,避免野指针的出现,原因:2个指针空间的值没有半毛钱的关系(它们之间仅仅是形参、实参的对应关系)!!!
抛出问题的代码:
//函数调用
destorySpace(char **p3){
......
p3 = NULL;
}
//主函数
int main(void){
char **p3 = NULL;
...
destorySpace(p3);
}模型如下: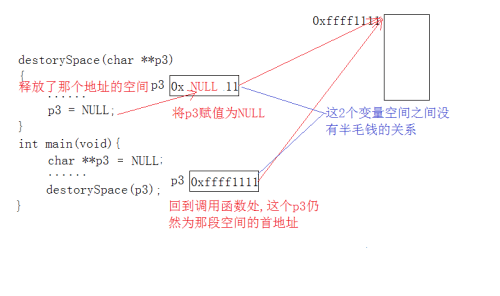
总结
类似于 我们 有一碗水,一碗肉糜,盐,辣椒。
你要做辣的肉酱,不辣的肉酱。
你是不是得拿第三个碗?
C语言文章原文地址:
blog.51cto.com/wait0804/1874777
防爬虫说明
禁止 学习某地爬虫,知乎爬虫,CSDN 爬虫。
本文,首发在 learnku 社区。
@author
汪春波(www.shxdledu.cn)
本作品采用《CC 协议》,转载必须注明作者和本文链接


 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu



