个人推荐的 laravel 或其它框架的编程规范
前情提要
在开发的时候,许多同学在文件命名方面,容易出现絮乱,随意性强,没有统一性。此种情况,在多人协同时,尤为突出。各开发人员都要去适应每个人的开发习惯,诸多不便,阻碍了多人协同开发的效率。
统一规范
使用统一的开发规范,好处甚多。减少开发间的磨合,是其一,举例:
app/Models/User.php
···
/**
* 获取 users.username
* @param int $user_id users.id
* @return string
*/
public static function getUsername(int $user_id): string
{
return self::where('id', $user_id)->value('username');
}// getUsername() end
/**
* 获取 users.age
* @param int $user_id users.id
* @return int
*/
public static function getAge(int $user_id): int
{
return (int)self::where('id', $user_id)->value('age');
}// getAge() end
/**
* 登录态校验
* @param string $token users.token
* @return bool, true-已登录
*/
public static function isLogin(string $token): bool
{
return self::select('token')->where('token', $token)->exists();
}// isLogin() end
···在形参 $user_id 的注释里,我使用的是 users.id 的形式。此形式是我主推的,优点是直观的知道此参数的由来(users 表中 id 字段)。
返回的参数也做了直观的说明,取值为 users 表中 username 字段的值。function 命名按照动作来区分命名,get + 字段 取值,set + 字段 更新值,is + 描述形容词 用于逻辑判断。
命名统一
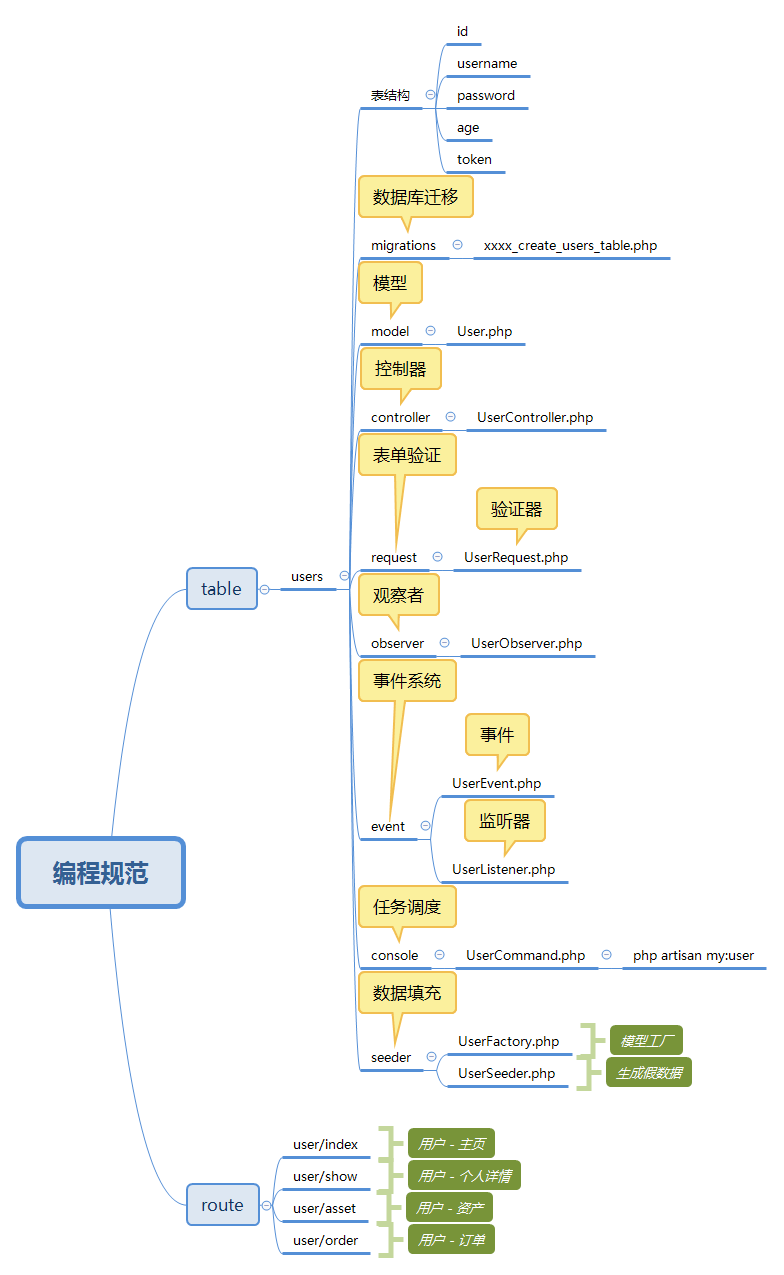
下面,我通过 users 表举例,列举我推荐命名的逻辑。
table - users
以 users 表来作为蓝本,向同学们推行此规范。
migrations - 数据库迁移
database/migrations/xxxx_create_users_table.php
···
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\DB;
···
Schema::create('users', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('username', 32)->unique()->nullable(false)->comment('名称');
$table->string('password', 128)->nullable(false)->comment('密码');
$table->unsignedInteger('age', 3)->default(0)->comment('年龄');
$table->string('token', 128)->nullable(true)->comment('登录态');
$table->dateTime('created_at')->useCurrent();
$table->dateTime('updated_at')->useCurrent();
$table->index('username', 'username_index');
});
DB::statement("ALTER TABLE `users` comment '用户表'");
···model - 模型
app/Models/User.php
controller - 控制器
app/Http/Controllers/UserController.php
<?php
namespace App\Http\Controllers;
