在 Go 中如何使用 go:embed 指令嵌入静态文件
有时候,将配置文件、模板甚至整个前端应用直接嵌入到 Go 二进制文件中,是一种提高应用部署效率和简化操作的有效方法。自从 Go 1.16 版本起,Go 语言官方引入了 //go:embed 指令,这使得嵌入静态资源变得异常简单而直接。本文将详细介绍如何在你的 Go 应用中使用这一强大的特性。
什么是 go:embed
//go:embed 在 Go 1.16 版本中被加入,这也是我接触 Go 语言的第一个版本。
//go:embed 是一个编译器指令,能够在程序编译时期在 Go 的二进制文件中嵌入任意文件和目录(除了少数 Go 官方限制不允许嵌入的指定类型文件或目录,后文会讲)。
//go:embed 用法非常简单,示例如下:
import "embed"
//go:embed hello.txt
var content string
//go:embed hello.txt
var contentBytes []byte
//go:embed hello.txt
var fileFS embed.FS
var data, _ = fileFS.ReadFile("hello.txt")
我们有且仅有 3 种方式可以将一个文件内容嵌入到 Go 变量中。
这 3 种方式各自适用场景如下:
对于第 1 种用法,将文件嵌入到
string中,适合嵌入单个文件(如配置数据、模板文件或一段文本)。对于第 2 种用法,将文件嵌入到
[]byte中,适合嵌入单个文件(如二进制文件:图片、字体或其他非文本数据)。对于第 3 种用法,将文件嵌入到
embed.FS中,适合嵌入多个文件或整个目录(embed.FS是一个只读的虚拟文件系统)。
//go:embed 指令语法格式为://go:embed patterns,其中 patterns 可以是文件名、目录名或 path.Match 所支持的路径通配符。
值得注意的是://go:embed 指令仅接受相对于包含 Go 源文件的目录的路径,即当前程序源码所在目录,不能直接嵌入父目录文件内容(后文会讲解解决方案)。
并且,//go:embed 指令要紧挨着写在被嵌入文件的变量上面,类似注释,//go:embed 是固定写法,字符中间不能含有任何空格。比如 // go:embed 这种写法是不能被解析的。
此外,//go:embed 指令需要配合 embed 包一起使用。
快速开始
下面我们来通过一个示例程序,演示下 //go:embed 的使用。
准备如下项目目录结构:
$ tree -a getting-started
getting-started
├── file
│ ├── hello1.txt
│ ├── hello2.txt
│ └── sub
│ └── sub.txt
├── go.mod
├── hello.txt
└── main.go
3 directories, 6 files
在 main.go 中编写示例代码如下:
package main
import (
"embed"
"fmt"
"io"
"io/fs"
)
//go:embed hello.txt
var content string
//go:embed hello.txt
var contentBytes []byte
//go:embed file
var fileFS embed.FS
//go:embed file/hello1.txt
//go:embed file/hello2.txt
var helloFS embed.FS
func main() {
fmt.Printf("hello.txt content: %s\n", content)
fmt.Printf("hello.txt content: %s\n", contentBytes)
// NOTE: embed.FS 提供了 ReadFile 功能,可以直接读取文件内容,文件路径需要指明父目录 `file`
hello1Bytes, _ := fileFS.ReadFile("file/hello1.txt")
fmt.Printf("file/hello1.txt content: %s\n", hello1Bytes)
// NOTE: embed.FS 提供了 ReadDir 功能,通过它可以遍历一个目录下的所有信息
dir, _ := fs.ReadDir(fileFS, "file")
for _, entry := range dir {
info, _ := entry.Info()
fmt.Printf("%+v\n", struct {
Name string
IsDir bool
Info struct {
Name string
Size int64
Mode fs.FileMode
}
}{
Name: entry.Name(),
IsDir: entry.IsDir(),
Info: struct {
Name string
Size int64
Mode fs.FileMode
}{Name: info.Name(), Size: info.Size(), Mode: info.Mode()},
})
}
// NOTE: embed.FS 实现了 io/fs.FS 接口,可以返回它的子文件夹作为新的 io/fs.FS 文件系统
subFS, _ := fs.Sub(helloFS, "file")
hello2F, _ := subFS.Open("hello2.txt")
hello2Bytes, _ := io.ReadAll(hello2F)
fmt.Printf("file/hello2.txt content: %s\n", hello2Bytes)
}
示例程序中,将 hello.txt 分别嵌入到 content string、contentBytes []byte 两个变量。
我们可以通过 //go:embed 目录名 的方式,将 file 目录嵌入到 fileFS embed.FS 文件系统。
对于 embed.FS 文件系统,我们可以连续写上多个 //go:embed 指令,来嵌入多个文件到 helloFS embed.FS。
并且,对于 helloFS embed.FS 这段代码:
//go:embed file/hello1.txt
//go:embed file/hello2.txt
var helloFS embed.FS
还有另一种写法:
//go:embed file/hello1.txt file/hello2.txt
var helloFS embed.FS
二者等价。
在 main 函数中,首先对 content string 和 contentBytes []byte 的字符串格式内容进行了打印。
接着,使用 embed.FS 提供的 ReadFile 方法读取 file/hello1.txt 文件内容(注意:文件路径必须要指明父目录 file,否则会找不到 hello1.txt 文件)并打印。
此外,embed.FS 还提供了 fs.ReadDir 方法可以读取指定目录下所有文件信息。
最后,由于 embed.FS 实现了 io/fs.FS 接口,我们可以使用 fs.Sub 获取指定目录的子文件系统,然后就可以用 subFS.Open("hello2.txt") 方式直接读取 hello2.txt 内容(无需再指明父目录)并打印了。
执行示例代码,输出结果如下:
$ go run main.go
hello.txt content: Hello World!
hello.txt content: Hello World!
file/hello1.txt content: Hello1!
{Name:hello1.txt IsDir:false Info:{Name:hello1.txt Size:7 Mode:-r--r--r--}}
{Name:hello2.txt IsDir:false Info:{Name:hello2.txt Size:7 Mode:-r--r--r--}}
{Name:sub IsDir:true Info:{Name:sub Size:0 Mode:dr-xr-xr-x}}
file/hello2.txt content: Hello2!
在 HTTP Server 中使用 go:embed
由于 //go:embed 的核心功能就是将静态文件嵌入到 Go 程序中,所以 //go:embed 存在两个最常见的使用场景:一个是托管静态资源服务器,另一个是解决单元测试文件依赖问题。
我们先来看下 //go:embed 在静态资源服务中的应用。
准备如下项目目录结构:
$ tree -a http
http
├── go.mod
├── main.go
├── static
│ ├── css
│ │ └── style.css
│ ├── hello.txt
│ ├── html
│ │ └── index.html
│ ├── img
│ │ └── subscribe.jpeg
│ └── js
│ └── script.js
└── template
└── email.tmpl
7 directories, 8 files
其中,static 是典型的静态资源目录,里面存储了前端三剑客 HTML、CSS 和 JavaScript 文件。内容分别如下:
http/static/html/index.html:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../css/style.css">
<script src="../js/script.js"></script>
<title>Hello World</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>关注我:Go编程世界</h1>
<div><img src="../img/subscribe.jpeg" alt="Go编程世界"></div>
</body>
</html>
http/static/css/style.css:
h1 {
text-align: center;
color: #2c49a7;
}
div {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
img {
width: 200px;
}
http/static/js/script.js:
window.onload = function () {
let body = document.querySelector("body")
body.style.background = "#f3f3f3";
}
template 是模板资源目录,使用 Go template 语法。email.tmpl 存储邮件模板,内容如下:
http/template/email.tmpl:
<pre>
尊敬的用户:
您好,欢迎您使用 XXX 服务!
您的 XXX 账号是:<b>{{ .Username }}</b>
请您点击下面的链接完成邮箱验证:
<a href="{{ .ConfirmURL }}">{{ .ConfirmURL }}</a>
若以上链接无法点击,请将该链接复制到浏览器(如 Chrome)的地址栏中访问。
温馨提示:
1\. 上述链接 24 小时内有效并且在激活过一次后失效。若验证链接失效,请登录网站 <a href="https://jianghushinian.cn">https://jianghushinian.cn</a> 重新验证;
2\. 如果您没有注册过 XXX 账号,请您忽略此邮件,由此给您带来的不便敬请谅解。
- 江湖十年
(这是一封自动产生的 Email,请勿回复)
</pre>
在 main.go 中编写示例代码如下:
package main
import (
"embed"
"io/fs"
"net/http"
"sync"
"text/template"
)
//go:embed static
var staticFS embed.FS
//go:embed template
var templateFS embed.FS
func main() {
var wg sync.WaitGroup
wg.Add(5)
// NOTE: 在 go:embed 出现之前托管静态文件服务的写法
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
http.Handle("/", http.FileServer(http.Dir("static")))
_ = http.ListenAndServe(":8000", nil)
}()
// NOTE: 使用 go:embed 实现静态文件服务
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
_ = http.ListenAndServe(":8001", http.FileServer(http.FS(staticFS)))
}()
// NOTE: 可以使用 http.StripPrefix 去除静态文件服务的 `/static/` 路由前缀
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
http.Handle("/static/", http.StripPrefix("/static/", http.FileServer(http.FS(staticFS))))
_ = http.ListenAndServe(":8002", nil)
}()
// NOTE: 也可以使用 fs.Sub 去除静态文件服务的 `/static/` 路由前缀
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
fsSub, _ := fs.Sub(staticFS, "static")
_ = http.ListenAndServe(":8003", http.FileServer(http.FS(fsSub)))
}()
// NOTE: text/template 和 html/template 同样可以从嵌入的文件系统中解析模板,这里以 text/template 为例
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
tmpl, _ := template.ParseFS(templateFS, "template/email.tmpl")
http.HandleFunc("/email", func(writer http.ResponseWriter, request *http.Request) {
// 设置 Content-Type 为 text/html
writer.Header().Set("Content-Type", "text/html; charset=utf-8")
// 执行模板并发送响应
_ = tmpl.ExecuteTemplate(writer, "email.tmpl", map[string]string{
"Username": "江湖十年",
"ConfirmURL": "https://jianghushinian.cn",
})
})
_ = http.ListenAndServe(":8004", nil)
}()
wg.Wait()
}
我们使用 staticFS embed.FS 和 templateFS embed.FS 分别嵌入静态文件和模版文件目录。
在 main 函数中,分别启动了 5 个 goroutine,用来对比演示使用 //go:embed 实现静态文件服务的效果。
第 1 个 goroutine 演示了在不使用 //go:embed 的情况下,我们如何来编写一个静态资源文件服务。可以直接使用 Go 在 net/http 中提供的 http.FileServer 将一整个目录作为静态资源目录。http.FileServer 返回一个 http.Handler 可以直接作为 Web Server 的 Handler 使用。这个服务监听 8000 端口。
第 2 个 goroutine 演示了如何使用 //go:embed 实现静态资源文件服务。因为 http.FileServer 参数接收 http/fs.FileSystem 类型,所以不能直接将 embed.FS 传递给它。http/fs.FileSystem 接口定义如下:
type FileSystem interface {
Open(name string) (File, error)
}
前文说过 embed.FS 实现了 io/fs.FS 接口,刚好 http 提供了 http.FS 函数可以将 io/fs.FS 类型转换成 http/fs.FileSystem。http.FS 定义如下:
// FS converts fsys to a [FileSystem] implementation,
// for use with [FileServer] and [NewFileTransport].
// The files provided by fsys must implement [io.Seeker].
func FS(fsys fs.FS) FileSystem {
return ioFS{fsys}
}
可以发现,我们能够非常方便的使用 //go:embed 来实现静态资源文件服务器。与第一种实现方式相比,这种方式在部署时更加简单,无需考虑静态资源目录依赖问题。
不过,使用 //go:embed 也引入了一个新问题,就是在我们访问 / 路由时,是不会直接显示 static 目录下内容的,而需要访问 /static/ 路由才行。
要解决这个问题也很简单,可以使用 http.StripPrefix 去除静态文件服务的 /static/ 路由前缀。
即第 3 个 goroutine 中的代码实现:
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
http.Handle("/static/", http.StripPrefix("/static/", http.FileServer(http.FS(staticFS))))
_ = http.ListenAndServe(":8002", nil)
}()
另外,我们也可以使用 fs.Sub 去除静态文件服务的 /static/ 路由前缀。
即第 4 个 goroutine 中的代码实现:
go func() {
defer wg.Done()
fsSub, _ := fs.Sub(staticFS, "static")
_ = http.ListenAndServe(":8003", http.FileServer(http.FS(fsSub)))
}()
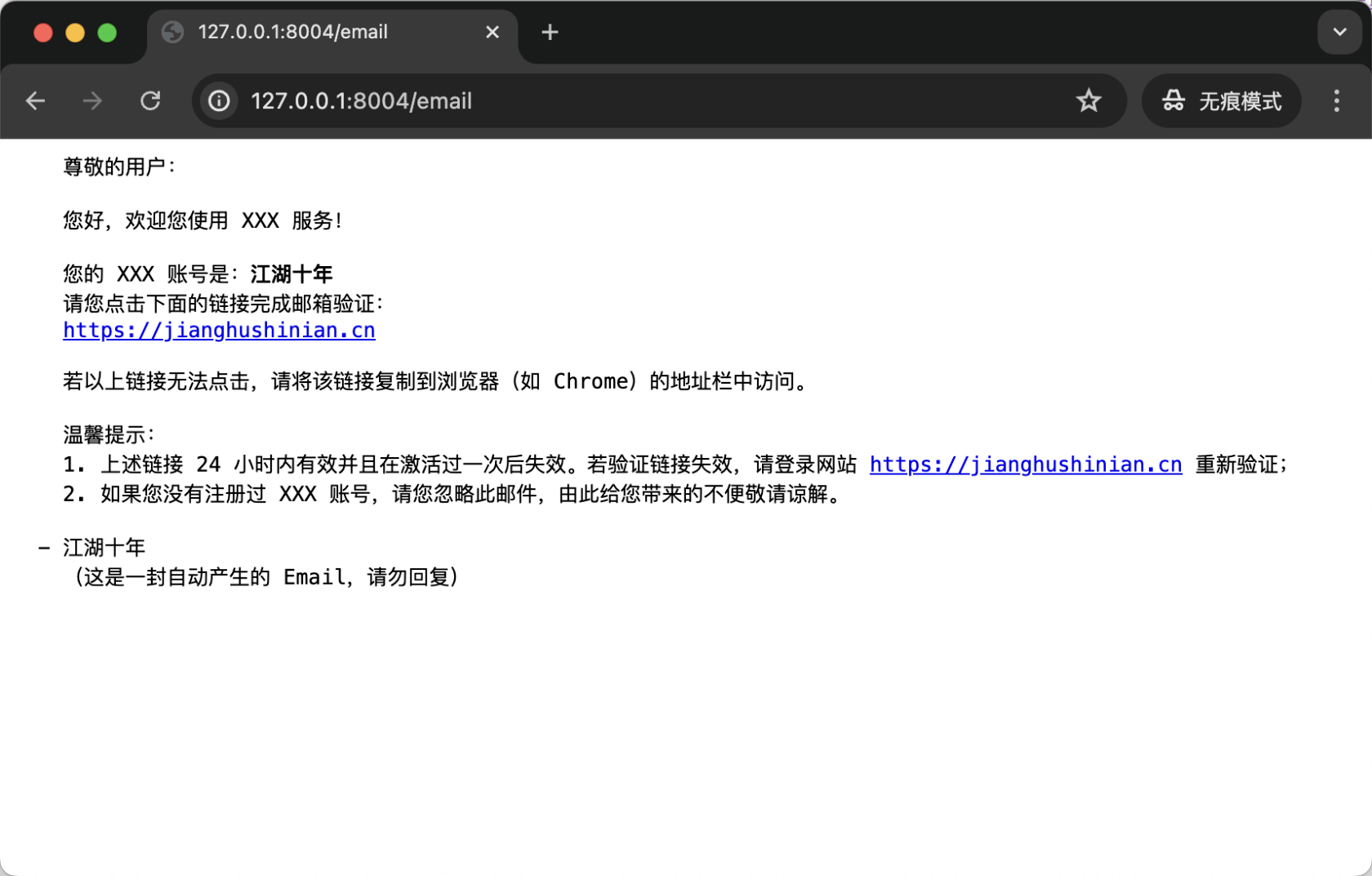
最后,第 5 个 goroutine 中使用 template.ParseFS(templateFS, "template/email.tmpl") 来解析邮件模板。之所以 template.ParseFS 函数能直接解析 embed.FS 类型变量,同样是因为 embed.FS 实现了 io/fs.FS 接口。
我们来执行下示例程序,看下效果:
$ go run main.go
浏览器中访问 http://127.0.0.1:8000/ 效果如下:
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8001/static/ 效果如下:
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8002/ 和 http://127.0.0.1:8003/ 的效果,与访问 http://127.0.0.1:8000/ 效果相同,你可以自行尝试。
访问 http://127.0.0.1:8004 效果如下:
其实这两种用法在 embed 的 go doc 中也能看到示例。
执行 go doc embed 命令,能在文档中找到如下内容:
For example, given the content variable in the example above, we can write:
http.Handle(“/static/“, http.StripPrefix(“/static/“, http.FileServer(http.FS(content))))
template.ParseFS(content, “*.tmpl”)
在单元测试中使用 go:embed
现在我们来介绍下在单元测试场景中如何使用 //go:embed。
准备如下项目目录结构:
$ tree -a test
test
├── go.mod
├── main.go
├── main_test.go
├── main_x_test.go
└── testdata
└── test.txt
2 directories, 5 files
这个示例程序中 main.go 代码并不重要,只要保证程序编译通过即可。
main_test.go 代码如下:
package main
import (
_ "embed"
"testing"
)
//go:embed testdata/test.txt
var testF string
func TestEmbed(t *testing.T) {
t.Log(testF)
}
可以发现,其实在单元测试中,//go:embed 的用法并没什么两样。
不过在单元测试中,测试依赖的静态文件通常放到 testdata 目录下,这是约定俗成的做法。
值得注意的是,示例代码中使用了匿名导入 import _ "embed",//go:embed 指令使用时必须要配合 embed 包一起使用,否则执行程序将得到 go:embed only allowed in Go files that import "embed" 报错。
main_x_test.go 文件是黑盒测试文件,其包名为 main_test,代码如下:
package main_test
import (
_ "embed"
"testing"
)
//go:embed testdata/test.txt
var testF string
func TestEmbed(t *testing.T) {
t.Log(testF)
}
执行测试代码,输出结果如下:
$ go test -v
=== RUN TestEmbed
main_test.go:12: test content
--- PASS: TestEmbed (0.00s)
=== RUN TestEmbed
main_x_test.go:12: test content
--- PASS: TestEmbed (0.00s)
PASS
ok github.com/jianghushinian/blog-go-example/embed/test 0.505s
顺便提一下,为了支持分析 Go 包的工具,通过 //go:embed 指令嵌入的目录或文件可以在 go list 输出中找到。
NOTE:
go list命令是一个强大的工具,用于列出当前模块中的包或者查询包的特定属性。此命令可以显示关于包的详细信息,这些信息对于理解包的结构和依赖非常有用。
执行 go help list 命令,可以在输出中找到如下几条信息:
// Embedded files
EmbedPatterns []string // //go:embed patterns
EmbedFiles []string // files matched by EmbedPatterns
TestEmbedPatterns []string // //go:embed patterns in TestGoFiles
TestEmbedFiles []string // files matched by TestEmbedPatterns
XTestEmbedPatterns []string // //go:embed patterns in XTestGoFiles
XTestEmbedFiles []string // files matched by XTestEmbedPatterns
对应用法和输出信息如下所示:
# 所有被直接嵌入的 patterns,包括目录和文件
$ go list -f '{{.EmbedPatterns}}'
[testdata]
# 嵌入的文件
$ go list -f '{{.EmbedFiles}}'
[testdata/test.txt]
# 测试文件中嵌入的 patterns
$ go list -f '{{.TestEmbedPatterns}}'
[testdata/test.txt]
# 黑盒测试文件中嵌入的 patterns
$ go list -f '{{.XTestEmbedPatterns}}'
[testdata/test.txt]
也可以以 JSON 格式输出以上信息:go list -json。
这里仅演示了在测试文件中使用 //go:embed 的简单用法,并不是真实案例。你可以在我另一篇文章:《在 Go 语言单元测试中如何解决文件依赖问题》,中找到单元测中使用 //go:embed 的真实案例,并详细讲解了如何使用 //go:embed 解决测试依赖。
使用 go:embed 嵌入父目录
前文有提到://go:embed 指令仅接受相对于包含 Go 源文件的目录的路径,即当前程序源码所在目录,不能直接嵌入父目录文件内容。
现在来讲解下如何解决这个问题。
准备如下项目目录结构:
$ tree -a parent-directory
parent-directory
├── go.mod
├── go.sum
├── internal
│ └── controller
│ └── controller.go
├── main.go
└── template
└── email.tmpl
4 directories, 5 files
这是一个微型的 Web Server 程序,main.go 是程序入口,代码如下:
package main
import (
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
"github.com/jianghushinian/blog-go-example/embed/parent-directory/internal/controller"
)
func main() {
r := gin.Default()
r.POST("/users", (&controller.Controller{}).CreateUser)
_ = r.Run(":8005")
}
示例程序提供了一个 创建用户 的接口,并监听 8005 端口。
template/email.tmpl 是邮件模板,内容与前文介绍的一样。
controller.go 中代码如下:
package controller
import (
"bytes"
"embed"
"net/http"
"text/template"
"github.com/gin-gonic/gin"
)
// 直接嵌入父目录
//go:embed ../../template
var templateFS embed.FS
type Controller struct{}
func (ctrl *Controller) CreateUser(c *gin.Context) {
// pretend to create user ...
// send email
tmpl, _ := template.ParseFS(templateFS, "template/*.tmpl")
var buf bytes.Buffer
_ = tmpl.ExecuteTemplate(&buf, "email.tmpl", map[string]string{
"Username": "江湖十年",
"ConfirmURL": "https://jianghushinian.cn",
})
c.Data(http.StatusOK, "text/html; charset=utf-8", buf.Bytes())
}
CreateUser 方法模拟实现了创建用户并返回邮件的逻辑。
示例代码中,我们尝试直接使用 //go:embed ../../template 来嵌入模版文件到变量 templateFS embed.FS 中。
执行示例代码:
$ go run main.go
internal/controller/controller.go:13:12: pattern ../../template: invalid pattern syntax
可以发现,程序直接报错了。
我在 issues/46056 中找到了这个问题的解决方案。
korya 提供了一种思路:
//go:generate cp -r ../../assets ./local-asset-dir
//go:embed local-asset-dir
var assetFs embed.FS
我们可以使用 //go:generate + //go:embed 的方式来解决此问题。
//go:generate 是一个用于自动化生成 Go 代码的指令。 在执行程序之前,可以通过 go generate 命令自动执行 //go:generate 指令。
所以这个解决问题的思路是:在执行主程序前,先通过 //go:generate 将父目录所有文件拷贝到当前目录,然后再将当前目录中的文件嵌入 Go 程序。
这个思路可行,但不是一个好的解决方案:
这样做相当于代码中存储了两份依赖文件。
我们很容易忘记执行
go generate命令。
我们确实还有更好的选择。
既然 //go:embed 不支持父目录,那么我们可以换个角度,在 template 目录下新建一个 Go 文件来嵌入模板文件 email.tmpl,这样就变成了从当前目录嵌入文件。然后在使用时,导入 template 目录下 Go 文件中嵌入静态文件的变量即可。
新建 template/template.go 文件,代码如下:
package template
import "embed"
//go:embed *
var TemplateFS embed.FS
//go:embed 的 patterns 参数不仅不支持 .. 这种父目录写法,表示当前目录的 . 写法也不支持。不过我们可以使用 * 来嵌入当前目录下的所有文件。
因为 TemplateFS 变量需要被外部引用,所以首字母大写,作为可导出变量。由此可见,//go:embed 可以将文件嵌入为 exported 的变量,也可以嵌入为 unexported 的变量。
现在对 controller.go 文件内容做如下修改:
package controller
import (
...
templatefs "github.com/jianghushinian/blog-go-example/embed/parent-directory/template"
)
...
func (ctrl *Controller) CreateUser(c *gin.Context) {
// pretend to create user ...
// send email
tmpl, _ := template.ParseFS(templatefs.TemplateFS, "*.tmpl") // 记得去掉 template 前缀
...
}
重新执行程序:
$ go run main.go
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Creating an Engine instance with the Logger and Recovery middleware already attached.
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] Running in "debug" mode. Switch to "release" mode in production.
- using env: export GIN_MODE=release
- using code: gin.SetMode(gin.ReleaseMode)
[GIN-debug] POST /users --> github.com/jianghushinian/blog-go-example/embed/parent-directory/internal/controller.(*Controller).CreateUser-fm (3 handlers)
[GIN-debug] [WARNING] You trusted all proxies, this is NOT safe. We recommend you to set a value.
Please check https://pkg.go.dev/github.com/gin-gonic/gin#readme-don-t-trust-all-proxies for details.
[GIN-debug] Listening and serving HTTP on :8005
根据输出的日志信息可知,Web Server 已经成功启动了。
使用 curl 来创建一个用户看看效果:
$ curl -X POST http://127.0.0.1:8005/users
<pre>
尊敬的用户:
您好,欢迎您使用 XXX 服务!
您的 XXX 账号是:<b>江湖十年</b>
请您点击下面的链接完成邮箱验证:
<a href="https://jianghushinian.cn">https://jianghushinian.cn</a>
若以上链接无法点击,请将该链接复制到浏览器(如 Chrome)的地址栏中访问。
温馨提示:
1. 上述链接 24 小时内有效并且在激活过一次后失效。若验证链接失效,请登录网站 <a href="https://jianghushinian.cn">https://jianghushinian.cn</a> 重新验证;
2. 如果您没有注册过 XXX 账号,请您忽略此邮件,由此给您带来的不便敬请谅解。
- 江湖十年
(这是一封自动产生的 Email,请勿回复)
</pre>
至此,使用 //go:embed 嵌入父目录的问题已经被我们解决了。
使用 go:embed 的注意事项
我们已经介绍了 //go:embed 的常见用法。不过还有一些注意事项值得讨论。
安全性
我们知道 //go:embed 能够将文件或目录嵌入到 3 种类型变量中,分别是 string、[]byte 和 embed.FS。其中 string 是 Go 语言本身限制为只读,而 []byte 是可以修改的,所以使用时需要注意这一点。对于 embed.FS,其为只读(read-only)集合,是故意这么设计的。如果声明中没有 //go:embed 指令对其进行初始化,那么 embed.FS 就是一个空文件系统。正因为 embed.FS 是一个只读的值,因此它是并发安全的,你可以尽情的在多个 goroutine 中使用它。
patterns 规则
//go:embed patterns 指令的 patterns 参数,不支持嵌入空目录,并且也不支持嵌入符号链接(symbolic links),即软链接。也不能匹配一些特殊符号:" * < > ? ` ' | / \。
根据前文的示例程序,patterns 指定为目录时,该目录下的所有文件都会被嵌入到变量中。但是以 . 或 _ 开头的文件是会被忽略的。如果想要嵌入 . 或 _ 开头的文件,可以让 patterns 以 all: 前缀开头,如 //go:embed all:testdata。也可以使用通配符 *,如 //go:embed testdata/*,不过 * 不具有递归性,子目录下的 . 或 _ 开头文件不会被嵌入。
比如:
image不会嵌入image/.tempfile文件。image/*会嵌入image/.tempfile文件。以上二者都不会嵌入
image/dir/.tempfile。all:image则会同时嵌入image/.tempfile和image/dir/.tempfile两个文件。
注意,使用 //go:embed 嵌入带有路径的文件时,目录分隔符采用正斜杠 /,如 //go:embed file/hello1.txt,即使是 Windows 系统也是如此。
patterns 支持使用双引号 " 或者反引号 ` 的方式应用到嵌入的文件名、目录名或者 pattern 上,这对名称中带有 空格 或 特殊字符 很有用。
此外,诸如 .bzr、.hg、.git、.svn 这几个版本控制管理目录,始终都不会被嵌入,embed 相关代码中会做检查。
不要在 patterns 路径中包含特殊字符,比如 -、$ 等。不然,根据我的实测结果,你将得到类似 imports embed/testdata: invalid input file name "$not-hidden/fortune.txt" 报错信息。
path.Match
patterns 支持文件名、目录名以及 path.Match 所支持的路径通配符。
对于 path.Match 我来更详细的讲解下。
path.Match 函数签名如下:
func Match(pattern, name string) (matched bool, err error)
对于匹配 path.Match 规则如下:
功能说明
path.Match函数的功能是:报告参数name是否符合指定的 shell 模式(pattern)。这个函数要求模式与整个
name完全匹配,而不是仅匹配其中的一个子串。
模式语法
pattern:由一个或多个
term构成。term:可以是以下几种类型:
*匹配任意序列的非/字符。?匹配任意单个非/字符。[character-range]定义一个字符类,必须是非空的。在字符类内部,如果以^开头([^character-range]),则表示取反,否定后续的字符范围。单个字符
c,可以直接匹配字符c(当c不是*、?、\、[中的一个时)。\\c用于转义匹配字符c,\\用于转义(例如\\、\*、\?等)。character-range:
单个字符
c,直接匹配字符c(当c不是\\、-、]中的一个时)。\\c用于转义匹配字符c。lo-hi匹配从lo到hi之间的任意字符(包括lo和hi)。
全局变量
//go:embed 指令只能用在包一级的全局变量中,不能用在函数或方法级别。
这个问题在 issues/43216 中有讨论。
大致原因如下:
如果嵌入资源只初始化一次,那么每次函数调用都将共享这些资源,考虑到任何函数都可以作为
goroutine运行,这会带来严重的潜在风险;如果每次函数调用时都重新初始化,这样做会产生额外的性能开销。
虽然 //go:embed 在设计之初是支持函数或方法级别变量的,但基于以上两点考虑,最终这个功能被移除了。
由于以上这些注意事项过于琐碎,我就不一一举例说明了,你可以自行尝试,也可以先跳过,等遇到问题了再过来查找原因。
总结
在 Go 1.16 版本发布时加入了 //go:embed 指令。
//go:embed 是一个编译器指令,能够在程序编译时期在 Go 的二进制文件中嵌入任意文件和目录。这使得在 Go 文件中嵌入静态资源变得异常简单而直接。
//go:embed 语法非常简单://go:embed patterns。//go:embed 能够将文件或目录分别嵌入到 string、[]byte 和 embed.FS 3 中类型变量中。
//go:embed 最常见的两个使用场景分别时:托管静态资源服务器,和解决单元测试文件依赖问题。
我们可以在静态文件目录下创建一个 Go 文件,然后使用 //go:embed * 将静态文件嵌入进来,然后在使用时,导入静态文件目录下 Go 文件中嵌入静态文件的变量。这样可以实现嵌入 Go 源文件的父目录内容。
//go:embed 还有很多使用细节值得注意:比如在考虑安全性时需要顾及被嵌入静态文件的变量是否可变;patterns 中不能随意包含特殊字符;和当 pattern 为 path.Match 时的语法规范等。
//go:embed 指令只能用在包一级的全局变量中,不能用在函数或方法级别。
此外,在 embed 的测试文件 源码 中,有一些写法我们也可以作为参考。
本文示例源码我都放在了 GitHub 中,欢迎点击查看。
希望此文能对你有所启发。
延伸阅读
embed Documentation: embed@go1.22.0"">https://pkg.go.dev/embed@go1.22.0
Go 1.16 Release Notes: go.dev/doc/go1.16#library-embed
issues/46056: github.com/golang/go/issues/46056
issues/43216: github.com/golang/go/issues/43216
path.Match Documentation: path@go1.22.0#Match"">https://pkg.go.dev/path@go1.22.0#Match
embed test: github.com/golang/go/blob/go1.22.0...
Go by Example: Embed Directive: gobyexample.com/embed-directive
Go command support for embedded static assets (files) — Draft Design: go.googlesource.com/proposal/+/mas...
Working with Embed in Go 1.16 Version: lakefs.io/blog/working-with-embed-...
How to use go:embed in Golang: www.educative.io/answers/how-to-us...
在 Go 语言单元测试中如何解决文件依赖问题: jianghushinian.cn/2023/07/19/how-t...
本文 GitHub 示例代码:github.com/jianghushinian/blog-go-...
联系我
公众号:Go编程世界
微信:jianghushinian
本作品采用《CC 协议》,转载必须注明作者和本文链接


 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu



