Vue 快速学习の自己整理的基本语法速查
创建 vue 实例
index.html 文件:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>My first Vue</title>
<!-- 引入样式文件 -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css">
<!-- 引入 vue 的包 -->
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue"></script>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 对应 app.js 文件中 el:'#vue-app' 的 vue 实例 -->
<div id="vue-app">
<h1>{{ name }}</h1>
</div>
<!-- 引入 js 文件 -->
<script src="app.js"></script>
</body>
</html>app.js 文件:
// 创建 vue 实例
new Vue({
// 与 index.html 文件中 id="vue-app" 的 div 对应, 包含在这个 vue 实例的数据和方法, 都可以作用于这个 div 中.
el:'#vue-app',
data:{
name:'Rachel'
}
});总结, 就是在 js 文件中处理数据以达到在页面上动态展现数据的效果.
data & methods
Html:
<div id="vue-app">
<p>{{ greet('afternoon') }}</p>
</div>JS:
new Vue({
el: '#vue-app',
data: {
name: 'Rachel'
},
methods: {
greet: function(time) {
return 'Good ' + time + ' ' + this.name;
}
}
});输出: Good afternoon Rachel
Data binding 数据绑定
流程/格式:
在 html 标签中添加:
v-bind: (标签的任意属性)="xxx"在 js 文件中:
给 xxx 赋值即可.
Html:
<!-- 绑定链接的三种方式 -->
<a v-bind:href="website">LearnKu</a>
<a :href="website">LearnKu</a>
<p v-html="websiteTag"></p>
<!-- 绑定 input 框的值 -->
<input v-bind:value="name" type="text">JS:
data: {
website: "https://learnku.com",
websiteTag: '<a href="https://learnku.com">LearnKu</a>',
},Events 事件
<div id="vue-app">
<p>My age is {{ age }}</p>
<!-- 绑定点击事件, 点击时触发 add 方法, 如果不需要传参, 事件中的方法可以不写括号 -->
<button v-on:click="add(1)">Add a year</button>
<!-- 简写方式 -->
<button @click="add(2)">Add 2 years</button>
<!-- 绑定双击事件 -->
<button v-on:dblclick="add(10)">Add 10 years</button>
<!-- 加上 once, 使点击事件只生效一次 -->
<button @click.once="add(3)">Add 3 years</button>
<!-- 在 a 标签上绑定点击事件, 可以加上 "prevent" 以阻止跳转 -->
<a v-on:click.prevent="click" href="https://learnku.com">LearnKu</a>
</div>new Vue({
el: '#vue-app',
data: {
age: 25
},
methods: {
add:function(inc) {
this.age += inc;
},
click: function() {
alert('You clicked me');
}
}
});Keyboard Events 键盘事件
<!-- 绑定键盘点击事件, 按键抬起一次, 就执行一次 logName 方法 -->
<input type="text" v-on:keyup="logName">
<!-- 回车时, 执行 logName 方法 -->
<input type="text" v-on:keyup.enter="logName">
<!-- 同时按下 alt 键和回车键, 执行 logName 方法 -->
<input type="text" v-on:keyup.alt.enter="logName">logName: function() {
console.log('You entered your name');
}Two-way Data Building 数据的双向传输
<!-- 接收用户输入的数据 -->
<input type="text" v-model="name">
<!-- 同步输出用户输入的每个字符-->
<span>{{ name }}</span>
<!-- 接收用户输入的数据 -->
<input type="text" v-model.lazy="title">
<!--当用户按 tab 键时, 一次性输出用户的输入-->
<span>{{ title }}</span>data: {
name: '',
title: ''
},双向传输图示: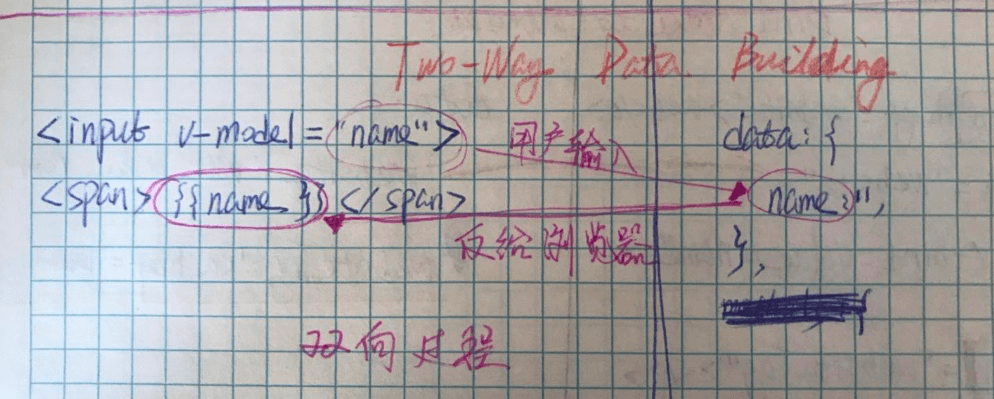
Computed Properties
<p>Age: {{ age }}</p>
<button v-on:click="a++">AddtoA</button>
<p>A: {{ a }}</p>
<p>Age + A = {{ addToA() }}</p>
<button v-on:click="b++">AddtoB</button>
<p>B: {{ b }}</p>
<p>Age + B = {{ addToB() }}</p>data: {
// 给 a 和 b 均设初始值为 0
a: 0,
b: 0,
age: 25,
},
methods: {
addToA: function() {
// 便于在控制台查看方法被触发的时机
console.log('addToA');
return this.a + this.age;
},
addToB: function() {
// 便于在控制台查看方法被触发的时机
console.log('addToB');
return this.b + this.age;
}
}按照上面这段代码, 单独点击哪个 button, 两个 methods 都会被执行, 这有损性能.
