PHP 程序员的堆学习
堆的基本存储
堆是一种数据结构,它是一颗完全二叉树(不清楚自行百度)。因此可以用数组存储二叉堆。堆分为最大堆和最小堆。
最大堆:任意节点的值不大于其父亲节点的值。
下图为最大堆的结构: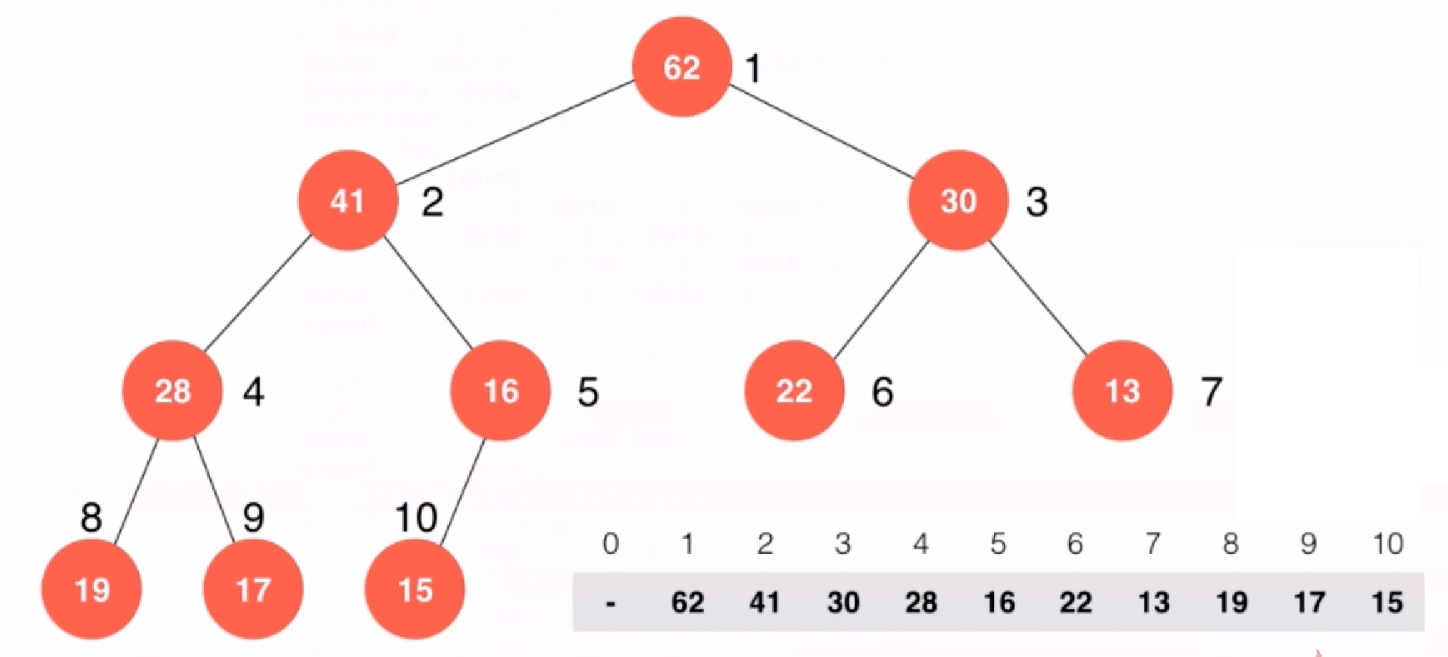
使用堆可以实现优先级队列,也可以实现多路归并排序。多路归并排序在常见数据结构书中都有涉及,主要用于外部排序,外部排序就是在内存容纳不下,需要存在文件中。优先级队列可以自己去百度,这里不展开。
重要:我们从1开始标号:对于完全二叉树有
父节点(i)=i/2
左孩子(i)= 2*i
右孩子(i)=2*i+1根据这个关系就可以用数组实现堆了。
堆的PHP实现
入堆
入堆即向堆中添加新的元素,然后将元素移动到合适的位置,以保证堆的性质不变。在入堆的时候,需要shift_up操作,向上调整。插入元素后,放在数组尾部,不停将元素和上方父亲元素比较,如果大于则交换元素;直到达到堆顶或者小于等于父亲元素。
public $array = [];
public $count = 0;//计数堆中元素
public function insert($random)
{
$this->array[$this->count + 1] = $random;
$this->count++;
$this->shift_up($this->count);
}
public function shift_up($k)
{
//如果新插入的值比父节点的值小, 则父节点的值下移,直到到达根节点满足最大堆
while ($k > 1 && $this->array[(int)($k / 2)] < $this->array[$k]) {
$this->swap($this->array[(int)($k / 2)], $this->array[$k]);
$k = (int)($k / 2);
}
}出堆
出堆只能弹出堆顶元素(最大堆就是最大的元素),然后将位于最后一个位置的元素放入堆顶,重新调整元素位置,这时需要shift_down操作。此时元素应该和子节点比较,如果大于等于子节点或者没有子节点,停止比较;否则,选择子节点中最大的元素,进行交换,执行此步,直到结束。
public function take()
{
$res = $this->array[1];
$this->swap($this->array[1], $this->array[$this->count]);
$this->count--;
//取出第一个元素,堆中第一个元素为最大值
$this->shift_down(1);
return $res;
}
public function shift_down($k)
{
while (2 * $k <= $this->count) {
//$j为左孩子
$j = 2 * $k;
//存在右孩子且比左孩子大就取右孩子
if ($j + 1 <= $this->count && $this->array[$j + 1] > $this->array[$j]) {
$j += 1;
}
//数据大于孩子的最大值则不需要交换
if ($this->array[$k] >= $this->array[$j]) {
break;
}
$this->swap($this->array[$k], $this->array[$j]);
$k=$j;
}
}改变堆元素
当你改变堆中某个元素的值之后,使用shift_up和shift_down来调整堆。
shift_up($k);
shift_down($k)堆排序
普通堆排序
实现堆排序很简单:将元素逐步insert进入堆,然后再take逐个取出即可。至此堆排序实现完成。
$xx = new Heap();
for ($i = 0; $i < 10; $i++) {
$xx->insert(random_int(10, 1000));
}
while (!$xx->isEmpty()) {
$res = $xx->take();
echo $res . PHP_EOL;
}
结果:
908
900
877
753
752
712
698
682
677这个建堆的平均时间复杂度是O(n*logn)
建堆可以优化,这个过程叫做heapify
将数组的值逐步复制到
$this->array从第一个非叶子节点开始,执行
shift_down重复第 2 步,直到堆顶元素
这种建堆方法的时间复杂度是:
O(n)
public function heapify($array)
{
$this->count = count($array);
for ($i = 0; $i < $this->count; $i++) {
$this->array[$i + 1] = $array[i];
}
//(int)($this->count/2)为第一个非叶子节点位置
for ($i = (int)($this->count / 2); $i >= 1; $i--) {
$this->shift_down($i);
}
} 完整代码如下:
<?php
class Heap
{
public $array = [];
public $count = 0;
public function insert($random)
{
$this->array[$this->count + 1] = $random;
$this->count++;
$this->shift_up($this->count);
}
public function heapify($array)
{
$this->count = count($array);
for ($i = 0; $i < $this->count; $i++) {
$this->array[$i + 1] = $array[$i];
}
for ($i = (int)($this->count / 2); $i >= 1; $i--) {
$this->shift_down($i);
}
}
public function shift_up($k)
{
//如果新插入的值比父节点的值小, 则父节点的值下移,直到到达根节点满足最大堆
while ($k > 1 && $this->array[(int)($k / 2)] < $this->array[$k]) {
$this->swap($this->array[(int)($k / 2)], $this->array[$k]);
$k = (int)($k / 2);
}
}
public function shift_down($k)
{
while (2 * $k <= $this->count) {
//$j为左孩子
$j = 2 * $k;
//存在右孩子且比左孩子大就取右孩子
if ($j + 1 <= $this->count && $this->array[$j + 1] > $this->array[$j]) {
$j += 1;
}
//数据大于孩子的最大值则不需要交换
if ($this->array[$k] >= $this->array[$j]) {
break;
}
$this->swap($this->array[$k], $this->array[$j]);
$k = $j;
}
}
public function take()
{
$res = $this->array[1];
$this->swap($this->array[1], $this->array[$this->count]);
$this->count--;
$this->shift_down(1);
return $res;
}
private function swap(&$a, &$b)
{
list ($a, $b) = [$b, $a];
}
public function isEmpty()
{
return $this->count == 0;
}
}
$xx = new Heap();
for ($i = 0; $i < 10; $i++) {
$xx->insert(random_int(10, 1000));
}
while (!$xx->isEmpty()) {
$res = $xx->take();
echo $res . PHP_EOL;
}原地堆排序
上面阐述的排序方法,借助实现的最大堆这个类需要开辟空间保存数组,空间复杂度为O(n)。其实借助shift_down可以实现原地堆排序
- Heapify先构成最大堆,第一个元素为最大值,与最后一个元素交换。
- 前面n-1元素进行
shift_down转化为最大堆,重复第一步直到所有元素都排序完整

此处
__heapify__shift_down函数均需要修改为对传入数组的修改,和之前代码类似,只是不是用$this->array,具体代码就不给出了,可以自己尝试实现。
···
public function sort($array) {
$this->count = count($array);
// 将一个无序的数组组成了一个最大堆,第 1 个元素就是最大值
$this->__heapify($array);
// 重复取出最大元素交换来排序完整
for ($i = $this->count-1; $i>=0; $i--) {
$this->swap($array[0],$array[$i]);
$this->__shift_down($i);
}
}
···
$xx = new Heap();
$xx->sort([1,2,4,6,3,9,11]);索引堆(Index Heap)
数组中的元素位置发生了改变,我们才能将其构建为最大堆。
由于数组中元素位置的改变,我们将面临着几个局限性:
- 如果我们的元素是十分复杂的话,那么交换它们之间的位置将产生大量的时间消耗。
- 由于我们的数组元素的位置在构建成堆之后发生了改变,那么我们之后就很难索引到它,很难去改变它。例如我们在构建成堆后,想去改变一个原来元素的优先级(值),将会变得非常困难。
针对以上问题,我们就需要引入索引堆(Index Heap)的概念。对于索引堆来说,我们将数据和索引这两部分分开存储。构建完堆之后,data域并没有发生改变,位置改变的是index域。


在实现索引堆的过程中,我想需要修改insert,shift_up,shift_down,take为其对应的索引进行操作。
具体PHP实现如下:
<?php
class HeapIndex
{
public $array = [];
public $index = [];
public $count = 0;
public function insert($random)
{
$this->count++;
$this->array[$this->count] = $random;
$this->index[$this->count] = $this->count;
$this->shift_up($this->count);
}
/***
* 堆的向上调整
* @param $k
*/
public function shift_up($k)
{
//如果新插入的值比父节点的值小, 则父节点的值下移,直到到达根节点满足最大堆
while ($k > 1 && $this->array[$this->index[(int)($k / 2)]]
< $this->array[$this->index[$k]]) {
$this->swap($this->index[(int)($k / 2)], $this->index[$k]);
$k = (int)($k / 2);
}
}
public function shift_down($k)
{
while (2 * $k <= $this->count) {
//$j为左孩子
$j = 2 * $k;
//存在右孩子且比左孩子大就取右孩子
if ($j + 1 <= $this->count &&
$this->array[$this->index[$j + 1]] > $this->array[$this->index[$j]]) {
$j += 1;
}
//数据大于孩子的最大值则不需要交换
if ($this->array[$this->index[$k]] >= $this->array[$this->index[$j]]) {
break;
}
$this->swap($this->index[$k], $this->index[$j]);
$k = $j;
}
}
public function take()
{
$res = $this->array[$this->index[1]];
$this->swap($this->index[1], $this->index[$this->count]);
$this->count--;
$this->shift_down(1);
return $res;
}
private function swap(&$a, &$b)
{
list ($a, $b) = [$b, $a];
}
public function isEmpty()
{
return $this->count == 0;
}
}
$xx = new HeapIndex();
for ($i = 0; $i < 10; $i++) {
$xx->insert(random_int(10, 1000));
}
while (!$xx->isEmpty()) {
$res = $xx->take();
echo $res . PHP_EOL;
}
码字不易。
本作品采用《CC 协议》,转载必须注明作者和本文链接





 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu




很少看到php语言描述的数据结构,加油
其实 PHP 也是自带一些基本的数据结构的用起来也挺简单的 PHP:数据结构
自带的SPL不香吗