《从0到1搭建一个IM项目》消息模块开发之消息体的设计
[toc]
概况
经过前四篇文章的讲解,完成了用户模块的开发,下面就进入到了IM项目的核心模块,即信息模块,这部分内容我们主要介绍信息结构的设计,信息的发送接收。
经过用户模块的开发,项目目录结构如下:
HiChat
├── common //放置公共文件
| |——md5.go
| |——resp.go
│
├── config //做配置文件
│
├── dao//数据库crud
│ |——user.go
| |——relation.go
| |——community.go
|
├── global //放置各种连接池,配置等
│ |——global.go
|
├── initialize //项目初始化文件
│ |——db.go
| |——logger.go
|
├── middlewear //放置web中间件
| |——jwt.go
├── models //数据库表设计
│ |——user_basic.go
| |——relation.go
| |——community.go
|
├── router //路由
| |——router.go
│
├── service //对外api
| |——user.go
| |——relation.go
| |——attach_upload.go
│
├── test //测试文件
│
├── main.go //项目入口
├── go.mod //项目依赖管理
├── go.sum //项目依赖管理
信息结构设计
每一个表都需要一个model来记录相应数据,在model下新建文件message.go
type Model struct {
ID uint `gorm:"primaryKey"`
CreatedAt time.Time
UpdatedAt time.Time
DeletedAt gorm.DeletedAt `gorm:"index"`
}消息体
信息发送者
信息接收者
聊天类型:单聊、群聊
信息类型:文字、表情包、图片、语音
信息内容
图片url
涉及文件
文件描述
文件大小
目前能只想到了这么多,后续有其他需求可以自行添加
信息结构体:
type Message struct {
Model
FormId int64 `json:"userId"` //信息发送者
TargetId int64 `json:"targetId"` //信息接收者
Type int //聊天类型:群聊 私聊 广播
Media int //信息类型:文字 图片 音频
Content string //消息内容
Pic string `json:"url"` //图片相关
Url string //文件相关
Desc string //文件描述
Amount int //其他数据大小
}
//MsgTableName 生成指定数据表名
func (m *Message) MsgTableName() string {
return "message"
}
通信逻辑
在正式开发信息模块前,我们需要梳理一下通信的逻辑
用户登录后与服务器建立websocket连接:
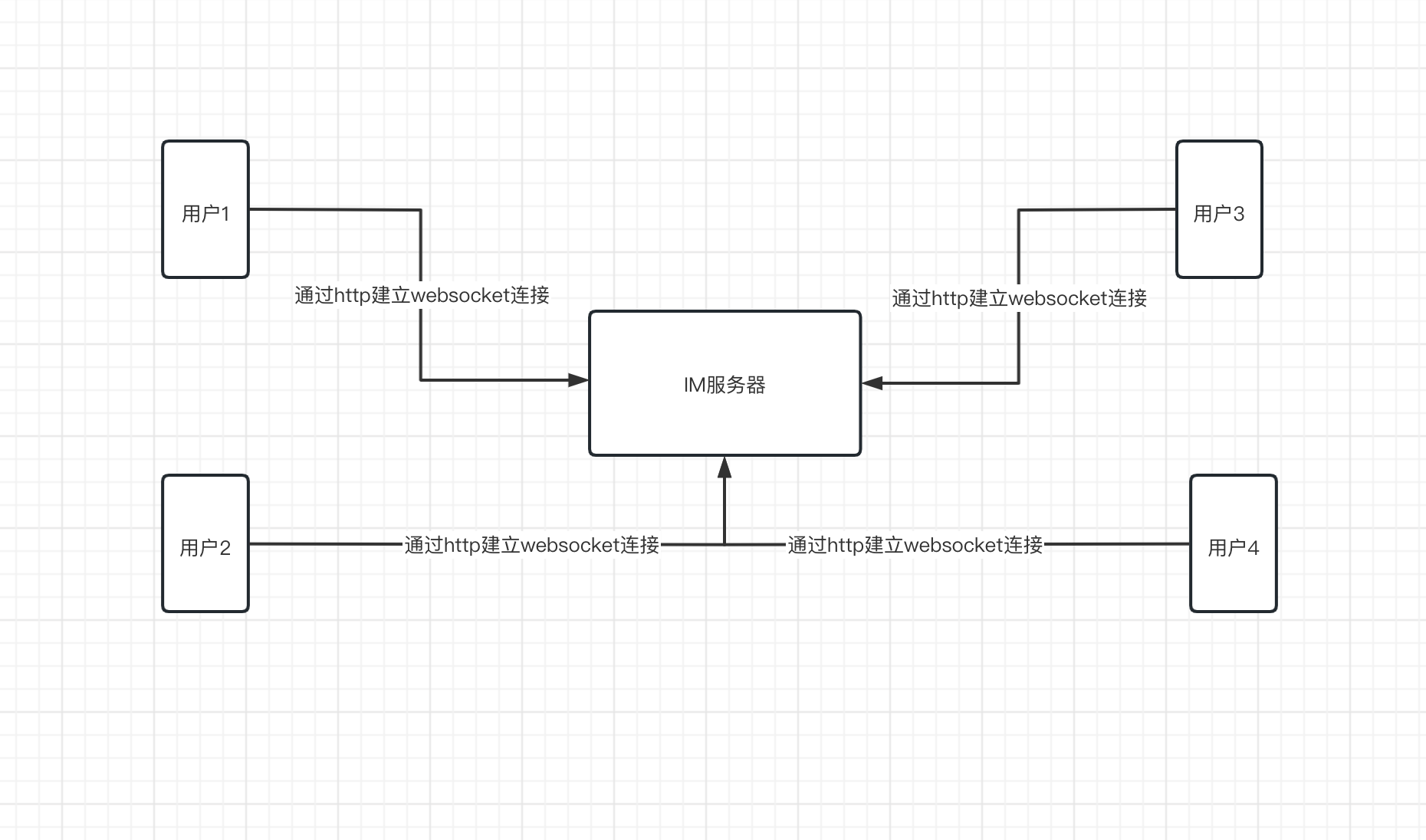
通信流程:
http升级为websocket
用户登录后,此时用户上线,通过发送http请求,将服务升级到websocket连接。
id与构造的node进行绑定
用户上线后,将其id和对应的websocket的构造体node绑定
发送消息
用户发送消息给指定用户时,带上接收者id,发送至websocket,通过一系列逻辑处理,使用接收者id查找到对应的node,然后将消息放入node,此时websocket连接,会将消息推送给接收者。
接收消息
接收者在线后,同样会连接到websocket,然后id绑定node,去node中的websocket中读取对应的信息。
举例
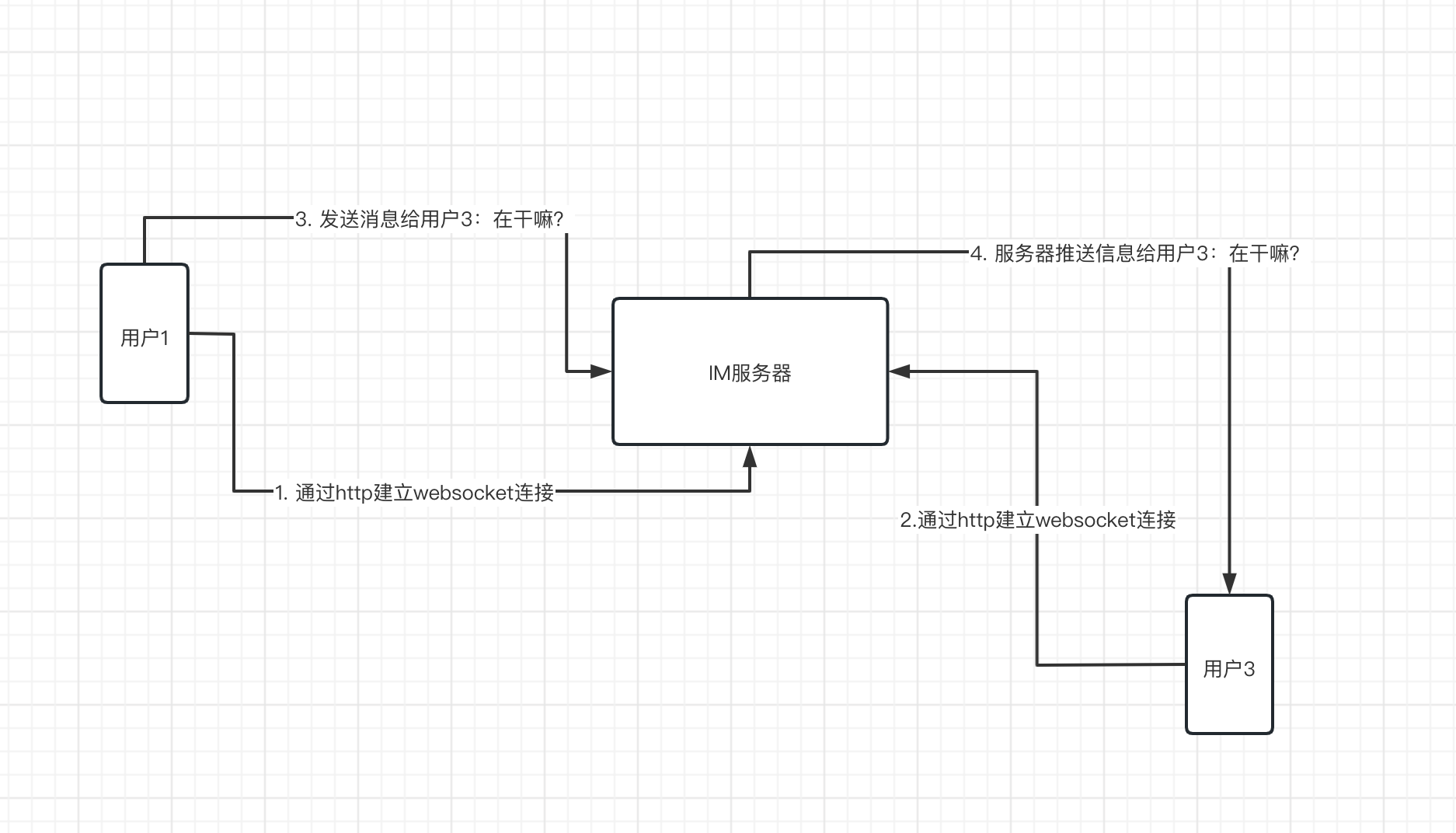
例如:用户小明(userID=1)和小红(userID=2)都在线,他们都有对应发node并且都与服务器建立了websocket连接,当小明要发送一条信息(您好,在干嘛?)给小红,服务器获取到小明发送的消息体,然后通过消息体里接收者小红的id=2, 然后匹配map[2] = node, 然后将消息写入小红(userID=2)对应的node中的websocket连接中(也就是小红与服务器的websocket连接),小红就可以收到小明的信息了。
构造node
用户登录后,为每一个用户绑定一个node
//Node 构造连接
type Node struct {
Conn *websocket.Conn //socket连接
Addr string //客户端地址
DataQueue chan []byte //消息内容
GroupSets set.Interface //好友 / 群
}消息发送接收核心
信息发送和接收的核心逻辑仍然在message.go中编写
package models
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"net"
"net/http"
"strconv"
"sync"
"HiChat/global"
"github.com/go-redis/redis/v8"
"github.com/gorilla/websocket"
"go.uber.org/zap"
"gopkg.in/fatih/set.v0"