改进: 把 methods 中的代码挪到 computed 属性中, 它跟 methods 的作用很像, 区别就是它会检查方法中的数据是否有改变, 如果没有改变, 就不会执行, 就是定位更准确点吧.
computed: {
addToA: function() {
console.log('addToA');
return this.a + this.age;
},
addToB: function() {
console.log('addToB');
return this.b + this.age;
}
}Html 中的代码稍作改动, 把调用方法的括号去掉, 否则报错:
<p>Age + A = {{ addToA }}</p>
<p>Age + B = {{ addToB }}</p>Dynamic CSS 动态样式
方式一:
<!-- 绑定属性, 属性名: 属性值(true/false), 用 true/false 控制是否添加此属性 -->
<div v-bind:class="{red:true, blue:false}"></div>方式二(更加动态的方式):
把属性 a 的值用变量 available 表示, 在 js 文件中控制其为 true or false
添加点击事件, 控制 js 文件中 available 的值, 从而控制 class a 是否生效.
index.html 文件
<div v-on:click="available = !available" v-bind:class="{a: available}">
<span>Rachel</span>
</div>app.js 文件
data: {
available: true,
},style.css 文件
span {
background: red;
display: inline-block;
}
.a span {
background: green
}方式三:
最解耦的方式, 特别适合于一个元素上有很多个类的情况, 不需要在 html 中罗列所有的类, 而只需要在指定一个变量名, 然后在 js 文件中编辑所有的类就可以了:
<!--当点击的时候改变 js 文件中 data 里的值 -->
<button v-on:click="available = !available">Toggle a</button>
<button v-on:click="nearby = !nearby">Toggle b</button>
<div v-bind:class="compClass">
<span>Rachel</span>
</div>data: {
available: false,
nearby: false
},
computed: {
compClass: function() {
return {
a: this.available,
b: this.nearby
}
}
}Conditionals 条件判断
<button v-on:click="error= !error">Toggle Error</button>
<button v-on:click="success= !success">Toggle Success</button>
<!-- 方式一 -->
<!-- 如果 false, 就不显示 p 标签 -->
<p v-if="error">Error</p>
<p v-else-if="success">Success</p>
<!-- 方式二 -->
<!-- 如果 false, 会在 p 标签上加上 style="display: none;" -->
<p v-show="error">Error</p>
<p v-show="success">Success</p>data: {
error: false,
success: false
}Loop for 循环
<ul>
<li v-for="character in characters">
{{ character }}
</li>
</ul>
<!-- 遍历含有对象的数组 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="info in infos">
{{info.name}} - {{ info.age}}
</li>
</ul>
<!-- 遍历时加索引 -->
<ul>
<li v-for="(info, index) in infos">
{{ index }}. {{info.name}} - {{ info.age}}
</li>
</ul>
<!-- template 标签不会被渲染 -->
<!-- 遍历数组 -->
<template v-for="info in infos">
<!-- 遍历输出对象的 key / value -->
<div v-for="(val, key) in info">
<p>{{ key }} - {{ val }}</p>
</div>
</template>data: {
characters: ['Rachel', 'Ross', 'Emma'],
infos: [
{name: 'Rachel', age: 25},
{name: 'Ross', age: 30},
{name: 'Emma', age: 2}
]
}Intro to Component
component is a reusable piece of code or template that we can use in different view instance.
<!-- 对应第一个 vue 实例 -->
<div id="vue-app-one">
<!-- 被复用的 template -->
<greeting></greeting>
</div>
<!-- 对应第二个 vue 实例 -->
<div id="vue-app-two">
<!-- 被复用的 template -->
<greeting></greeting>
</div>// 对于 greeting 标签, 在此定义一次, 就可以在多个 vue 实例中复用
Vue.component('greeting', {
template: "<p>Hey there, I am {{name}}. <button v-on:click='changeName'>Change</button></p>",
// 在这里的 data 不是对象, 而是一个函数, 在函数里返回对象, data 函数有下面两种写法, 都可以
// 写法一
data:function() {
return {
name: 'Rachel'
}
},
// 写法二
data() {
return {
name: 'Rachel'
}
},
methods: {
changeName: function() {
this.name = 'Mario'
}
}
});
// 第一个 vue 实例
var one = new Vue({
el: '#vue-app-one',
});
// 第二个 vue 实例
var two = new Vue({
el: '#vue-app-two',
});Refs
通过标签的 ref 属性, 可以在 js 文件中获取这个标签的所有信息.
<!--给 input 标签加 ref 属性, 名字是自定义的, 在 js 中取的时候可以定位到这个标签-->
<input type="text" ref="input">
<button v-on:click="readRefs">Submit</button>
<p>Your fav food is {{ output }}</p>
<!--给 div 标签加 ref 属性-->
<div ref="test">Hello</div>data: {
output: "Your fav food"
},
methods: {
readRefs: function() {
// 获取 input 标签的信息
this.output = this.$refs.input.value;
// 获取 div 标签的信息
alert(this.$refs.test.innerHTML);
}
}单独打印 this.$refs 可以看到所有带 ref 属性的元素的详细信息:
console.log(this.$refs);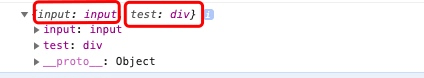
本作品采用《CC 协议》,转载必须注明作者和本文链接





 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu



