Go语言不依赖第三方接口通过本地数据xdb文件查询获取IP地址的归属地区及运营商名称
功能说明:
用本地数据,离线识别ip属地,用于显示用户ip属地,不依赖第三方的api接口,本地数据包解析,解析速度快10微秒级别的查询效率。返回数据固定格式:国家|区域|省份|城市|ISP,例如:中国|0|云南省|昆明市|移动。
特性:
1、IP 数据管理框架
xdb 支持亿级别的 IP 数据段行数,默认的 region 信息都固定了格式:国家|区域|省份|城市|ISP,缺省的地域信息默认是0。 region 信息支持完全自定义,例如:你可以在 region 中追加特定业务需求的数据,例如:GPS信息/国际统一地域信息编码/邮编等。也就是你完全可以使用 ipregion 来管理你自己的 IP 定位数据。
2、数据去重和压缩
xdb 格式生成程序会自动去重和压缩部分数据,默认的全部 IP 数据,生成的 ipregion.xdb 数据库是 11MiB,随着数据的详细度增加数据库的大小也慢慢增大。
3、极速查询响应
即使是完全基于 xdb 文件的查询,单次查询响应时间在十微秒级别,可通过如下两种方式开启内存加速查询:
vIndex 索引缓存 :使用固定的 512KiB 的内存空间缓存 vector index 数据,减少一次 IO 磁盘操作,保持平均查询效率稳定在10-20微秒之间。
xdb 整个文件缓存:将整个 xdb 文件全部加载到内存,内存占用等同于 xdb 文件大小,无磁盘 IO 操作,保持微秒级别的查询效率。
使用方法:
1.下封装解析插件和
到这:下载代码地址,在右边的“代码下载”下载插件代码,并在下面的代码附件下载 下载“xdb数据文件”解压后,复制ipregion.xdb文件到resource/static目录下。
- 下载到的插件代码目录
├── plugin # 扩展插件目录 │ ├── ipregion # “ip地址解析属地区”目录文件夹 │ │ ├── searcher.go # 编写业务 │ │ └── util.go # 工具函数 │ └── ipregion.go # “ip地址解析属地区”文件 用于app开发时调用 - 其中代码插件源码:
searcher.go文件的源码如:
// ---
// ipregion database v2.0 searcher.
// @Note this is a Not thread safe implementation.
//
// @Author gofly
// @Date 2024/08/19
package ipregion
import (
"encoding/binary"
"fmt"
"os"
"path/filepath"
)
const (
HeaderInfoLength = 256
VectorIndexRows = 256
VectorIndexCols = 256
VectorIndexSize = 8
SegmentIndexBlockSize = 14
)
// --- Index policy define
type IndexPolicy int
const (
VectorIndexPolicy IndexPolicy = 1
BTreeIndexPolicy IndexPolicy = 2
)
func (i IndexPolicy) String() string {
switch i {
case VectorIndexPolicy:
return "VectorIndex"
case BTreeIndexPolicy:
return "BtreeIndex"
default:
return "unknown"
}
}
// --- Header define
type Header struct {
// data []byte
Version uint16
IndexPolicy IndexPolicy
CreatedAt uint32
StartIndexPtr uint32
EndIndexPtr uint32
}
func NewHeader(input []byte) (*Header, error) {
if len(input) < 16 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid input buffer")
}
return &Header{
Version: binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(input),
IndexPolicy: IndexPolicy(binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(input[2:])),
CreatedAt: binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(input[4:]),
StartIndexPtr: binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(input[8:]),
EndIndexPtr: binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(input[12:]),
}, nil
}
// --- searcher implementation
type Searcher struct {
handle *os.File
// header info
header *Header
ioCount int
// use it only when this feature enabled.
// Preload the vector index will reduce the number of IO operations
// thus speedup the search process
vectorIndex []byte
// content buffer.
// running with the whole xdb file cached
contentBuff []byte
}
func baseNew(vIndex []byte, cBuff []byte) (*Searcher, error) {
var err error
path, _ := os.Getwd()
dbFile := filepath.Join(path, "/resource/static/ipregion.xdb")
// content buff first
if cBuff != nil {
return &Searcher{
vectorIndex: nil,
contentBuff: cBuff,
}, nil
}
// open the xdb binary file
handle, err := os.OpenFile(dbFile, os.O_RDONLY, 0600)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &Searcher{
handle: handle,
vectorIndex: vIndex,
}, nil
}
func NewWithFileOnly() (*Searcher, error) {
return baseNew(nil, nil)
}
func NewWithVectorIndex(vIndex []byte) (*Searcher, error) {
return baseNew(vIndex, nil)
}
func NewWithBuffer(cBuff []byte) (*Searcher, error) {
return baseNew(nil, cBuff)
}
func (s *Searcher) Close() {
if s.handle != nil {
err := s.handle.Close()
if err != nil {
return
}
}
}
// GetIOCount return the global io count for the last search
func (s *Searcher) GetIOCount() int {
return s.ioCount
}
// SearchByStr find the region for the specified ip string
func (s *Searcher) SearchByStr(str string) (string, error) {
ip, err := CheckIP(str)
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return s.Search(ip)
}
// Search find the region for the specified long ip
func (s *Searcher) Search(ip uint32) (string, error) {
// reset the global ioCount
s.ioCount = 0
// locate the segment index block based on the vector index
var il0 = (ip >> 24) & 0xFF
var il1 = (ip >> 16) & 0xFF
var idx = il0*VectorIndexCols*VectorIndexSize + il1*VectorIndexSize
var sPtr, ePtr = uint32(0), uint32(0)
if s.vectorIndex != nil {
sPtr = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(s.vectorIndex[idx:])
ePtr = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(s.vectorIndex[idx+4:])
} else if s.contentBuff != nil {
sPtr = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(s.contentBuff[HeaderInfoLength+idx:])
ePtr = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(s.contentBuff[HeaderInfoLength+idx+4:])
} else {
// read the vector index block
var buff = make([]byte, VectorIndexSize)
err := s.read(int64(HeaderInfoLength+idx), buff)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("read vector index block at %d: %w", HeaderInfoLength+idx, err)
}
sPtr = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(buff)
ePtr = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(buff[4:])
}
// fmt.Printf("sPtr=%d, ePtr=%d", sPtr, ePtr)
// binary search the segment index to get the region
var dataLen, dataPtr = 0, uint32(0)
var buff = make([]byte, SegmentIndexBlockSize)
var l, h = 0, int((ePtr - sPtr) / SegmentIndexBlockSize)
for l <= h {
m := (l + h) >> 1
p := sPtr + uint32(m*SegmentIndexBlockSize)
err := s.read(int64(p), buff)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("read segment index at %d: %w", p, err)
}
// decode the data step by step to reduce the unnecessary operations
sip := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(buff)
if ip < sip {
h = m - 1
} else {
eip := binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(buff[4:])
if ip > eip {
l = m + 1
} else {
dataLen = int(binary.LittleEndian.Uint16(buff[8:]))
dataPtr = binary.LittleEndian.Uint32(buff[10:])
break
}
}
}
//fmt.Printf("dataLen: %d, dataPtr: %d", dataLen, dataPtr)
if dataLen == 0 {
return "", nil
}
// load and return the region data
var regionBuff = make([]byte, dataLen)
err := s.read(int64(dataPtr), regionBuff)
if err != nil {
return "", fmt.Errorf("read region at %d: %w", dataPtr, err)
}
return string(regionBuff), nil
}
// do the data read operation based on the setting.
// content buffer first or will read from the file.
// this operation will invoke the Seek for file based read.
func (s *Searcher) read(offset int64, buff []byte) error {
if s.contentBuff != nil {
cLen := copy(buff, s.contentBuff[offset:])
if cLen != len(buff) {
return fmt.Errorf("incomplete read: readed bytes should be %d", len(buff))
}
} else {
_, err := s.handle.Seek(offset, 0)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("seek to %d: %w", offset, err)
}
s.ioCount++
rLen, err := s.handle.Read(buff)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("handle read: %w", err)
}
if rLen != len(buff) {
return fmt.Errorf("incomplete read: readed bytes should be %d", len(buff))
}
}
return nil
}util.go源码:
package ipregion
import (
"fmt"
"strconv"
"strings"
)
// 工具函数
var shiftIndex = []int{24, 16, 8, 0}
func CheckIP(ip string) (uint32, error) {
var ps = strings.Split(strings.TrimSpace(ip), ".")
if len(ps) != 4 {
return 0, fmt.Errorf("invalid ip address `%s`", ip)
}
var val = uint32(0)
for i, s := range ps {
d, err := strconv.Atoi(s)
if err != nil {
return 0, fmt.Errorf("the %dth part `%s` is not an integer", i, s)
}
if d < 0 || d > 255 {
return 0, fmt.Errorf("the %dth part `%s` should be an integer bettween 0 and 255", i, s)
}
val |= uint32(d) << shiftIndex[i]
}
// convert the ip to integer
return val, nil
}3.调用ip解析方法
import引入插件包
import (
"gofly/utils/plugin"
)在接口业务中使用, data, err := plugin.NewIpRegion(ip),调用NewIpRegion()方法即可解析出IP归属地信息,代码如下:
// get请求获取ip属地
func (api *Iptest) GetIpRegion(c *gf.GinCtx) {
ip := c.DefaultQuery("ip", "")
data, err := plugin.NewIpRegion(ip)
gf.Success().SetMsg("获取ip属地").SetData(data).SetExdata(err).Regin(c)
}插件调用测试:
我们添加一个接口测试调用data, err := plugin.NewIpRegion(ip) 返回数据为:中国|0|云南省|昆明市|移动 ,如下图: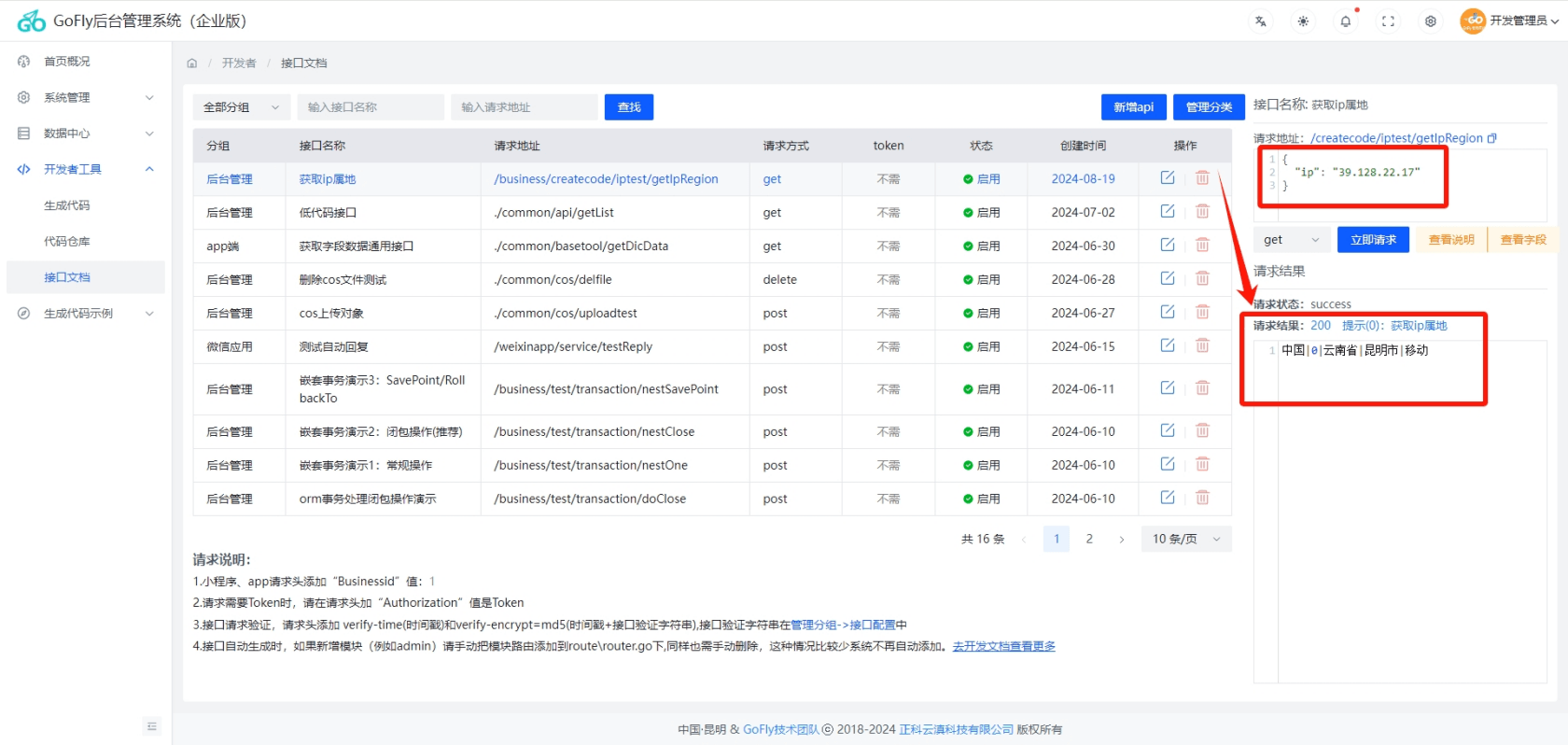
本作品采用《CC 协议》,转载必须注明作者和本文链接


 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu




也可以使用geoip2导入本地,使用定期任务定时更新就可以了