)
type Message struct {
Model
FormId int64 `json:"userId"` //信息发送者
TargetId int64 `json:"targetId"` //信息接收者
Type int //聊天类型:群聊 私聊 广播
Media int //信息类型:文字 图片 音频
Content string //消息内容
Pic string `json:"url"` //图片相关
Url string //文件相关
Desc string //文件描述
Amount int //其他数据大小
}
func (m *Message) MsgTableName() string {
return "message"
}
//Node 构造连接
type Node struct {
Conn *websocket.Conn //连接
Addr string //客户端地址
DataQueue chan []byte //消息
GroupSets set.Interface //好友 / 群
}
//映射关系
var clientMap map[int64]*Node = make(map[int64]*Node, 0)
//读写锁,绑定node时需要线程安全
var rwLocker sync.RWMutex
Chat初始化node进行信息收发调度
编写一个chat方法:核心作用就是升级连接, 初始化node, 用户id绑定node, 使用协程并发调用sendProc(node)和recProc(node)进行信息收发。
//Chat 需要 :发送者ID ,接受者ID ,消息类型,发送的内容,发送类型
func Chat(w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) {
//1. 获取参数信息发送者userId
query := r.URL.Query()
Id := query.Get("userId")
userId, err := strconv.ParseInt(Id, 10, 64)
if err != nil {
zap.S().Info("类型转换失败", err)
return
}
//升级为socket
var isvalida = true
conn, err := (&websocket.Upgrader{
CheckOrigin: func(r *http.Request) bool {
return isvalida
},
}).Upgrade(w, r, nil)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
//获取socket连接,构造消息节点
node := &Node{
Conn: conn,
DataQueue: make(chan []byte, 50),
GroupSets: set.New(set.ThreadSafe),
}
//将userId和Node绑定
rwLocker.Lock()
clientMap[userId] = node
rwLocker.Unlock()
//服务发送消息
go sendProc(node)
//服务接收消息
go recProc(node)
//sendMsg(userId, []byte("欢迎进入聊天系统"))
}服务器发送信息
从node中获取信息并写入websocket中
//sendProc 从node中获取信息并写入websocket中
func sendProc(node *Node) {
for {
select {
