笔记四十三:文档的父子关系
Parent / Child
- 对象和 Nested 对象的局限性
- 每次更新,需要重新索引整个对象(包括跟对象和嵌套对象)
- ES 提供了类似关系型数据库中Join 的实现。使用Join数据类型实现,可以通过Parent / Child 的关系,从而分离两个对象
- 父文档和子文档是两个独立的文档
- 更新父文档无需重新索引整个子文档。子文档被新增,更改和删除也不会影响到父文档和其他子文档。
父子关系
- 定义父子关系的几个步骤
- 设置索引的Mapping
- 索引父文档
- 索引子文档
- 按需查询文档
设置Mapping
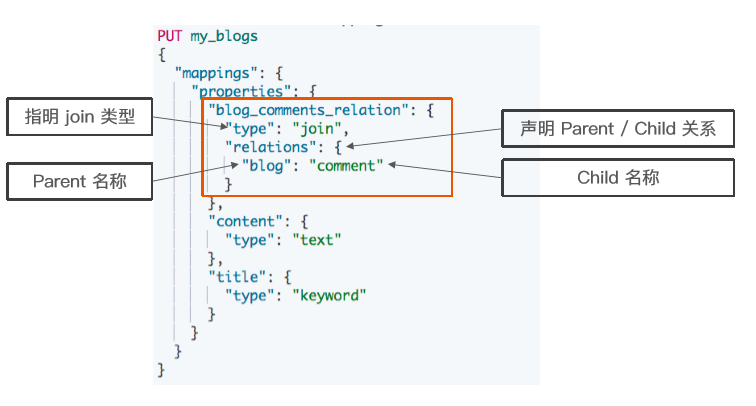
DELETE my_blogs
# 设定 Parent/Child Mapping
PUT my_blogs
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 2
},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"blog_comments_relation": {
"type": "join",
"relations": {
"blog": "comment"
}
},
"content": {
"type": "text"
},
"title": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
}索引父文档
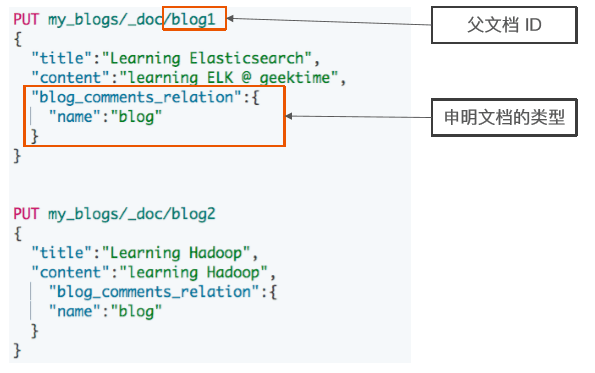
PUT my_blogs/_doc/blog1
{
"title":"Learning Elasticsearch",
"content":"learning ELK @ geektime",
"blog_comments_relation":{
"name":"blog"
}
}
PUT my_blogs/_doc/blog2
{
"title":"Learning Hadoop",
"content":"learning Hadoop",
"blog_comments_relation":{
"name":"blog"
}
}索引子文档
- 父文档和子文档必须存在相同的分片上
- 确保查询 join 的性能
- 当指定文档时候,必须指定它的父文档ID
- 使用route参数来保证,分配到相同的分片
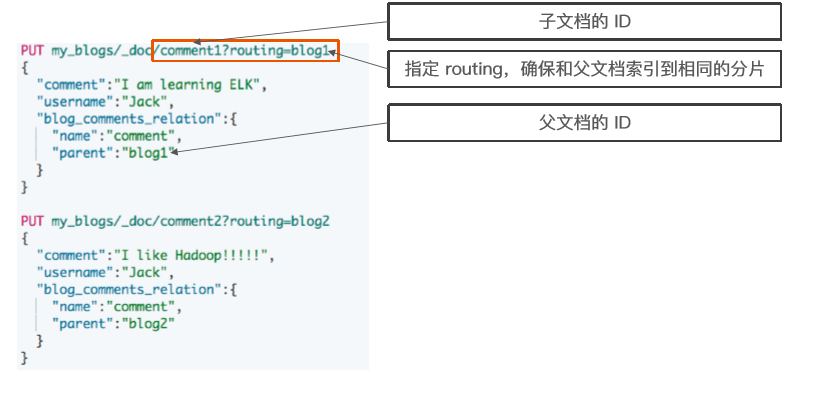
#索引子文档
PUT my_blogs/_doc/comment1?routing=blog1
{
"comment":"I am learning ELK",
"username":"Jack",
"blog_comments_relation":{
"name":"comment",
"parent":"blog1"
}
}
PUT my_blogs/_doc/comment2?routing=blog2
{
"comment":"I like Hadoop!!!!!",
"username":"Jack",
"blog_comments_relation":{
"name":"comment",
"parent":"blog2"
}
}
PUT my_blogs/_doc/comment3?routing=blog2
{
"comment":"Hello Hadoop",
"username":"Bob",
"blog_comments_relation":{
"name":"comment",
"parent":"blog2"
}
}Parent / Child 所支持的查询
- 查询所有文档
- Parent Id 查询
- Has Child 查询
- Has Parent 查询
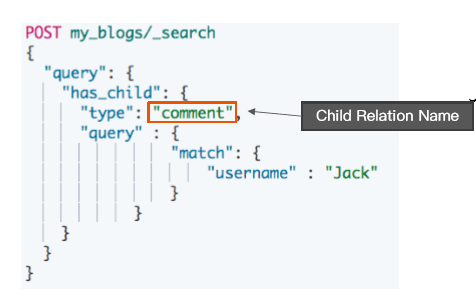
# 查询所有文档 POST my_blogs/_search {} #根据父文档ID查看 GET my_blogs/_doc/blog2 # Parent Id 查询 POST my_blogs/_search { "query": { "parent_id": { "type": "comment", "id": "blog2" } } } # Has Child 查询,返回父文档 POST my_blogs/_search { "query": { "has_child": { "type": "comment", "query" : { "match": { "username" : "Jack" } } } } } # Has Parent 查询,返回相关的子文档 POST my_blogs/_search { "query": { "has_parent": { "parent_type": "blog", "query" : { "match": { "title" : "Learning Hadoop" } } } } }使用 has_child 查询
- 返回父文档
- 通过对子文档进行查询
- 返回具体相关子文档的父文档
- 父子文档在相同的分片上,因此Join 效率高
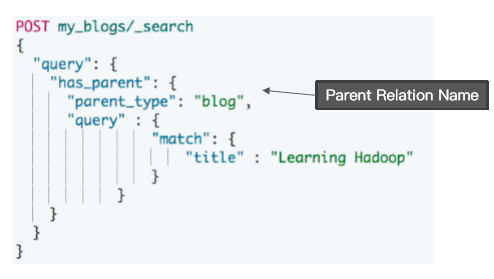
使用 has_parent 查询
- 返回相关性的子文档
- 通过对父文档进行查询
- 返回相关的子文档
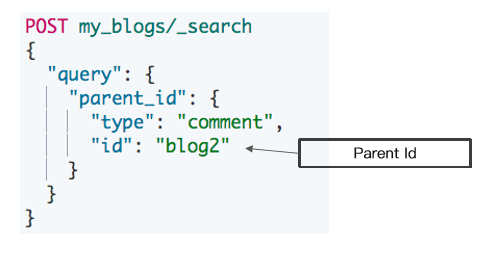
使用 parent_id 查询
- 返回所有相关子文档
- 通过对付文档Id 进行查询
- 返回所有相关的子文档
访问子文档
- 需指定父文档 routing 参数
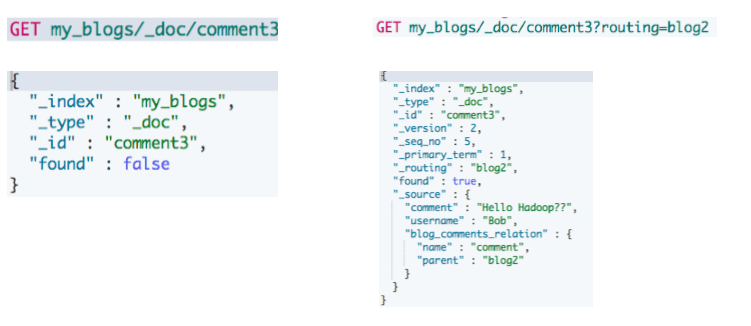
#通过ID ,访问子文档
GET my_blogs/_doc/comment2
#通过ID和routing ,访问子文档
GET my_blogs/_doc/comment3?routing=blog2更新子文档
- 更新子文档不会影响到父文档
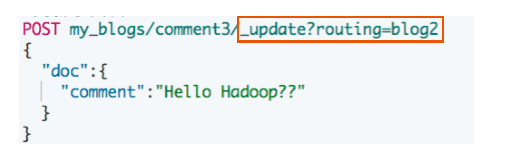
#更新子文档
PUT my_blogs/_doc/comment3?routing=blog2
{
"comment": "Hello Hadoop??",
"blog_comments_relation": {
"name": "comment",
"parent": "blog2"
}
}
嵌套对象 v.s 父子文档
| Nested Object | Parent / Child | |
|---|---|---|
| 优点 | 文档存储在一起,读取性能高 | 父子文档可以独立更新 |
| 缺点 | 更新嵌套的子文档时,需要更新整个文档 | 需要额外的内存去维护关系。读取性能相对差 |
| 适用场景 | 子文档偶尔更新,以查询为主 | 子文档更新频繁 |
本作品采用《CC 协议》,转载必须注明作者和本文链接



 关于 LearnKu
关于 LearnKu