use App\Http\Controllers\Controller;
use Illuminate\Http\Request;
use App\Models\User;
class UserController extends Controller
{
public function index(Request $request)
{
// todo
}// index() end
public function show(Request $request)
{
// 变量命名,对应的是表字段的话,变量名建议以该字段为名,
// 注释时采用 表名.字段 的形式
// users.username
$username = $request->post('username');
}// show() end
public function store(Request $request)
{
$user_id = $request->post('user_id');// users.id
$age = $request->post('age'); // users.age
// 更新数据
User::where('id', $user_id)->update(['age' => $age]);
}// store() end
}request - 表单验证
app/Http/Requests/UserRequest.php
observer - 观察者
app/Observers/UserObserver.php
event - 事件系统
- app/Events/UserEvent.php 事件
- app/Listeners/UserListener.php 监听器
console - 任务调度
app/Console/Commands/UserCommand.php
$ php artisan my:userseeder - 数据填充
- database/seeds/UserSeeder.php 生成假数据
- database/factories/UserFactory.php 模型工厂
规范定义
我将上面此种规范定义为 以表规名,对此的解释是,以表名为主线,规定其相关业务的文件,均以表名为关键字进行后续文件的命名。
命名 - 思维导图
数据库迁移 & 模型补充
在定义表字段时,会出现一个字段需要长注释,举例 orders.status 负责订单状态:
···
$table->string('status', 20)->default('wait_payment')->comment('订单状态');
···建议对 orders.status 字段的注释,放在模式中,好处在于,不管何处获取订单状态,都是统一的,避免出错。
app/Models/Order.php
···
// orders.status 订单状态-所有类型
public static $t_status = [
'wait_payment',
'wait_deliver_goods',
'wait_receiving_goods',
'wait_comment',
'done',
'cancel',
'rejection',
];
// orders.status 订单状态-中文注释
public static $t_status_cn = [
'wait_payment' => '待支付',
'wait_deliver_goods' => '待发货',
'wait_receiving_goods' => '待收货',
'done' => '已完成',
'cancel' => '已取消',
'rejection' => '已拒收',
];
···不管是自己还是团队成员进行查看,都是一目了然,只要这种形式养成了团队习惯,方便大家查找对应表字段的注释。
结语
希望我的个人建议,能在同学们间推行与流行起来。谢谢同学们的阅读,记得帮我 点赞、评论、收藏、转发。





 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu




参考下这个 github.com/jupeter/clean-code-php
验证 post put两个方法不一样的,你怎么区分
laravel 手册里有介绍此知识点,
路由>表单方法伪造,同学你可以借鉴。感觉少了广播、和通知