case data := <-node.DataQueue:
err := node.Conn.WriteMessage(websocket.TextMessage, data)
if err != nil {
zap.S().Info("写入消息失败", err)
return
}
fmt.Println("数据发送socket成功")
}
}
}服务器接收消息
从websocket中将消息体拿出,然后进行解析,再进行聊天类型判断, 最后将消息发送至目的用户的node中
//recProc 从websocket中将消息体拿出,然后进行解析,再进行信息类型判断, 最后将消息发送至目的用户的node中
func recProc(node *Node) {
for {
//获取信息
_, data, err := node.Conn.ReadMessage()
if err != nil {
zap.S().Info("读取消息失败", err)
return
}
//这里是简单实现的一种方法
msg := Message{}
err = json.Unmarshal(data, &msg)
if err != nil {
zap.S().Info("json解析失败", err)
return
}
if msg.Type == 1 {
zap.S().Info("这是一条私信:", msg.Content)
tarNode, ok := clientMap[msg.TargetId]
if !ok {
zap.S().Info("不存在对应的node", msg.TargetId)
return
}
tarNode.DataQueue <- data
fmt.Println("发送成功:", string(data))
}
}
}
整个单聊服务就完成了。
配置api
将逻辑编写完成后,在service目录下user.go中编写
//SendUserMsg 发送消息
func SendUserMsg(ctx *gin.Context) {
models.Chat(ctx.Writer, ctx.Request)
}然后在router中配置路由
//用户模块
user := v1.Group("user")
{
……
……
……
user.GET("/SendUserMsg", middlewear.JWY(), service.SendUserMsg)
}测试
注意事项
在测试之前我已经将jwt中token验证,改成了get请求:
//token := c.PostForm("token")
token := c.Query("token")
user := c.Query("userId")当然最简单的测试方法是,直接在router中:
user.GET("/SendUserMsg", middlewear.JWY(), service.SendUserMsg)将middlewear.JWY()扔掉,最后参数只需要这样:ws://127.0.0.1:8000/v1/user/SendUserMsg?userId=13就可以直接参数了
测试网站
stackoverflow.org.cn/websocket/
用户13:ws://127.0.0.1:8000/v1/user/SendUserMsg?userId=13&token=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VySWQiOjEzLCJleHAiOjE2NzgxNzUwNjgsImlzcyI6InlrIn0.VNOp7G4T3BGkCUNe_yyDcw7b8hZvjqTGDRWUe9mNims
用户14:ws://127.0.0.1:8000/v1/user/SendUserMsg?userId=14&token=eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJ1c2VySWQiOjE0LCJleHAiOjE2NzgxNzUwMDcsImlzcyI6InlrIn0.nkVjhbSNnZLVNfFstWQNOgzrNMIcmgyvDIlCn6oAsDU
这里你想要重新登录,然后获取到ws://127.0.0.1:8000/v1/user/SendUserMsg?后续参数userId和token
消息体:
{"TargetId":13,"Type":1,"CreateTime":1672996855236,"userId":14,"Media":1,"Content":"在干嘛"}测试如下:
13发送消息给14
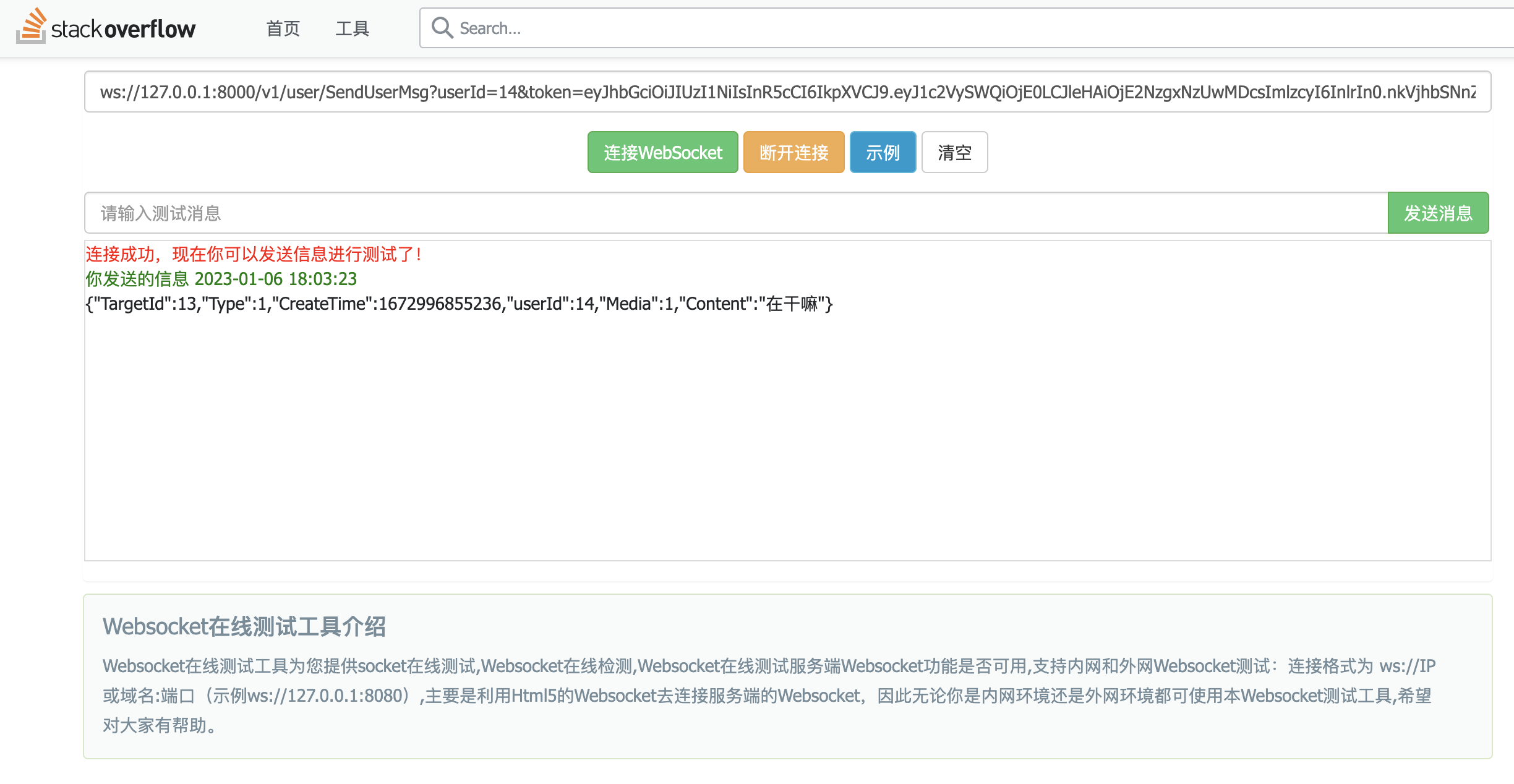
14收到来自13的信息:
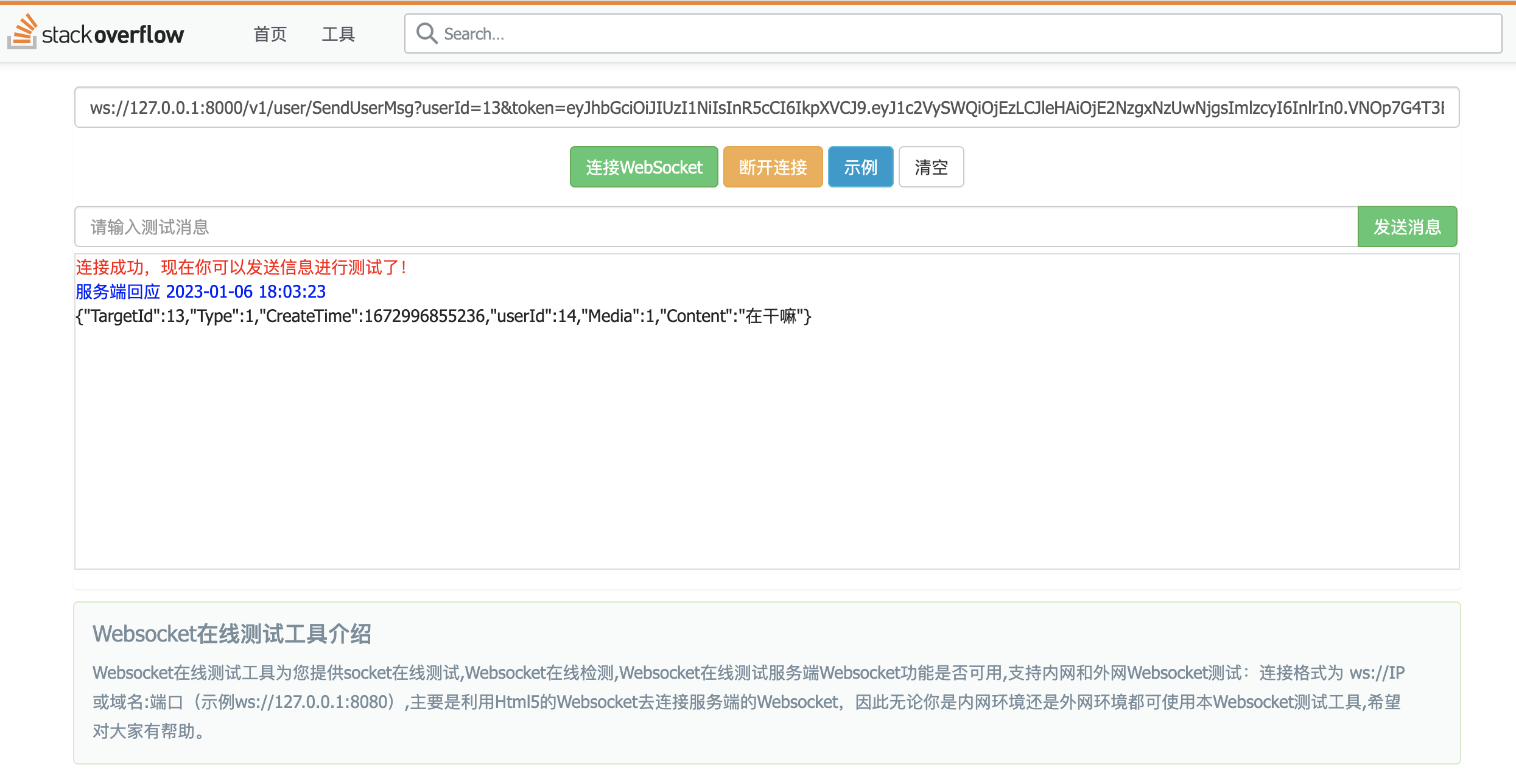
14回复13信息:
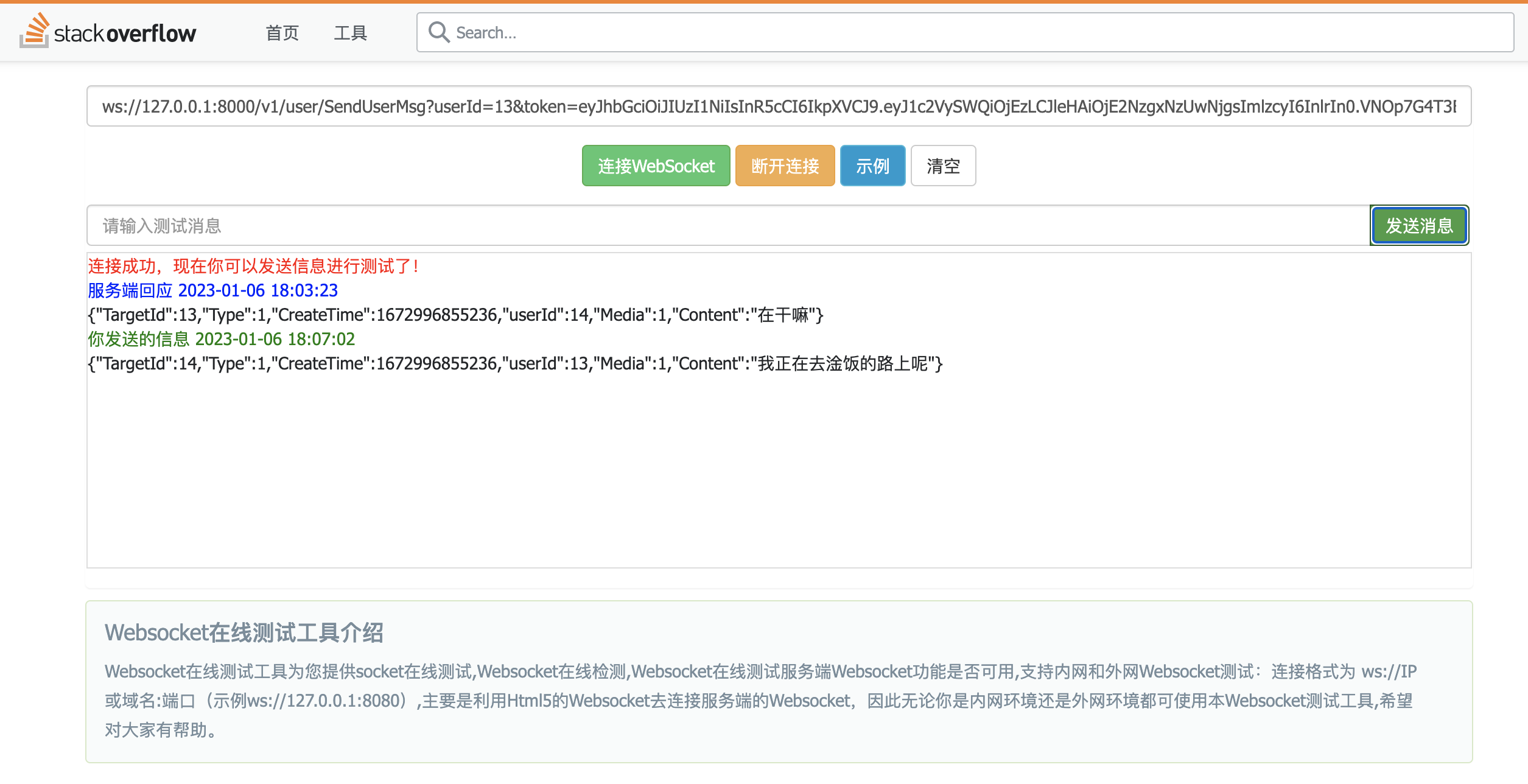
13收到14的回复:
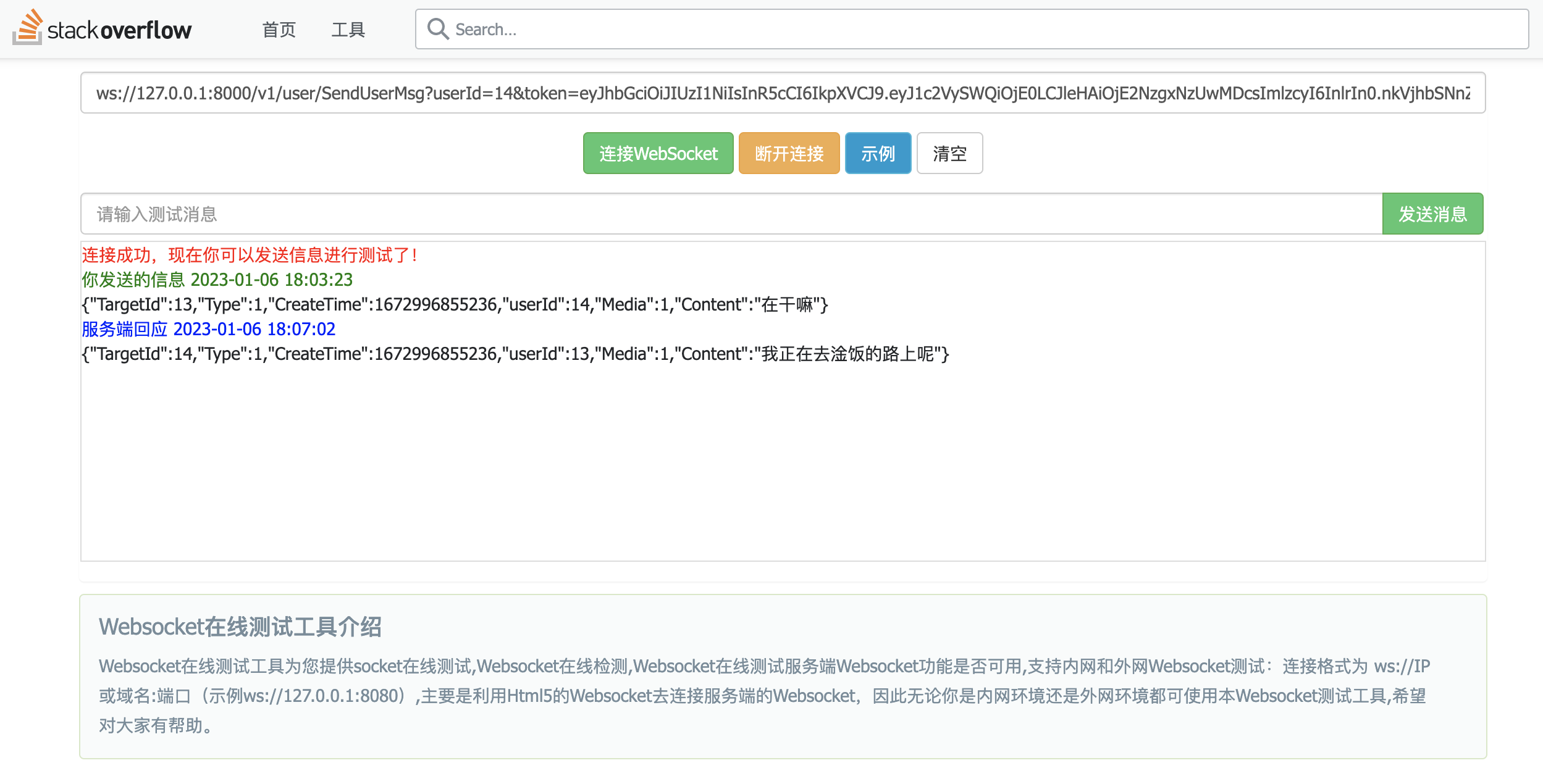
这样用户信息的发送和接收都完成了。
总结
这一部分的内容,主要就是对信息的发送和接收进行理解,当然这里的信息收发都只是使用websocket就行简单的使用,在下一篇文章中,我们将信息的收发核心加入udp连接。
本作品采用《CC 协议》,转载必须注明作者和本文链接


 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu




写的不错 :+1: